Read Article - Equinox Landscape
... our feet billions of organisms, some microscopic, some much larger, are busy decomposing today’s dead material, turning it into tomorrow’s living nutrients. They are the most efficient recyclers on the planet, with next to nothing being wasted. For the last billion years the soil food web, as these ...
... our feet billions of organisms, some microscopic, some much larger, are busy decomposing today’s dead material, turning it into tomorrow’s living nutrients. They are the most efficient recyclers on the planet, with next to nothing being wasted. For the last billion years the soil food web, as these ...
Figure 18.1
... Relatively high amounts of mineralization of available nutrients is produced by a combination of rapid decomposition plus previously accumulated POM or a high amount of added residues. Rapid decomposition is stimulated by intensive tillage, good soil drainage, coarse texture, and alternating wet and ...
... Relatively high amounts of mineralization of available nutrients is produced by a combination of rapid decomposition plus previously accumulated POM or a high amount of added residues. Rapid decomposition is stimulated by intensive tillage, good soil drainage, coarse texture, and alternating wet and ...
TEST #1 CH`s 4, 5, 10 FRQ`s
... Describe how humus originated in the soils of this biome and 2 ways that humus improves soil conditions for plant growth? FRQ 2. Suppose you are an ecologist for the US Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS). Your current research is studying the life cycle of monarch butterflies and the relationships of ...
... Describe how humus originated in the soils of this biome and 2 ways that humus improves soil conditions for plant growth? FRQ 2. Suppose you are an ecologist for the US Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS). Your current research is studying the life cycle of monarch butterflies and the relationships of ...
Activity: Earthworm Food Chain
... decompose matter in a detrital web may sprout mushrooms that are consumed by squirrels, mice, and deer in a grazing web. Robins are omnivores, that is, consumers of both plants and animals, and thus are in both detrital and grazing webs. Robins typically feed on earthworms, which are detritivores th ...
... decompose matter in a detrital web may sprout mushrooms that are consumed by squirrels, mice, and deer in a grazing web. Robins are omnivores, that is, consumers of both plants and animals, and thus are in both detrital and grazing webs. Robins typically feed on earthworms, which are detritivores th ...
THE ROLES OF VARIOUS FUNCTIONAL GROUPS OF
... food web simulation is one way to better estimate the importance of that group for ...
... food web simulation is one way to better estimate the importance of that group for ...
Lecture 4
... thus easily transported. The five materials and plant nutrients are removed. Seeds may be separated and washed out of the soil. ...
... thus easily transported. The five materials and plant nutrients are removed. Seeds may be separated and washed out of the soil. ...
Factors Affecting Plant Growth
... Stems will be leggy or stretched out Leaves turn yellow Leaves are too small Leave or stems are spindly Brown edges or tips on leaves Lower leaves dry up ...
... Stems will be leggy or stretched out Leaves turn yellow Leaves are too small Leave or stems are spindly Brown edges or tips on leaves Lower leaves dry up ...
Soil and the Rhizosphere
... nitrate, sulfate, carbon dioxide) will partly determine which anaerobic respiring bacteria thrive where. ...
... nitrate, sulfate, carbon dioxide) will partly determine which anaerobic respiring bacteria thrive where. ...
Soil Science Big Ideas
... Within the soil there are ecosystems where the organisms, (living or non living, plant or animal) are interdependent. They are also dependent on climatic conditions. Forming of soil is an ever changing slow process which can be hugely impacted by natural events and human actions. Humans are totally ...
... Within the soil there are ecosystems where the organisms, (living or non living, plant or animal) are interdependent. They are also dependent on climatic conditions. Forming of soil is an ever changing slow process which can be hugely impacted by natural events and human actions. Humans are totally ...
Soil entomology
... L. Rueß Soils harbour an enormous diversity of organisms connected by multitrophic interactions that are central to nutrient cycling. Microarthropods, in particular microbial grazers such as Collembola, are important determinants for the energy and carbon flow through belowground food webs. Regardle ...
... L. Rueß Soils harbour an enormous diversity of organisms connected by multitrophic interactions that are central to nutrient cycling. Microarthropods, in particular microbial grazers such as Collembola, are important determinants for the energy and carbon flow through belowground food webs. Regardle ...
Lecture 12 Food, Soil, and Pest Management Core Case Study
... C. Acute Food Shortages Can Lead to Famines Usually caused by crop failures from Drought, Flooding, War, Other catastrophic events D. Many People Have Health Problems from Eating Too Much Overnutrition Similar health problems to those who are underfed Lower life expectancy, Greater susceptibility to ...
... C. Acute Food Shortages Can Lead to Famines Usually caused by crop failures from Drought, Flooding, War, Other catastrophic events D. Many People Have Health Problems from Eating Too Much Overnutrition Similar health problems to those who are underfed Lower life expectancy, Greater susceptibility to ...
5 - Human Activities in Ecosystems
... – Drive away birds and insects that used it as a home and nutrient source. – At the roots, the insects and worms living there can no longer get nutrients. – As the roots die, they no longer help keep the soil together. ...
... – Drive away birds and insects that used it as a home and nutrient source. – At the roots, the insects and worms living there can no longer get nutrients. – As the roots die, they no longer help keep the soil together. ...
What`s in an ecosystem? - dpsrenenvironmentalscience
... •They’re able to exploit a wide range of food resources either as direct or indirect herbivores, predators and scavengers. Most species are omnivorous generalists but a few are specialist feeders. •It was 2 of them but they weren’t interacting with each ...
... •They’re able to exploit a wide range of food resources either as direct or indirect herbivores, predators and scavengers. Most species are omnivorous generalists but a few are specialist feeders. •It was 2 of them but they weren’t interacting with each ...
Soil Study Guide
... 2. Topsoil is a natural product of subsoil and bedrock. It is rich with a lot of humus. It is the top layer of soil made up of the smallest grains with the most humus. 3. Soil is formed by broken down rocks, moving water, the air ( wind), and/or decaying plants and animals. 4. Rocks are made of mine ...
... 2. Topsoil is a natural product of subsoil and bedrock. It is rich with a lot of humus. It is the top layer of soil made up of the smallest grains with the most humus. 3. Soil is formed by broken down rocks, moving water, the air ( wind), and/or decaying plants and animals. 4. Rocks are made of mine ...
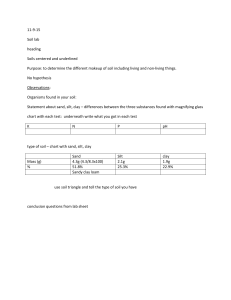
11-9-15 Soils Lab
... Soils centered and underlined Purpose: to determine the different makeup of soil including living and non-living things. No hypothesis Observations: Organisms found in your soil: Statement about sand, silt, clay – differences between the three substances found with magnifying glass chart with each t ...
... Soils centered and underlined Purpose: to determine the different makeup of soil including living and non-living things. No hypothesis Observations: Organisms found in your soil: Statement about sand, silt, clay – differences between the three substances found with magnifying glass chart with each t ...
Summative Assessment Questions on Soils (LCA Ag,Hort Basic Hort
... 3. Name the three main soil types. 4. Soils can have different pH. What does pH mean when referring to soils? 5. Which type of soil is good for crops? 6. Where would you find acid soils? 7. Why is lime added to soil? 8. What is humus and why is it good for soil? 9. What test would a horticulturalist ...
... 3. Name the three main soil types. 4. Soils can have different pH. What does pH mean when referring to soils? 5. Which type of soil is good for crops? 6. Where would you find acid soils? 7. Why is lime added to soil? 8. What is humus and why is it good for soil? 9. What test would a horticulturalist ...
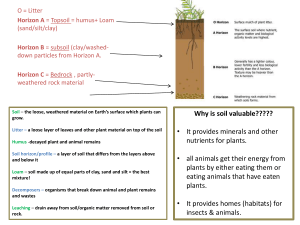
soil study guide 2015
... Soil – the loose, weathered material on Earth’s surface which plants can grow. Litter – a loose layer of leaves and other plant material on top of the soil Humus -decayed plant and animal remains Soil horizon/profile – a layer of soil that differs from the layers above and below it ...
... Soil – the loose, weathered material on Earth’s surface which plants can grow. Litter – a loose layer of leaves and other plant material on top of the soil Humus -decayed plant and animal remains Soil horizon/profile – a layer of soil that differs from the layers above and below it ...
New soil test - Washtenaw County
... Cost: Mailers for landscapes, vegetable & flower gardens are available at your local MSU Extension office for $25.00. Sampling: for garden soils, sample 6 inches to 8 inches deep. For lawns, lift the sod and sample 3 inches deep. Take 15 or 20 sub samples in the area you are testing and mix them tho ...
... Cost: Mailers for landscapes, vegetable & flower gardens are available at your local MSU Extension office for $25.00. Sampling: for garden soils, sample 6 inches to 8 inches deep. For lawns, lift the sod and sample 3 inches deep. Take 15 or 20 sub samples in the area you are testing and mix them tho ...
Life in an Ecosystem
... plants and animals. Green plants are the ‘sun catchers’ that transform some of the sun’s energy by photosynthesis. Plants are producers that make their own food and become a useable form of energy for other organisms. A consumer cannot make its own food and obtains its energy by eating other organis ...
... plants and animals. Green plants are the ‘sun catchers’ that transform some of the sun’s energy by photosynthesis. Plants are producers that make their own food and become a useable form of energy for other organisms. A consumer cannot make its own food and obtains its energy by eating other organis ...
slides
... plants when they need them • In biotic regulation, nutrients are held in resistant forms, not readily lost from soil • When plants need nutrients, they stimulate soil biota to release the nutrients • Synthetic fertilizers cause physiological changes in plants that make them withhold energy from soil ...
... plants when they need them • In biotic regulation, nutrients are held in resistant forms, not readily lost from soil • When plants need nutrients, they stimulate soil biota to release the nutrients • Synthetic fertilizers cause physiological changes in plants that make them withhold energy from soil ...
TAKS Review - Greenslime
... A. air is pumped into flowers B. water moves into cells C. minerals turn to crystals D. more sugar is produced E. water is pumped out of the cells F. more sugar is consumed ...
... A. air is pumped into flowers B. water moves into cells C. minerals turn to crystals D. more sugar is produced E. water is pumped out of the cells F. more sugar is consumed ...
Soil food web

The soil food web is the community of organisms living all or part of their lives in the soil. It describes a complex living system in the soil and how it interacts with the environment, plants, and animals. Food webs describe the transfer of energy between species in an ecosystem. While a food chain examines one, linear, energy pathway through an ecosystem, a food web is more complex and illustrates all of the potential pathways. Much of this transferred energy comes from the sun. Plants use the sun’s energy to convert inorganic compounds into energy-rich, organic compounds, turning carbon dioxide and minerals into plant material by photosynthesis. Plants are called autotrophs because they make their own energy; they are also called producers because they produce energy available for other organisms to eat. Heterotrophs are consumers that cannot make their own food. In order to obtain energy they eat plants or other heterotrophs.