Land Resources - WordPress.com
... a) Barren and waste land b) Land put to non-agricultural uses. E.g. buildings, roads, factorie.etc. 3. Other uncultivated land (excluding fallow land) a)Permanent pastures and grazing land. b)land under miscellaneous tree crop groves (not included sown area) c)cultural waste land (left uncultivated ...
... a) Barren and waste land b) Land put to non-agricultural uses. E.g. buildings, roads, factorie.etc. 3. Other uncultivated land (excluding fallow land) a)Permanent pastures and grazing land. b)land under miscellaneous tree crop groves (not included sown area) c)cultural waste land (left uncultivated ...
Part 5: Soil
... Wind carries small particles of soil. When wind blows against rock the soil particles beat against the rock and slowly wear away the rock to form more soil. 6. Plants Mosses and lichens are tiny plants that grow on the surface of rocks. This causes the rocks to break up into smaller pieces. The root ...
... Wind carries small particles of soil. When wind blows against rock the soil particles beat against the rock and slowly wear away the rock to form more soil. 6. Plants Mosses and lichens are tiny plants that grow on the surface of rocks. This causes the rocks to break up into smaller pieces. The root ...
15A NCAC 18A .1941 SOIL CHARACTERISTICS (MORPHOLOGY
... ABSENCE OF SOIL STRUCTURE - Soils which are single grained and exhibit no structural aggregates shall be considered SUITABLE as to structure. Soils which are massive and exhibit no structural peds within 36 inches of the naturally occurring soil surface shall be considered UNSUITABLE as to structure ...
... ABSENCE OF SOIL STRUCTURE - Soils which are single grained and exhibit no structural aggregates shall be considered SUITABLE as to structure. Soils which are massive and exhibit no structural peds within 36 inches of the naturally occurring soil surface shall be considered UNSUITABLE as to structure ...
essential guide
... and covers whether stones, weeds, roots or rhizomes of pernicious weeds are present. The sample is then submitted to a UKAS and MCERTS accredited laboratory for a range of physical and chemical tests to confirm the composition and fertility of the soil, and the absence of potential contaminants. ...
... and covers whether stones, weeds, roots or rhizomes of pernicious weeds are present. The sample is then submitted to a UKAS and MCERTS accredited laboratory for a range of physical and chemical tests to confirm the composition and fertility of the soil, and the absence of potential contaminants. ...
NAME_________________________________________ DATE
... 14. What is the advantage of the needle shaped leaves of conifer trees? Retain water for trees and protects trees against snow. 15. Why are desert soils rich in minerals but poor in organic matter? No water ...
... 14. What is the advantage of the needle shaped leaves of conifer trees? Retain water for trees and protects trees against snow. 15. Why are desert soils rich in minerals but poor in organic matter? No water ...
Mortality of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in Two Soils with Different
... soil, atmospheric conditions, and biological interactions with other soil organisms (Crane et al., 1980; Gerba and Bitton, 1984; Morrison and Martin, 1977). Fine soil particles have also been shownto increase E. coli survival. Soils of fine texture and high organic matter content have been observed ...
... soil, atmospheric conditions, and biological interactions with other soil organisms (Crane et al., 1980; Gerba and Bitton, 1984; Morrison and Martin, 1977). Fine soil particles have also been shownto increase E. coli survival. Soils of fine texture and high organic matter content have been observed ...
Al NEWBURY LOCAL PLAN SITE 15: DARK LANE, TILEHURST
... borings became heavier at depth but the majority became more sandy. The volume of stones, greater than 2cm in diameter,in the topsoil cause a significant limitation in terms of wear and damage to farm machinery and adverse affects on crop establishment and growth. In addition the combination of the ...
... borings became heavier at depth but the majority became more sandy. The volume of stones, greater than 2cm in diameter,in the topsoil cause a significant limitation in terms of wear and damage to farm machinery and adverse affects on crop establishment and growth. In addition the combination of the ...
View Full Text-PDF
... reconsidering their strategy. It is increasingly recognised in Malwa region that the land users have valuable environmental knowledge themselves. This review explores two hypotheses: first, that much can be learned from previously ignored indigenous soil and water conservation practices; second, tha ...
... reconsidering their strategy. It is increasingly recognised in Malwa region that the land users have valuable environmental knowledge themselves. This review explores two hypotheses: first, that much can be learned from previously ignored indigenous soil and water conservation practices; second, tha ...
Sculpting the Earth`s Surface
... Important factors Rock characteristics • Mineral composition and solubility • Physical features such as joints ...
... Important factors Rock characteristics • Mineral composition and solubility • Physical features such as joints ...
Comparison of Methods for the Assessment of Soil Organic
... become more accurate and less costly. Advances in information technology and the development of new sensors and instruments have facilitated the collection and analysis of data, making possible the formulation of more complex models. Carbon is of great importance to soils. It has a strong relationsh ...
... become more accurate and less costly. Advances in information technology and the development of new sensors and instruments have facilitated the collection and analysis of data, making possible the formulation of more complex models. Carbon is of great importance to soils. It has a strong relationsh ...
1.0 Introduction What is soil? Soil is the upper most layer of earth
... Soil Textural Class: Grouping based on relative proportion and specifically on % sand, silt and clay in given soil sample. The class name essentially describes the separate which most influence the sample physical/chemical/biological properties. ...
... Soil Textural Class: Grouping based on relative proportion and specifically on % sand, silt and clay in given soil sample. The class name essentially describes the separate which most influence the sample physical/chemical/biological properties. ...
Fertilizers and Fertilizer Management
... Soil as defined by scientists … natural product formed from weathered rock by the action of climate and living organisms modified by topography over a period of time. ...
... Soil as defined by scientists … natural product formed from weathered rock by the action of climate and living organisms modified by topography over a period of time. ...
Soil acidity
... nutrients are taken up in the cationic forms, so it is important that the soil be able to supply these. Most soils have at least some ability to hold onto these ions at the negatively charged sites within the soil. The amount that they can hold is denoted as the Cation Exchange Capacity. Cations tha ...
... nutrients are taken up in the cationic forms, so it is important that the soil be able to supply these. Most soils have at least some ability to hold onto these ions at the negatively charged sites within the soil. The amount that they can hold is denoted as the Cation Exchange Capacity. Cations tha ...
Nitrogen Management in Irrigated Crops
... - Generally higher cost per pound of N than dry or gaseous nitrogen - Urea portion of liquid N source is susceptible to volatilization losses with surface applications - Potential for excessive crop injury if applied undiluted following crop emergence ...
... - Generally higher cost per pound of N than dry or gaseous nitrogen - Urea portion of liquid N source is susceptible to volatilization losses with surface applications - Potential for excessive crop injury if applied undiluted following crop emergence ...
THE DISTRIBUTION OF MICROORGANISMS IN DIFFERENT
... The distribution of fungi, as an important component of the soil microbiota, depending on soil depth and nutrient conditions such as nature of the organic content of the soil and other soil and climatic conditions, surface vegetation and soil texture (MARSCHNER et al., 2003). In our research, the hi ...
... The distribution of fungi, as an important component of the soil microbiota, depending on soil depth and nutrient conditions such as nature of the organic content of the soil and other soil and climatic conditions, surface vegetation and soil texture (MARSCHNER et al., 2003). In our research, the hi ...
Earth Science: 5.2 Soil - sleepingdogstudios.com
... Soil, an important product of weathering, covers most land surfaces. Along with air and water, soil is one of our most important resources. ...
... Soil, an important product of weathering, covers most land surfaces. Along with air and water, soil is one of our most important resources. ...
IOSR Journal of Environmental Science, Toxicology and Food Technology (IOSR-JESTFT)
... numerous microbes and soils biota, and space for natural organic material recycle which are important to provide nutrient for plant and soil biotic organism. Soil is also important in global water cycle. There are physical and chemical characteristics of soils which are contribute to the land produc ...
... numerous microbes and soils biota, and space for natural organic material recycle which are important to provide nutrient for plant and soil biotic organism. Soil is also important in global water cycle. There are physical and chemical characteristics of soils which are contribute to the land produc ...
... a maximum value around 2035. Then they decrease significantly again as less new land will be available for sequestration and soils saturate with carbon. This illustrates that SOC will increase only over a limited time, up to the point where a new SOC equilibrium is reached. In addition, adoption of ...
Soil Structure - ASCE Philadelphia Section
... occurring through the sides of percolation hole. It assumes that the percolation rate is affected by the depth of water in the hole and that the percolating surface of the hole is in uniform soil. ...
... occurring through the sides of percolation hole. It assumes that the percolation rate is affected by the depth of water in the hole and that the percolating surface of the hole is in uniform soil. ...
Benchmark Science Map - Troup County Schools
... Determine how water and wind can change rocks and soil over time using observation and research. Explain the difference between a rock and a mineral. Recognize the physical attributes of rocks and minerals using observation (shape, color, texture), measurement, and simple tests (hardness). Describe ...
... Determine how water and wind can change rocks and soil over time using observation and research. Explain the difference between a rock and a mineral. Recognize the physical attributes of rocks and minerals using observation (shape, color, texture), measurement, and simple tests (hardness). Describe ...
residual .vs. transported soils(cont)
... LANDFILLS ARE NOT COVERED IN THIS COURSE. HOWEVER, THEY ARE RELEVANT RELATED TOPICS ...
... LANDFILLS ARE NOT COVERED IN THIS COURSE. HOWEVER, THEY ARE RELEVANT RELATED TOPICS ...
Soil of Atlas Europe
... •Full scale draft completed and dispatched •Processing feedback. Soil Atlas of Europe: Editorial Board Meeting November 2004 ...
... •Full scale draft completed and dispatched •Processing feedback. Soil Atlas of Europe: Editorial Board Meeting November 2004 ...
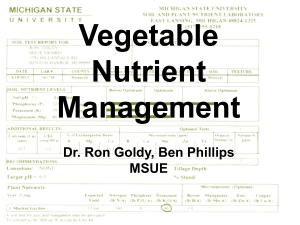
Vegetable Nutrient Management Dr. Ron Goldy, Ben Phillips
... Primarily through roots but can come in through leaves as SO2 Enzymes and vitamins, nodulation, ...
... Primarily through roots but can come in through leaves as SO2 Enzymes and vitamins, nodulation, ...
Environmental Science - University of Tennessee Extension
... On humus. Humus is the “leftovers” after bacteria, fungi, arthropods and worms have had their fill of plant litter. Fungi are common here because they can make some of the enzymes needed to degrade the hard-to-digest compounds in humus. On the surface of soil aggregates. Many aggregates (“clumps”) a ...
... On humus. Humus is the “leftovers” after bacteria, fungi, arthropods and worms have had their fill of plant litter. Fungi are common here because they can make some of the enzymes needed to degrade the hard-to-digest compounds in humus. On the surface of soil aggregates. Many aggregates (“clumps”) a ...