Molten-core fabrication of novel optical fibers
... The resultant core glasses contain much higher yttria and alumina concentrations than would otherwise be possible, opening the door to “novel fibers from common materials” (just not common when it comes to optical fibers). For example, the YAG-derived fibers with high yttria and alumina contents hav ...
... The resultant core glasses contain much higher yttria and alumina concentrations than would otherwise be possible, opening the door to “novel fibers from common materials” (just not common when it comes to optical fibers). For example, the YAG-derived fibers with high yttria and alumina contents hav ...
Spectroscopy – I. Gratings and Prisms
... order 1 – and so on. (But note that the amount of light will be less in the higher orders – see the section on Young’s experiment). Even in the case of low orders, the orders begin to overlap – even if restricted to just the visible region of the spectrum: ...
... order 1 – and so on. (But note that the amount of light will be less in the higher orders – see the section on Young’s experiment). Even in the case of low orders, the orders begin to overlap – even if restricted to just the visible region of the spectrum: ...
Theory of the transmission properties of an optical far-field superlens
... transmitted and incident transverse wavenumbers, respectively; ⌳ = 2 / d is the grating wavenumber, where d is the periodicity; and p is the diffraction order. We are interested only in waves transmitted in the far field, i.e., far enough from the FSL and the object plan that the contribution of ev ...
... transmitted and incident transverse wavenumbers, respectively; ⌳ = 2 / d is the grating wavenumber, where d is the periodicity; and p is the diffraction order. We are interested only in waves transmitted in the far field, i.e., far enough from the FSL and the object plan that the contribution of ev ...
Technologies - E
... These devices are responsible for the light distribution from one or several input fibers to one or several output fibers ...
... These devices are responsible for the light distribution from one or several input fibers to one or several output fibers ...
Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography
... Compared with traditional TDOCT, SDOCT technology yields unprecedented acquisition speeds and significantly higher axial resolutions using a potentially affordable SLD source. This system produced high quality images while operating at safe ocular exposure levels, even below that of the commercially ...
... Compared with traditional TDOCT, SDOCT technology yields unprecedented acquisition speeds and significantly higher axial resolutions using a potentially affordable SLD source. This system produced high quality images while operating at safe ocular exposure levels, even below that of the commercially ...
Practical aspects of Microscopy
... too small to be easily viewed by the human eye. Viewing and studying objects that range in size from millimeters (1 mm = 10-3 meter) to nanometers (1 nm = 10-9 meter) intrigues everyone and is currently applied to every field of science and technology in use today. Microscopes, devices which magnify ...
... too small to be easily viewed by the human eye. Viewing and studying objects that range in size from millimeters (1 mm = 10-3 meter) to nanometers (1 nm = 10-9 meter) intrigues everyone and is currently applied to every field of science and technology in use today. Microscopes, devices which magnify ...
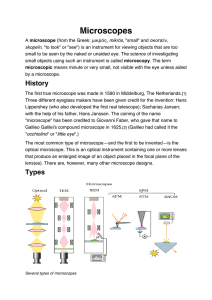
Microscopes - Biozentrum
... name "microscope" a year latter by fellow Lincean Giovanni Faber. Faber coined the name from the Greek words μικρόν (micron) meaning "small", and σκοπεῖν (skopein) meaning "to look at", a name meant to be analogus with "telescope", another word coined by the Linceans[3]. Christiaan Huygens, another ...
... name "microscope" a year latter by fellow Lincean Giovanni Faber. Faber coined the name from the Greek words μικρόν (micron) meaning "small", and σκοπεῖν (skopein) meaning "to look at", a name meant to be analogus with "telescope", another word coined by the Linceans[3]. Christiaan Huygens, another ...
Electron diffraction for analysing crystal orientation of thin films
... diffraction, a phenomenon based on the wave nature of these small particles, was able to provide diffraction patterns of crystalline materials very similar to those obtained by X-rays [4, 5, 18]. Today, electron diffraction has developed into a very powerful tool in structural crystallography and ma ...
... diffraction, a phenomenon based on the wave nature of these small particles, was able to provide diffraction patterns of crystalline materials very similar to those obtained by X-rays [4, 5, 18]. Today, electron diffraction has developed into a very powerful tool in structural crystallography and ma ...
Technological Education Institute (TEI) of Piraeus
... Fiber optic sensors: distributed fiber sensors Raman and stimulated Brillouin scatter distributed optical sensors - Modification of the spectral content of the light propagating through the fiber in response to an external measurand - The measurand is determined by evaluating the spectral content ...
... Fiber optic sensors: distributed fiber sensors Raman and stimulated Brillouin scatter distributed optical sensors - Modification of the spectral content of the light propagating through the fiber in response to an external measurand - The measurand is determined by evaluating the spectral content ...
Fourier-domain holography in photorefractive quantum-well films
... intensity variation of the Fourier transform across the recording medium,6,13 which results in the loss of either high-frequency or low-frequency components in reconstructed images. To solve this problem, diffusers such as random,13 deterministic,14 and pseudorandom15 diffusers were developed after ...
... intensity variation of the Fourier transform across the recording medium,6,13 which results in the loss of either high-frequency or low-frequency components in reconstructed images. To solve this problem, diffusers such as random,13 deterministic,14 and pseudorandom15 diffusers were developed after ...
Sample manuscript showing specifications and style
... somewhat further for a reconstruction with red light and still see the 3D scene than would be the case for a reconstruction with blue light. But the lateral position of the reconstructed points in space remains unchanged for red green an blue. There is only a small z-shift of the object points with ...
... somewhat further for a reconstruction with red light and still see the 3D scene than would be the case for a reconstruction with blue light. But the lateral position of the reconstructed points in space remains unchanged for red green an blue. There is only a small z-shift of the object points with ...
Optical amplifiers
... whisky goes into the student, but instantly comes back out, magnified several times with a flurry of liquid from the earlier pumping. And so the optical signal exits the EDFA having been increased in intensity several times over. Erbium has several energy levels, but its ions are usually in the grou ...
... whisky goes into the student, but instantly comes back out, magnified several times with a flurry of liquid from the earlier pumping. And so the optical signal exits the EDFA having been increased in intensity several times over. Erbium has several energy levels, but its ions are usually in the grou ...
1 L5: Diffraction L5 DIFFRACTION Objectives Aims From this
... about 1679 and was modified much later into the form we now use by Augustin Fresnel (1788 1827). Huygens' construction is a method for locating the new position of a wave front. Starting from a known wavefront, we imagine each point on the wavefront to be a new source of secondary wavelets. The wave ...
... about 1679 and was modified much later into the form we now use by Augustin Fresnel (1788 1827). Huygens' construction is a method for locating the new position of a wave front. Starting from a known wavefront, we imagine each point on the wavefront to be a new source of secondary wavelets. The wave ...
Mie theory for light scattering by a spherical
... exhibit the refractive index of the medium as well as that of the sphere. These equations are formally identical to those obtained for the case of an absorbing medium, where both refractive indices can be complex. In this section the formal scattering solution is briefly reviewed by use of the notat ...
... exhibit the refractive index of the medium as well as that of the sphere. These equations are formally identical to those obtained for the case of an absorbing medium, where both refractive indices can be complex. In this section the formal scattering solution is briefly reviewed by use of the notat ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.