Structure and Imaging of a Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
... electrons from the source. In TEM, particularly, the “Koeller illumination mode” is used, where the lens works for making a parallel beam along the optical axis for a specimen. In a sense of wave optics, the incident wave is considered as a plane wave. For HRTEM, brighter illumination is crucial. Th ...
... electrons from the source. In TEM, particularly, the “Koeller illumination mode” is used, where the lens works for making a parallel beam along the optical axis for a specimen. In a sense of wave optics, the incident wave is considered as a plane wave. For HRTEM, brighter illumination is crucial. Th ...
1346732768.
... (d) Calculate the angular separation of red and violet rays which emerge from a 600 glass prism when a ray of white light is incident on a prism at an angle of 45, the glass prism has refractive index of 1.64 for a red light and 1.66 for a violet light. (4marks) (e) In a certain experiment, a pendul ...
... (d) Calculate the angular separation of red and violet rays which emerge from a 600 glass prism when a ray of white light is incident on a prism at an angle of 45, the glass prism has refractive index of 1.64 for a red light and 1.66 for a violet light. (4marks) (e) In a certain experiment, a pendul ...
Glass Analysis Powerpoint
... Forensic Examination of Glass • Goals in examining glass evidence: – Determine the types of glass at the scene – Determine how the glass was fractured – Use physical characteristics to classify it – Individualize the glass to a source • Compare physical and chemical characteristics: – Optical prope ...
... Forensic Examination of Glass • Goals in examining glass evidence: – Determine the types of glass at the scene – Determine how the glass was fractured – Use physical characteristics to classify it – Individualize the glass to a source • Compare physical and chemical characteristics: – Optical prope ...
Laser Molecular Spectroscopy CHE466 Fall 2007
... This term refers to the required pumping ability to maintain lasing action. Since resonance inside a cavity decreases the potential output of a laser (call cavity loses), an additional amount of energy is required to overcome such losses. Pumping is performed using electrical power (electrical disch ...
... This term refers to the required pumping ability to maintain lasing action. Since resonance inside a cavity decreases the potential output of a laser (call cavity loses), an additional amount of energy is required to overcome such losses. Pumping is performed using electrical power (electrical disch ...
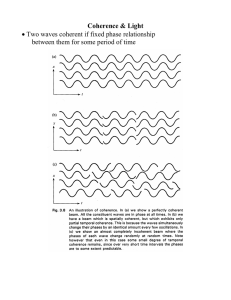
Week 9 Wed. (Lesson 15) Coherence and Optical Tomography
... • Single atom on 10-8 sec coherent lifetime of atom in an excited state • Much shorter for groups of atoms • For lasers in single mode much longer time ...
... • Single atom on 10-8 sec coherent lifetime of atom in an excited state • Much shorter for groups of atoms • For lasers in single mode much longer time ...
n 1n d
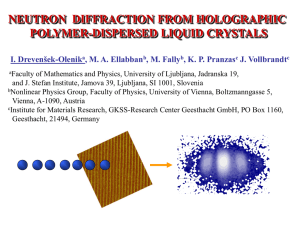
... • The diffraction efficiency of the 1st diffraction orders is around 10% !!! • Diffraction peaks up to the 2nd order are visible. (non-deuterated sample!!) ...
... • The diffraction efficiency of the 1st diffraction orders is around 10% !!! • Diffraction peaks up to the 2nd order are visible. (non-deuterated sample!!) ...
S.72-227 Digital Communication Systems
... Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory Digital Hierarchy as applied in PSTN ...
... Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory Digital Hierarchy as applied in PSTN ...
conclusion
... forms the hologram structure (Fig. 1B). The phase distribution (x’,y’) can be approximated by each pixel structure using different regions inside the pixel that modulate the phase values 0, /2, , and 3/2. Figure 5A shows the structure of a particular pixel that can modulate the phase between 0 a ...
... forms the hologram structure (Fig. 1B). The phase distribution (x’,y’) can be approximated by each pixel structure using different regions inside the pixel that modulate the phase values 0, /2, , and 3/2. Figure 5A shows the structure of a particular pixel that can modulate the phase between 0 a ...
Department of Physics, Technical University Ostrava 17. listopadu
... have confirmed that in contrary to standard spatial-domain white-light interferometry employing dispersion balanced interferometers our measurement techniques are characterized by the range of measurable distances dependent on the amount of dispersion in the interferometer [13–15]. We have also demo ...
... have confirmed that in contrary to standard spatial-domain white-light interferometry employing dispersion balanced interferometers our measurement techniques are characterized by the range of measurable distances dependent on the amount of dispersion in the interferometer [13–15]. We have also demo ...
Plasmonic Nearfield Scanning Probe with High Transmission
... NSOM probes, the local intensity of plasmonic NSOM probes should be ∼20 times higher than that of normal NSOM probes. This result confirms the high resolution and high optical throughput of the plasmonic lens. The central concern of the conic plasmonic lens is how much energy can be concentrated int ...
... NSOM probes, the local intensity of plasmonic NSOM probes should be ∼20 times higher than that of normal NSOM probes. This result confirms the high resolution and high optical throughput of the plasmonic lens. The central concern of the conic plasmonic lens is how much energy can be concentrated int ...
Wave Optics
... For each point in the upper half of the opening, in the direction , there is a point in the lower half that interferes destructively with it. A dark fringe occurs in this direction. Condition for dark fringes: ...
... For each point in the upper half of the opening, in the direction , there is a point in the lower half that interferes destructively with it. A dark fringe occurs in this direction. Condition for dark fringes: ...
Retroreflector

A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.