Measurement of the Wavelength of Light
... Phys 303 Lab Experiment 0 Justin M. Sanders January 15, 2013 Abstract Light waves diffract when reflecting off a grated surface and the diffraction angles are related to the wavelength of the light. In this experiment, we measured the angles of diffraction for a red laser pointer and used them to ob ...
... Phys 303 Lab Experiment 0 Justin M. Sanders January 15, 2013 Abstract Light waves diffract when reflecting off a grated surface and the diffraction angles are related to the wavelength of the light. In this experiment, we measured the angles of diffraction for a red laser pointer and used them to ob ...
Femto-Photography: Capturing and Visualizing the
... We present femto-photography, a novel imaging technique to capture and visualize the propagation of light. With an effective exposure time of 1.85 picoseconds (ps) per frame, we reconstruct movies of ultrafast events at an equivalent resolution of about one half trillion frames per second. Because c ...
... We present femto-photography, a novel imaging technique to capture and visualize the propagation of light. With an effective exposure time of 1.85 picoseconds (ps) per frame, we reconstruct movies of ultrafast events at an equivalent resolution of about one half trillion frames per second. Because c ...
Lecture 2
... • Chromatic aberration – arise from variations in the refractive indices of the wide range of frequencies in visible light Astigmatism, field curvature and comatic aberrations are easily corrected with proper lens fabrication. ...
... • Chromatic aberration – arise from variations in the refractive indices of the wide range of frequencies in visible light Astigmatism, field curvature and comatic aberrations are easily corrected with proper lens fabrication. ...
Brightfield Contrasting Techniques
... • Need to selectively shift the phase of the surround wave. How to do this? • The sample will scatter light in all directions, so if we illuminate with a small range of angles we can specifically alter the phase at those angles ...
... • Need to selectively shift the phase of the surround wave. How to do this? • The sample will scatter light in all directions, so if we illuminate with a small range of angles we can specifically alter the phase at those angles ...
DOWNLOAD Lesson 201 Handout
... 1. Why is light so very important to astronomy? What kinds of information can you get from it? 2. Why is light called electromagnetic radiation? Is radio a form of light? 3. Put the following forms of light in order of increasing frequency (lowest frequency first): ultraviolet, infrared, gamma rays, ...
... 1. Why is light so very important to astronomy? What kinds of information can you get from it? 2. Why is light called electromagnetic radiation? Is radio a form of light? 3. Put the following forms of light in order of increasing frequency (lowest frequency first): ultraviolet, infrared, gamma rays, ...
BioE 123 Teaching Material Stanford University
... wavefronts are in blue in diagram at right). These are “light rays.” The bending of light at interfaces between materials results in shifting in the direction of wavefronts and thus it is easy to use vectors to show where the peaks of the wavefronts will be headed. Rays are perpendicular to wavefron ...
... wavefronts are in blue in diagram at right). These are “light rays.” The bending of light at interfaces between materials results in shifting in the direction of wavefronts and thus it is easy to use vectors to show where the peaks of the wavefronts will be headed. Rays are perpendicular to wavefron ...
First Order Optics
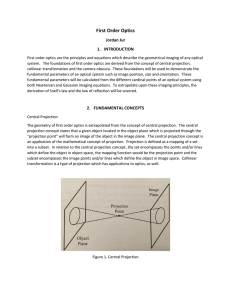
... The cardinal points define points of angular and spatial significance within an optical system. Any optical system can be decomposed in terms of the six cardinal planes. The six cardinal planes are the front and rear focal planes, nodal planes and the principle planes. The focal planes are the plane ...
... The cardinal points define points of angular and spatial significance within an optical system. Any optical system can be decomposed in terms of the six cardinal planes. The six cardinal planes are the front and rear focal planes, nodal planes and the principle planes. The focal planes are the plane ...
r - Nano[studijní] materiály - Technical University of Liberec
... functions J1 was checked • Good agreement with prediction was achieved • Due a technical limits of our EOM (maximal applied voltage), it is not be able to work at the maximum of Bessel function (highest signal) • We work at phase shift amplitude about 1 rad ...
... functions J1 was checked • Good agreement with prediction was achieved • Due a technical limits of our EOM (maximal applied voltage), it is not be able to work at the maximum of Bessel function (highest signal) • We work at phase shift amplitude about 1 rad ...
L4 INTERFERENCE
... (vector sum if the wave property is a vector) of the wave property for the individual waves. The contribution from one wave is just that which would occur if the other waves were not there. In the case of the water waves the appropriate wave property is the linear displacement (change in position) o ...
... (vector sum if the wave property is a vector) of the wave property for the individual waves. The contribution from one wave is just that which would occur if the other waves were not there. In the case of the water waves the appropriate wave property is the linear displacement (change in position) o ...
Fresnel Equations. In Encyclopedia of Optical Engineering
... where n1 and n2 are the refractive indices of the two media. The angle θr of the reflected wave is equal to θi according to the law of reflection. We denote the amplitudes of these two waves as Et and Er, respectively. Our goal is to determine these amplitudes. To accomplish this, we apply the bound ...
... where n1 and n2 are the refractive indices of the two media. The angle θr of the reflected wave is equal to θi according to the law of reflection. We denote the amplitudes of these two waves as Et and Er, respectively. Our goal is to determine these amplitudes. To accomplish this, we apply the bound ...
Nano-optomechanical Actuator and Pull-Back Instability
... low cost. However, the microscale dimensions limit both the speed and precision of actuation. Nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS) scale down the dimensions.7,8 In particular, NEMS employing electrostatic forces have been developed.9,10 For parallel-plate electrostatic actuators, the pull-in instabi ...
... low cost. However, the microscale dimensions limit both the speed and precision of actuation. Nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS) scale down the dimensions.7,8 In particular, NEMS employing electrostatic forces have been developed.9,10 For parallel-plate electrostatic actuators, the pull-in instabi ...
Consequences of the WFC3 IR detector 24 degrees tilt
... primary for the 1 mm substrate. It is hard to estimate the amount of energy in the secondary image from first principles since this number depends among others from the refraction index mismatch between HgCdTe and CdZnTe and on the precise nature of the AR coating. Assuming pessimistically that 15 p ...
... primary for the 1 mm substrate. It is hard to estimate the amount of energy in the secondary image from first principles since this number depends among others from the refraction index mismatch between HgCdTe and CdZnTe and on the precise nature of the AR coating. Assuming pessimistically that 15 p ...
Retroreflector

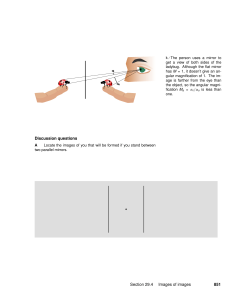
A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.










![r - Nano[studijní] materiály - Technical University of Liberec](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007925985_1-5e55f54db686ed86c2131eb21f7dd098-300x300.png)