Introduction_to_decision_analysis
... Decisions by an individual vs. in a society • In theory, decision analysis is straightforward with a single decision-maker: she just has to assess her subjective probabilities and utilities and maximize expected utility. • In practice, there are severe problems: assessing probabilities and utilitie ...
... Decisions by an individual vs. in a society • In theory, decision analysis is straightforward with a single decision-maker: she just has to assess her subjective probabilities and utilities and maximize expected utility. • In practice, there are severe problems: assessing probabilities and utilitie ...
ADD-ON 9B - Ateneonline
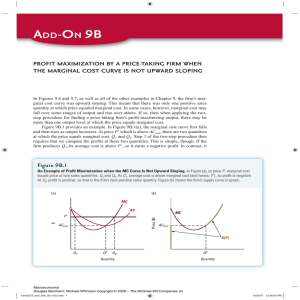
... In Figures 9.6 and 9.7, as well as all of the other examples in Chapter 9, the firm’s marginal cost curve was upward sloping. This meant that there was only one positive sales quantity at which price equaled marginal cost. In some cases, however, marginal cost may fall over some ranges of output and ...
... In Figures 9.6 and 9.7, as well as all of the other examples in Chapter 9, the firm’s marginal cost curve was upward sloping. This meant that there was only one positive sales quantity at which price equaled marginal cost. In some cases, however, marginal cost may fall over some ranges of output and ...
Principles of Economics, Case and Fair,9e
... The Income Effect Price changes affect households in two ways. First, if we assume that households confine their choices to products that improve their well-being, then a decline in the price of any product, ceteris paribus, will make the household unequivocally better off. ...
... The Income Effect Price changes affect households in two ways. First, if we assume that households confine their choices to products that improve their well-being, then a decline in the price of any product, ceteris paribus, will make the household unequivocally better off. ...
13. Acting under Uncertainty Maximizing Expected Utility
... If one action is better than all others, then the exact values of the states involved need not to be known. Policy iteration alternates the following two steps beginning with an initial policy π0 : Policy evaluation: given a policy πt , calculate Ut = U πt , the utility of each state if πt were exec ...
... If one action is better than all others, then the exact values of the states involved need not to be known. Policy iteration alternates the following two steps beginning with an initial policy π0 : Policy evaluation: given a policy πt , calculate Ut = U πt , the utility of each state if πt were exec ...
solutions
... can’t happen, given an example . . . ”. I meant to say “If you think one of these can happen, give an example that demonstrates it; if you think it must happen, explain why. (Note: 1-2 sentence explanations suffice in each case.)” Most people figured out the intent of the question. Solution: (a) Wit ...
... can’t happen, given an example . . . ”. I meant to say “If you think one of these can happen, give an example that demonstrates it; if you think it must happen, explain why. (Note: 1-2 sentence explanations suffice in each case.)” Most people figured out the intent of the question. Solution: (a) Wit ...
Name: JJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJ Date: JJJJJJJJJJJJJJ
... inputs and factors of production in the production process. Which of the following is a factor of production? A) the raw meat used for the hamburgers B) the hamburger buns C) the cook D) the concentrate that is diluted to make the soft drinks 20. Human capital is the improvement in ________ created ...
... inputs and factors of production in the production process. Which of the following is a factor of production? A) the raw meat used for the hamburgers B) the hamburger buns C) the cook D) the concentrate that is diluted to make the soft drinks 20. Human capital is the improvement in ________ created ...