If a monopolist finds a way of producing a good at lower cost, he will
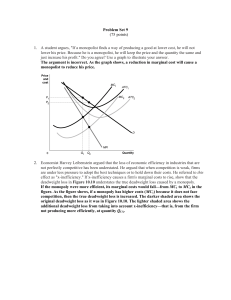
... effect as "x-inefficiency." If x-inefficiency causes a firm's marginal costs to rise, show that the deadweight loss in Figure 10.10 understates the true deadweight loss caused by a monopoly. If the monopoly were more efficient, its marginal costs would fall—from MC1 to MC2 in the figure. As the figu ...
... effect as "x-inefficiency." If x-inefficiency causes a firm's marginal costs to rise, show that the deadweight loss in Figure 10.10 understates the true deadweight loss caused by a monopoly. If the monopoly were more efficient, its marginal costs would fall—from MC1 to MC2 in the figure. As the figu ...
HotellingsRule - Kleykamp in Taiwan
... Hotelling’s Rule In what follows I will use the term “price” to denote unit profit. That is, the nominal money price minus the average cost of production. We begin with competition. Suppose that a firm owns a small part, a, of the total amount of an exhaustible resource. This small competitive firm ...
... Hotelling’s Rule In what follows I will use the term “price” to denote unit profit. That is, the nominal money price minus the average cost of production. We begin with competition. Suppose that a firm owns a small part, a, of the total amount of an exhaustible resource. This small competitive firm ...
THE THEORY OF ECONOMIC VALUE
... willing to supply, as a function of the price at which he can sell it. If the price of chocolate goes up, chocolate companies will be willing to make more chocolate. Conversely, if the price of chocolate goes down, less chocolate will be supplied. Unfortunately, it costs Hershey money to supply us w ...
... willing to supply, as a function of the price at which he can sell it. If the price of chocolate goes up, chocolate companies will be willing to make more chocolate. Conversely, if the price of chocolate goes down, less chocolate will be supplied. Unfortunately, it costs Hershey money to supply us w ...
AP Micro Problem Set 3 Production Costs and Perfect Competition
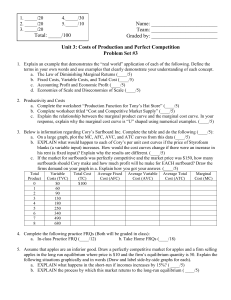
... 1. Explain an example that demonstrates the “real world” application of each of the following. Define the terms in your own words and use examples that clearly demonstrate your understanding of each concept. a. The Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns (____/5) b. Fixed Costs, Variable Costs, and Tota ...
... 1. Explain an example that demonstrates the “real world” application of each of the following. Define the terms in your own words and use examples that clearly demonstrate your understanding of each concept. a. The Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns (____/5) b. Fixed Costs, Variable Costs, and Tota ...
Boating Business Booms Despite Slowing Economy
... 2. Which of the following best describes the concept of opportunity cost for a particular decision? a. The prices and quantities of all goods that were not purchased but could have been purchased with the same money. b. The amount of income left over after the purchase. c. The value to you of the ne ...
... 2. Which of the following best describes the concept of opportunity cost for a particular decision? a. The prices and quantities of all goods that were not purchased but could have been purchased with the same money. b. The amount of income left over after the purchase. c. The value to you of the ne ...
ECON308: Monopoly = Price Searcher
... B. As more close substitutes enter the market, the demand facing the monopoly will decline and become more elastic. This means competition will bring lower prices and lower profits. There are no profits in the long run, UNLESS the firm can limit competition. ...
... B. As more close substitutes enter the market, the demand facing the monopoly will decline and become more elastic. This means competition will bring lower prices and lower profits. There are no profits in the long run, UNLESS the firm can limit competition. ...
Ch 5 - gcisd
... Setting Output •The best level of output is to find the output level where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost. •Ex. IPHONE To Shutdown or to not shutdown •If shuts down – still have to pay ___________________. •Sometimes keeping a money-losing factory open is the better choice. •Amazon.com ( ...
... Setting Output •The best level of output is to find the output level where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost. •Ex. IPHONE To Shutdown or to not shutdown •If shuts down – still have to pay ___________________. •Sometimes keeping a money-losing factory open is the better choice. •Amazon.com ( ...
Topic 5 - CSUSAP
... 11) When the quantity of all inputs is increased, for example by 50%, output will increase. If output increases by more than 50%, there are increasing returns to scale. If output increases by exactly 50%, there constant returns to scale. If output increases by less than 50%, there are decreasing ret ...
... 11) When the quantity of all inputs is increased, for example by 50%, output will increase. If output increases by more than 50%, there are increasing returns to scale. If output increases by exactly 50%, there constant returns to scale. If output increases by less than 50%, there are decreasing ret ...
Study guide 2005 1 st mid-term
... a. The total product is at the maximum when marginal product is also at a maximum. Sample Answer: False. Marginal product is at a maximum when the change in output given a change in input is largest. It indicates that the slope of the TP curve is steepest. When TP is at a maximum, it passes from a p ...
... a. The total product is at the maximum when marginal product is also at a maximum. Sample Answer: False. Marginal product is at a maximum when the change in output given a change in input is largest. It indicates that the slope of the TP curve is steepest. When TP is at a maximum, it passes from a p ...