Review of key models used
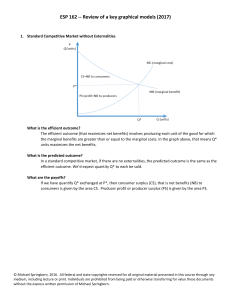
... Without intervention, we’d predict that the producer would choose the quantity that maximizes their profit, i.e. where marginal benefit is equal to the marginal private cost. Thus, we’d predict that Q’ units would be sold at P’. Note that Q’>Q* and P’
... Without intervention, we’d predict that the producer would choose the quantity that maximizes their profit, i.e. where marginal benefit is equal to the marginal private cost. Thus, we’d predict that Q’ units would be sold at P’. Note that Q’>Q* and P’
Theory of Consumer Behavior
... consumer no longer wants any more units of that good. Secondly, different goods are not perfect substitutes for each other in the satisfaction of various particular wants. As such the marginal utility will decline as the consumer gets additional units of a specific good. Thirdly, the marginal utilit ...
... consumer no longer wants any more units of that good. Secondly, different goods are not perfect substitutes for each other in the satisfaction of various particular wants. As such the marginal utility will decline as the consumer gets additional units of a specific good. Thirdly, the marginal utilit ...
Chapter 4, 5, 6, 7 with Graph Explained
... • A classmate ate chocolate chip cookies until he didn’t want anymore. This student paid for every cookie he ate. The amount he paid decreased as he continued to eat the cookies. • This illustrated the point of decreasing SATISFACTION! ...
... • A classmate ate chocolate chip cookies until he didn’t want anymore. This student paid for every cookie he ate. The amount he paid decreased as he continued to eat the cookies. • This illustrated the point of decreasing SATISFACTION! ...
Lesson 6 - BYU
... The resulting ranking or utility values are subjective or individual. They are also ordinal rather than cardinal. Ordinal means that the utility values simply define a ranking of preferences rather than an actual cardinal measurement. Imagine a class has 10 students in the class and the teacher line ...
... The resulting ranking or utility values are subjective or individual. They are also ordinal rather than cardinal. Ordinal means that the utility values simply define a ranking of preferences rather than an actual cardinal measurement. Imagine a class has 10 students in the class and the teacher line ...
ECON 2105H
... Your congressman is not applying basic principle number 2: rational choice balances costs and benefits at the margin. The “optimal” amount of marijuana consumption is most likely not zero, since the cost of a law totally banning marijuana consumption (the lost value people get from consuming it) it ...
... Your congressman is not applying basic principle number 2: rational choice balances costs and benefits at the margin. The “optimal” amount of marijuana consumption is most likely not zero, since the cost of a law totally banning marijuana consumption (the lost value people get from consuming it) it ...
Vocabulary Lists for
... good required to compensate a consumer for a small decrease in the quantity of another, or how much of one good a consumer has to sacrifice in order to obtain another. It is measured by the ratio of the marginal utilities of two goods. ...
... good required to compensate a consumer for a small decrease in the quantity of another, or how much of one good a consumer has to sacrifice in order to obtain another. It is measured by the ratio of the marginal utilities of two goods. ...
Consumer Behavior - The Digital Economist
... The second assumption states that if 'b' is preferred to 'a' and 'a' is preferred to 'c' then it must be true that 'b' is preferred to 'c'. This is known as the transitivity condition. The third assumption is straight-forward in that greater quantities provide greater levels of satisfaction to the i ...
... The second assumption states that if 'b' is preferred to 'a' and 'a' is preferred to 'c' then it must be true that 'b' is preferred to 'c'. This is known as the transitivity condition. The third assumption is straight-forward in that greater quantities provide greater levels of satisfaction to the i ...
Unit 3 Lesson 1
... These costs are the same no matter how many of the products that are produced. This is because the firm has had to buy things for production. They are paying for them. (Ex. plant, equipment...) These can only be changed in the long run. ...
... These costs are the same no matter how many of the products that are produced. This is because the firm has had to buy things for production. They are paying for them. (Ex. plant, equipment...) These can only be changed in the long run. ...
Study Guide Sample Chapter 2
... A person has a utility function with MRS=Y/X The price of good X is $1.00 The price of good Y is $2.00 The person has budgeted $1000 for purchases of X and Y. ...
... A person has a utility function with MRS=Y/X The price of good X is $1.00 The price of good Y is $2.00 The person has budgeted $1000 for purchases of X and Y. ...