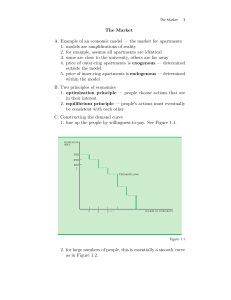
Short-Run Cost
... Economies of scale are features of a firm’s technology that lead to falling long-run average cost as output increases. Diseconomies of scale are features of a firm’s technology that lead to rising long-run average cost as output increases. Constant returns to scale are features of a firm’s technolog ...
... Economies of scale are features of a firm’s technology that lead to falling long-run average cost as output increases. Diseconomies of scale are features of a firm’s technology that lead to rising long-run average cost as output increases. Constant returns to scale are features of a firm’s technolog ...
Eco 300 Intermediate Micro
... So if one tries to divide every input by two, one gets much less than half the output. Therefore, if one multiplies by two from that half input, one gets much more than twice the output. An example of an indivisible input is information. For instance, information about how to run a machine. One eith ...
... So if one tries to divide every input by two, one gets much less than half the output. Therefore, if one multiplies by two from that half input, one gets much more than twice the output. An example of an indivisible input is information. For instance, information about how to run a machine. One eith ...
Demand, elasticities and Consumer theory
... Exceptions to the law of demand Giffen goods – a special type of inferior good that does not respect the law of demand. As price goes up, quantity also goes up. E.g Discounted products Conspicuous consumption – like art or diamonds (bought by the rich). Its only when the price goes up that people ...
... Exceptions to the law of demand Giffen goods – a special type of inferior good that does not respect the law of demand. As price goes up, quantity also goes up. E.g Discounted products Conspicuous consumption – like art or diamonds (bought by the rich). Its only when the price goes up that people ...
Chapter 6
... 2) Marginal benefit is the A) total benefit we receive from consuming a good or service. B) additional benefit we receive from consuming one more unit of a good or service. C) minimum amount of other goods or services we are willing to give up. D) opportunities given up to get one more unit of a goo ...
... 2) Marginal benefit is the A) total benefit we receive from consuming a good or service. B) additional benefit we receive from consuming one more unit of a good or service. C) minimum amount of other goods or services we are willing to give up. D) opportunities given up to get one more unit of a goo ...
ECONOMIC ANALYSIS FOR BUSINESS UNIT II CONSUMER AND
... to engage in the production of medicines rather than rat poison because it makes them feel more important in society, we expect more medicines and less rat poison to be produced than if producers held all commodities in equal regard. If producers of some commodity want to sell as much as possible, e ...
... to engage in the production of medicines rather than rat poison because it makes them feel more important in society, we expect more medicines and less rat poison to be produced than if producers held all commodities in equal regard. If producers of some commodity want to sell as much as possible, e ...
Chapter 5: Income and Substitution Effects
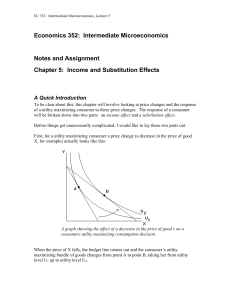
... The Hicksian demand curve is called the compensated demand curve because the consumer is compensated for the price change. That is, when the price changes they receive compensation that allows them to remain on their original indifference curve. If the price of the good rises this compensation is po ...
... The Hicksian demand curve is called the compensated demand curve because the consumer is compensated for the price change. That is, when the price changes they receive compensation that allows them to remain on their original indifference curve. If the price of the good rises this compensation is po ...