Algebraic Production Functions and Their Uses Before Cobb
... the trend of the relative shares as the economy approaches the classical stationary state. In roughly the same period, pioneer marginalist Johann Heinrich von Thünen hypothesized geometrical series of declining marginal products implying an exponential production function. Before he died in 1850, T ...
... the trend of the relative shares as the economy approaches the classical stationary state. In roughly the same period, pioneer marginalist Johann Heinrich von Thünen hypothesized geometrical series of declining marginal products implying an exponential production function. Before he died in 1850, T ...
Lecture 4: Topic #1 Extent (How Much) Decisions Marginal Revenue
... • American Express offers a Platinum Card to affluent customers • In 2001, there were approximately 2,000 Platinum cardholders in the Japanese market. Numbers had been limited to ensure high quality customer service • With customer service technology advances, company considered expanding number ...
... • American Express offers a Platinum Card to affluent customers • In 2001, there were approximately 2,000 Platinum cardholders in the Japanese market. Numbers had been limited to ensure high quality customer service • With customer service technology advances, company considered expanding number ...
PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
... Though point measurements are more accurate they relate to (theoretical) infinitesmally small changes in price and quantity Arc measurements are used in practice though there is a degree of arbitrariness due to two equally valid ways of calculation (which give opposite answers) So the most correct a ...
... Though point measurements are more accurate they relate to (theoretical) infinitesmally small changes in price and quantity Arc measurements are used in practice though there is a degree of arbitrariness due to two equally valid ways of calculation (which give opposite answers) So the most correct a ...
Chapter 16: Perfect Competition in the Short Run
... The goal of a company is to maximize its economic profits. Economic profits are simply the difference between the total revenues and the total costs of production. We examined the costs of production first because the principles affecting costs are the same for all companies regardless of the indust ...
... The goal of a company is to maximize its economic profits. Economic profits are simply the difference between the total revenues and the total costs of production. We examined the costs of production first because the principles affecting costs are the same for all companies regardless of the indust ...
Profits
... • Marginal revenue (MR) – the change in total revenue associated with a change in quantity. • Marginal cost (MC) – the change in total cost associated with a change in quantity. ...
... • Marginal revenue (MR) – the change in total revenue associated with a change in quantity. • Marginal cost (MC) – the change in total cost associated with a change in quantity. ...
File
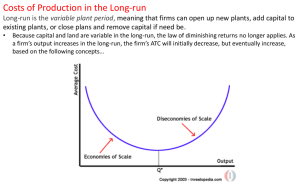
... Increasing Returns to Scale (Economies of scale): the range of plant size over which increasing output leads to lower and lower average total cost. As new plants open, ATC declines. WHY? ·better specialization, division of labor, bulk buying, lower interest on loans, lower per unit transport costs, ...
... Increasing Returns to Scale (Economies of scale): the range of plant size over which increasing output leads to lower and lower average total cost. As new plants open, ATC declines. WHY? ·better specialization, division of labor, bulk buying, lower interest on loans, lower per unit transport costs, ...
Competition, Consumer Welfare, and the Social Cost of Monopoly
... utility levels. Second, the analysis relies on the questionable assumption of profitmaximization for firms with market power, not taking into consideration that where the shares of firms are widely-held—as is the case with most firms that have monopoly— managers may be motivated by goals other than ...
... utility levels. Second, the analysis relies on the questionable assumption of profitmaximization for firms with market power, not taking into consideration that where the shares of firms are widely-held—as is the case with most firms that have monopoly— managers may be motivated by goals other than ...