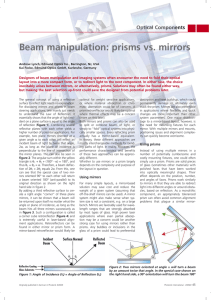
5. INTERFERENCE. Introduction.
... handed elliptically and circularly polarised light and plane polarised light. In this section interest is in the change in amplitude of the electric field vector (and consequently light intensity) as a result of superposition or addition of waves from multiple sources or from one source first split ...
... handed elliptically and circularly polarised light and plane polarised light. In this section interest is in the change in amplitude of the electric field vector (and consequently light intensity) as a result of superposition or addition of waves from multiple sources or from one source first split ...
Kerr effect
... As long ago as 1875 Kerr discovered that a glass plate to which a strong electric field was applied became birefractive. It soon became clear that this effect was not based on deformation caused by the electric field as the same phenomenon was observed in liquids and even in gases. The PLZT element ...
... As long ago as 1875 Kerr discovered that a glass plate to which a strong electric field was applied became birefractive. It soon became clear that this effect was not based on deformation caused by the electric field as the same phenomenon was observed in liquids and even in gases. The PLZT element ...
Chapter 32 Optical Images
... the ways in which these two systems accommodate. That is, the difference between how an eye adjusts and how a camera adjusts (or can be adjusted) to form a focused image for objects at both large and short distances from the camera. ...
... the ways in which these two systems accommodate. That is, the difference between how an eye adjusts and how a camera adjusts (or can be adjusted) to form a focused image for objects at both large and short distances from the camera. ...
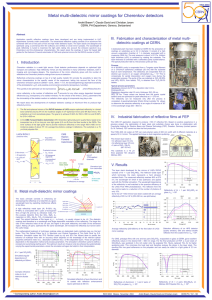
CHAPTER 3 Optical Components of Spectrometers
... such as absorption, refraction, and reflection depend on the polarization of the incident radiation. • Substances that rotate the plane of vibration of plane-polarized radiation are termed optically active. • These include anisotropic crystals and liquids or solutes in solution that can exist as ena ...
... such as absorption, refraction, and reflection depend on the polarization of the incident radiation. • Substances that rotate the plane of vibration of plane-polarized radiation are termed optically active. • These include anisotropic crystals and liquids or solutes in solution that can exist as ena ...
Nonlinear optical properties of nanocomposite materials
... † Institute of Optics, University of Rochester, Rochester, NY 14627, USA ‡ Department of Physics, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada Abstract. This paper reviews some of the authors’ recent research aimed at obtaining an understanding of the physical processes that determine the linear ...
... † Institute of Optics, University of Rochester, Rochester, NY 14627, USA ‡ Department of Physics, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada Abstract. This paper reviews some of the authors’ recent research aimed at obtaining an understanding of the physical processes that determine the linear ...
Noise-equivalent sensitivity of photoacoustics
... A photoacoustic signal is generated by intensity-modulated light in the frequency range of hundreds of kilohertz to a few gigahertz. The generated pressure amplitude is proportional to the modulated light intensity, which implies that the generated acoustic intensity is proportional to the square of ...
... A photoacoustic signal is generated by intensity-modulated light in the frequency range of hundreds of kilohertz to a few gigahertz. The generated pressure amplitude is proportional to the modulated light intensity, which implies that the generated acoustic intensity is proportional to the square of ...
Page 251 - eCM Journal
... crossed lattice planes can be viewed. For simplicity, we require that the lattice planes of each set are orthogonal and have the same spacing. Different sets may have different spacings. Since each set of parallel lattice planes leads to a pair of diffraction spots, corresponding to ± u, two pairs o ...
... crossed lattice planes can be viewed. For simplicity, we require that the lattice planes of each set are orthogonal and have the same spacing. Different sets may have different spacings. Since each set of parallel lattice planes leads to a pair of diffraction spots, corresponding to ± u, two pairs o ...
Volume Holographic Recording and Readout for 90
... material, to be made more precise later. Also, the angle of the grating vector is terms in the surviving Laplace variable. It is pointed outthat the inverse transformation of 2-D Laplace functions as derived here is rather difficult even under weak diffraction limits, even for uniform plane wave or ...
... material, to be made more precise later. Also, the angle of the grating vector is terms in the surviving Laplace variable. It is pointed outthat the inverse transformation of 2-D Laplace functions as derived here is rather difficult even under weak diffraction limits, even for uniform plane wave or ...
Chapter 25: Interference and Diffraction
... for about 1ns, and produces a wave about 1 million wavelengths long. ...
... for about 1ns, and produces a wave about 1 million wavelengths long. ...
Transparent mirrors: rays, waves and localization
... all individual stacks. Many studies have explored the application of this theory to the difficult calculation of the decay exponent (inverse localization length) of piles of plates, for example numerically (Kondilis and Tzanetakis 1992) or at critical incidence (Bouchaud and Le Doussal 1986), and in ...
... all individual stacks. Many studies have explored the application of this theory to the difficult calculation of the decay exponent (inverse localization length) of piles of plates, for example numerically (Kondilis and Tzanetakis 1992) or at critical incidence (Bouchaud and Le Doussal 1986), and in ...
A Coaxial Optical Scanner for Synchronous Acquisition of 3D
... the output that are difficult to detect and characterize. Second, systems often use separate sensors to measure reflectance and geometry, and this leads to a difficult and error-prone 2D-3D data registration problem that can cause a reduction in accuracy. Third, most existing systems involve a serie ...
... the output that are difficult to detect and characterize. Second, systems often use separate sensors to measure reflectance and geometry, and this leads to a difficult and error-prone 2D-3D data registration problem that can cause a reduction in accuracy. Third, most existing systems involve a serie ...
Tao Yuan, Jingzhou Xu, and Xicheng Zhang Rensselaer
... Introduction and State of Art The resolution of conventional image system is limited by diffraction: x /NA, which is the so called Rayleigh Criterion. The limitation is more serious for THz image system because of the long wavelength used (~300 m for 1THz). Sub-wavelength resolution can be achi ...
... Introduction and State of Art The resolution of conventional image system is limited by diffraction: x /NA, which is the so called Rayleigh Criterion. The limitation is more serious for THz image system because of the long wavelength used (~300 m for 1THz). Sub-wavelength resolution can be achi ...
Chapter 4: Two-Beam Interference
... from areas where the waves are “in phase,” half a cycle out of phase, a whole cycle out of phase (and thus back in phase), and so on, until we reach the maximum phase difference of 2.5 cycles. Quantitative discussion of interference contrast: We can fairly easily describe the interference effects be ...
... from areas where the waves are “in phase,” half a cycle out of phase, a whole cycle out of phase (and thus back in phase), and so on, until we reach the maximum phase difference of 2.5 cycles. Quantitative discussion of interference contrast: We can fairly easily describe the interference effects be ...
On-chip gas detection in silicon optical microcavities
... Interaction of light with matter in a gaseous state is an important functionality for sensors as well as for addressing isolated atomic or molecular states for quantum optic applications [1]. The vast majority of room-temperature experiments involving light-matter interactions in integrated photonic ...
... Interaction of light with matter in a gaseous state is an important functionality for sensors as well as for addressing isolated atomic or molecular states for quantum optic applications [1]. The vast majority of room-temperature experiments involving light-matter interactions in integrated photonic ...
APPLICATIONS OF CLASSICAL PHYSICS
... III. Optics — by which we mean classical waves of all sorts: light waves, radio waves, sound waves, water waves, waves in plasmas, and gravitational waves. The major concepts we develop for dealing with all these waves include geometric optics, diffraction, interference, and nonlinear wave-wave mixi ...
... III. Optics — by which we mean classical waves of all sorts: light waves, radio waves, sound waves, water waves, waves in plasmas, and gravitational waves. The major concepts we develop for dealing with all these waves include geometric optics, diffraction, interference, and nonlinear wave-wave mixi ...
Chapter One: Light Dr.Muayyed Jabar Zoory
... could also explain reflection and refraction. In 1801, Thomas Young (1773–1829) provided the first clear demonstration of the wave nature of light. Young showed that, under appropriate conditions, light rays interfere with each other. Such behavior could not be explained at that time by a particle t ...
... could also explain reflection and refraction. In 1801, Thomas Young (1773–1829) provided the first clear demonstration of the wave nature of light. Young showed that, under appropriate conditions, light rays interfere with each other. Such behavior could not be explained at that time by a particle t ...