Waveguide&Fiber modes, Saleh&Teich
... are separable in r, φ, and z. The φ and z functions are exponentials of the form eix. The z function is a propagation oscillation. The function in φ is an azmuthal function that must have the same value at (φ + 2π) that it does at φ. With the azmuthal coordinate separated, the residual wave equation ...
... are separable in r, φ, and z. The φ and z functions are exponentials of the form eix. The z function is a propagation oscillation. The function in φ is an azmuthal function that must have the same value at (φ + 2π) that it does at φ. With the azmuthal coordinate separated, the residual wave equation ...
Collective electronic states in inhomogeneous media at critical and subcritical... *
... for calculation of systems with up to 106 metal particles. We should point out that, while the system size used in the calculations, 1 m, is of the order of the incident wavelength, the quasistatic approximation is still applicable since 共i兲 normal illumination is assumed 共no phase change along the ...
... for calculation of systems with up to 106 metal particles. We should point out that, while the system size used in the calculations, 1 m, is of the order of the incident wavelength, the quasistatic approximation is still applicable since 共i兲 normal illumination is assumed 共no phase change along the ...
L4 INTERFERENCE
... The key to understanding interference is the principle of superposition which says simply that the combined effect of several waves at any place at a particular instant of time is given by the sum (vector sum if the wave property is a vector) of the wave property for the individual waves. The contri ...
... The key to understanding interference is the principle of superposition which says simply that the combined effect of several waves at any place at a particular instant of time is given by the sum (vector sum if the wave property is a vector) of the wave property for the individual waves. The contri ...
Experiment Guide - Industrial Fiber Optics
... stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise) without prior written permission from Industrial Fiber Optics. ...
... stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise) without prior written permission from Industrial Fiber Optics. ...
Bandgap-assisted surface-plasmon sensing Arnaud J. Benahmed* and Chih-Ming Ho
... superscript. For example, the branch that corresponds to the SPW propagation on a flat surface in the forward direction is indexed 0⫹. Bandgaps appear at branch crossings. In the past, SP bandgaps have been observed at normal incidence at the crossing of the ⫹1⫺ and ⫺1⫹ branches. In this situation, ...
... superscript. For example, the branch that corresponds to the SPW propagation on a flat surface in the forward direction is indexed 0⫹. Bandgaps appear at branch crossings. In the past, SP bandgaps have been observed at normal incidence at the crossing of the ⫹1⫺ and ⫺1⫹ branches. In this situation, ...
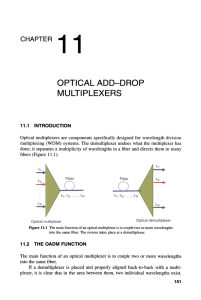
OPTICAL ADD-DROP MULTIPLEXERS
... added between demultiplexer and multiplexer to support more drop-add wavelengths. OADMs are classified as fixed-wavelength and as dynamically wavelengthselectable OADMs. In fixed-wavelength OADM, the wavelength has been selected and remains the same until human intervention changes it. In dynamicall ...
... added between demultiplexer and multiplexer to support more drop-add wavelengths. OADMs are classified as fixed-wavelength and as dynamically wavelengthselectable OADMs. In fixed-wavelength OADM, the wavelength has been selected and remains the same until human intervention changes it. In dynamicall ...
Enpolarization and depolarization of light
... be strongly increased. This is the reason why this assumption was abandoned in this paper, which allowed us to revisit the DoP histograms and provide a more complete analysis. Hence new DoP signatures can now be emphasized to characterize either (local) enpolarization or (local) depolarization effec ...
... be strongly increased. This is the reason why this assumption was abandoned in this paper, which allowed us to revisit the DoP histograms and provide a more complete analysis. Hence new DoP signatures can now be emphasized to characterize either (local) enpolarization or (local) depolarization effec ...
Planar Integrated Optical Waveguide Spectroscopy
... general term for structures that transport electromagnetic radiation via repeated TIR. Although waveguides can be created in numerous geometries, this article focuses on waveguides with a planar geometry that are used to study thin films and interfaces. The fundamental work of Harrick and Fahrenfort ...
... general term for structures that transport electromagnetic radiation via repeated TIR. Although waveguides can be created in numerous geometries, this article focuses on waveguides with a planar geometry that are used to study thin films and interfaces. The fundamental work of Harrick and Fahrenfort ...
babinet compensator - Foctek Photonics, Inc.
... a variable path length difference to an optical beam passing through the instrument. The compensating block ensures that this difference is uniform across the aperture. The Compensator is aligned so that its axis lies at 45° to the polarization direction of the input beam. This beam can be considere ...
... a variable path length difference to an optical beam passing through the instrument. The compensating block ensures that this difference is uniform across the aperture. The Compensator is aligned so that its axis lies at 45° to the polarization direction of the input beam. This beam can be considere ...
Polarization-dependent Goos-Hänchen shift at a graded dielectric
... The first index profile we discuss is a linear refractive index gradient n( x̃) = n0 (1 − x̃) in the configuration shown in Fig. 1. The resulting differential GH shift is plotted in Fig. 2 for different gradient thicknesses. The largest shift (black curve) depicts the well-known case of an abrupt in ...
... The first index profile we discuss is a linear refractive index gradient n( x̃) = n0 (1 − x̃) in the configuration shown in Fig. 1. The resulting differential GH shift is plotted in Fig. 2 for different gradient thicknesses. The largest shift (black curve) depicts the well-known case of an abrupt in ...
Designing Fiber Optic Systems
... Electrical to optical video converters generally have a BNC coaxial cable connector at the input and a fiber optic connector on the output. In order to get the digital bits down the fiber optic cable, a light emitting device is used, onto which the digital signal is modulated. Either a laser or an L ...
... Electrical to optical video converters generally have a BNC coaxial cable connector at the input and a fiber optic connector on the output. In order to get the digital bits down the fiber optic cable, a light emitting device is used, onto which the digital signal is modulated. Either a laser or an L ...
Physical Properties of Lead Molybdate Relevant to Acousto
... that make this material exceptionally well suited for acousto-optic device applications. Interest in lead molybdate for this application has continued at a high level at this laboratory and elsewhere. Accordingly we felt it worthwhile to make a more complete determination of its physical properties ...
... that make this material exceptionally well suited for acousto-optic device applications. Interest in lead molybdate for this application has continued at a high level at this laboratory and elsewhere. Accordingly we felt it worthwhile to make a more complete determination of its physical properties ...
Paper Title
... in the latter – due to change of wavelength. The resonance effects take place when λ ~ Λ where Λ is the corrugated surface structure (or refractive index variation) period. In this case, leaky waves are supported by the relief configuration7-10. The resonance width (FWHM) was estimated to vary from ...
... in the latter – due to change of wavelength. The resonance effects take place when λ ~ Λ where Λ is the corrugated surface structure (or refractive index variation) period. In this case, leaky waves are supported by the relief configuration7-10. The resonance width (FWHM) was estimated to vary from ...
Chapter 8
... Anisotropy of the binding force of an electron cloud causes the anisotropy in the refractive indexes for different light polarizations. 8.4.1 Calcite (CaCO3) Optic axis: Inside the (uniaxial) crystal there is a special direction along which when light is propagating there is no birefringence occurs. ...
... Anisotropy of the binding force of an electron cloud causes the anisotropy in the refractive indexes for different light polarizations. 8.4.1 Calcite (CaCO3) Optic axis: Inside the (uniaxial) crystal there is a special direction along which when light is propagating there is no birefringence occurs. ...
Optics of Gaussian Beams
... mirrors to slightly different orientations will usually change the output transverse mode, although if the mirrors are adjusted too far from optimum the laser will go out. ...
... mirrors to slightly different orientations will usually change the output transverse mode, although if the mirrors are adjusted too far from optimum the laser will go out. ...
Effective Wavelength Scaling for Optical Antennas
... In the radio frequency and microwave regimes antennas are widely employed to convert electromagnetic radiation into localized energy and vice versa. However, at optical frequencies, lenses and mirrors are used to redirect the wave fronts of propagating radiation and the antenna concept is widely une ...
... In the radio frequency and microwave regimes antennas are widely employed to convert electromagnetic radiation into localized energy and vice versa. However, at optical frequencies, lenses and mirrors are used to redirect the wave fronts of propagating radiation and the antenna concept is widely une ...
Partially coherent beam shaping and imaging
... order to make numerical calculations feasible, so-called modal approaches [46–51] are used extensively, especially to describe partial spatial coherence. Such modal approaches, in which the partially coherent field is represented as a superposition of fully coherent fields, lead to the evaluation of ...
... order to make numerical calculations feasible, so-called modal approaches [46–51] are used extensively, especially to describe partial spatial coherence. Such modal approaches, in which the partially coherent field is represented as a superposition of fully coherent fields, lead to the evaluation of ...