D - Purdue Physics
... Magnifying power MP, or angular magnification - the ratio of the size of the retinal image as seen through the instrument to that as seen by bare eye at a normal viewing distance: ...
... Magnifying power MP, or angular magnification - the ratio of the size of the retinal image as seen through the instrument to that as seen by bare eye at a normal viewing distance: ...
Light Sources
... point source lies at the first minimum of the Airy pattern of the other point (R = diameter of circle) • The numerical aperture (NA) of a lens represents the ability of the lens to collect diffracted light and is given by NA = n sin a in this expression n is the index of refraction of the medium sur ...
... point source lies at the first minimum of the Airy pattern of the other point (R = diameter of circle) • The numerical aperture (NA) of a lens represents the ability of the lens to collect diffracted light and is given by NA = n sin a in this expression n is the index of refraction of the medium sur ...
Refraction of Light
... Note index of refraction varies with the frequency and wavelength of the light ...
... Note index of refraction varies with the frequency and wavelength of the light ...
VII-I
... • If an ideal mirror is stroked by rays coming parallel with the principal axis the rays either focus in the focal point – in the case of concave mirrors or they seem to come from a virtual focal point behind the mirror, if the mirror is convex. • Optical properties of ideal mirror are described by ...
... • If an ideal mirror is stroked by rays coming parallel with the principal axis the rays either focus in the focal point – in the case of concave mirrors or they seem to come from a virtual focal point behind the mirror, if the mirror is convex. • Optical properties of ideal mirror are described by ...
Physics 212 HW17 - University of St. Thomas
... which is typically 2.45 cm behind the lens. The eye’s lens is special in that it can change its focal length in order to focus images from very far and very close onto the retina, which stays 2.45 cm away. The average person with “20/20 vision” can focus on objects at infinity and objects no closer ...
... which is typically 2.45 cm behind the lens. The eye’s lens is special in that it can change its focal length in order to focus images from very far and very close onto the retina, which stays 2.45 cm away. The average person with “20/20 vision” can focus on objects at infinity and objects no closer ...
Lobster eye: Data processing from two 1D modules
... then can be used as an 2D optics. Parameters of used optics are following: fV = 960 mm fH = 1190 mm In front of both optics is placed shade, in Fig. 2. ...
... then can be used as an 2D optics. Parameters of used optics are following: fV = 960 mm fH = 1190 mm In front of both optics is placed shade, in Fig. 2. ...
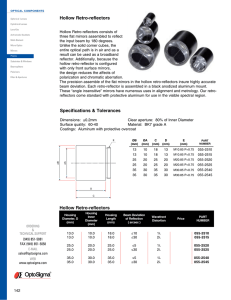
Hollow Retro-Reflectors
... The precision assemble of the flat mirrors in the hollow retro-reflectors insure highly accurate beam deviation. Each retro-reflector is assembled in a black anodized aluminum mount. These “angle insensitive” mirrors have numerous uses in alignment and metrology. Our retroreflectors come standard wi ...
... The precision assemble of the flat mirrors in the hollow retro-reflectors insure highly accurate beam deviation. Each retro-reflector is assembled in a black anodized aluminum mount. These “angle insensitive” mirrors have numerous uses in alignment and metrology. Our retroreflectors come standard wi ...
Nano-optical Imaging using Scattering Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy
... optical microscopy (s-SNOM) and image several different materials using said technique. We report our data provide potential paths for future work. I. INTRODUCTION Scientists have long studied optical spectroscopy due to its ability to directly interact with the electronic, spin, and lattice excitat ...
... optical microscopy (s-SNOM) and image several different materials using said technique. We report our data provide potential paths for future work. I. INTRODUCTION Scientists have long studied optical spectroscopy due to its ability to directly interact with the electronic, spin, and lattice excitat ...
PochPHYS104-Obj_Chapt23Sp13
... draw a ray diagram for an image given the object’s distance and focal length of the lens and describe the image’s character, i.e. relative size, erect or inverted, real or virtual. using the lens equation, solve for the object distance, image distance and/or focal length (radius) in terms of the oth ...
... draw a ray diagram for an image given the object’s distance and focal length of the lens and describe the image’s character, i.e. relative size, erect or inverted, real or virtual. using the lens equation, solve for the object distance, image distance and/or focal length (radius) in terms of the oth ...
Ray Box Lab - Iona Physics
... 1. Place the ray box near the edge of a piece of paper in such a way that the rays cross most of the width of the page. Note the rays are diverging. 2. Place the plano-convex lens in front of the ray box with the flat side facing the ray box. 3. Adjust the position of the lens so that the rays are p ...
... 1. Place the ray box near the edge of a piece of paper in such a way that the rays cross most of the width of the page. Note the rays are diverging. 2. Place the plano-convex lens in front of the ray box with the flat side facing the ray box. 3. Adjust the position of the lens so that the rays are p ...
GRADE 10 SA2 PHYSICS revision worksheet-2
... 5. How can you distinguish between a plane mirror, a convex mirror and a concave mirror, just by looking at the image formed by them. (b) The lens prescribed by the doctor has a power equal to +2.0 D. What does it mean? (c) What would be the approximate focal length of a spherical lens preferred to ...
... 5. How can you distinguish between a plane mirror, a convex mirror and a concave mirror, just by looking at the image formed by them. (b) The lens prescribed by the doctor has a power equal to +2.0 D. What does it mean? (c) What would be the approximate focal length of a spherical lens preferred to ...
PDF - Bridgend Astronomical Society
... The f-number is the same as for a camera. For a telescope it is obtained by dividing the focal length by the aperture. The lower the f-number the “faster” is the optical system. Important for those interested in imaging. Refractor The very simplest telescope is the refractor, as used by Galileo. It ...
... The f-number is the same as for a camera. For a telescope it is obtained by dividing the focal length by the aperture. The lower the f-number the “faster” is the optical system. Important for those interested in imaging. Refractor The very simplest telescope is the refractor, as used by Galileo. It ...
The Laser Marketplace
... IR Laser Illuminator invisible to human eye Penetrates fog, dust, debris better than visible light Search and Rescue and underwater surveillance ...
... IR Laser Illuminator invisible to human eye Penetrates fog, dust, debris better than visible light Search and Rescue and underwater surveillance ...
Lecture 1. Introduction. Nature of light, geometric optics.
... Spherical Aberration could also be caused by the use of the cover glass-slip. A correction collar might be found on the objective to set the thickness of the glass-slip. If no correction collar can be found, the objective is corrected for a 0.17 mm glass-slip. ...
... Spherical Aberration could also be caused by the use of the cover glass-slip. A correction collar might be found on the objective to set the thickness of the glass-slip. If no correction collar can be found, the objective is corrected for a 0.17 mm glass-slip. ...
Geometrical Optics
... Aberrations are imperfections in the optical image formed by a spherical lens (or optical mirror). There are five main aberrations: 1. Chromatic aberration. The refractive index of glass varies with wavelength. This results in different focal lengths and image magnifications for different colours. ...
... Aberrations are imperfections in the optical image formed by a spherical lens (or optical mirror). There are five main aberrations: 1. Chromatic aberration. The refractive index of glass varies with wavelength. This results in different focal lengths and image magnifications for different colours. ...
Modulation Transfer Function
... Modulation Transfer Function The Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) is a useful tool in system evaluation. It describes if, and how well, different spatial frequencies are transferred from object to image. The MTF also relates the diffraction limit to the aberrations in a very clear way. So in order ...
... Modulation Transfer Function The Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) is a useful tool in system evaluation. It describes if, and how well, different spatial frequencies are transferred from object to image. The MTF also relates the diffraction limit to the aberrations in a very clear way. So in order ...
Chapter 35 Light: Reflection and Refraction
... At some critical angle of incidence, θc, the light is totally reflected back into the medium of higher refractive index. This is called the total internal reflection and was first noted by Kepler in 1604. ...
... At some critical angle of incidence, θc, the light is totally reflected back into the medium of higher refractive index. This is called the total internal reflection and was first noted by Kepler in 1604. ...
Subject: Precision Optics II Grade: 10
... order aberrations. Students will construct an illustrated essay. This essay will indicate the student’s level of understanding about how lenses are designed to control light. ...
... order aberrations. Students will construct an illustrated essay. This essay will indicate the student’s level of understanding about how lenses are designed to control light. ...
Principles of light guidance
... 64,000 bits/sec. Quality does not suffer by discrete sampling if it is fast enough. This is analogous to projecting 25 discrete movie frames per second, which fools the eye into seeing a continuous picture sequence. ...
... 64,000 bits/sec. Quality does not suffer by discrete sampling if it is fast enough. This is analogous to projecting 25 discrete movie frames per second, which fools the eye into seeing a continuous picture sequence. ...
Aspheric Lenses
... Fluorite elements, and Aspherical elements to truly push the optical envelope." The truth is long lenses may use ULD and Fluorite glass, but wide angles and lenses of shorter than 200mm do not. Wide angles may use aspheric lens elements but not LD glass types. Long lenses do not use aspheric lenses. ...
... Fluorite elements, and Aspherical elements to truly push the optical envelope." The truth is long lenses may use ULD and Fluorite glass, but wide angles and lenses of shorter than 200mm do not. Wide angles may use aspheric lens elements but not LD glass types. Long lenses do not use aspheric lenses. ...
Physics 161 Lecture 26 Mirrors and Lenses December 6, 2016
... You will be able to explain images formed by atmospheric refraction, such as mirages. You will be able to apply the lens-maker’s equation to thin lenses. You will be able to master the sign conventions for: concave and convex mirrors; refracting surfaces; and thin lenses. Sep. 1, 20152 ...
... You will be able to explain images formed by atmospheric refraction, such as mirages. You will be able to apply the lens-maker’s equation to thin lenses. You will be able to master the sign conventions for: concave and convex mirrors; refracting surfaces; and thin lenses. Sep. 1, 20152 ...