Thin Lenses - Saddleback College
... a) Calculate the experimental focal length from equation (3) and compare it to the actual focal length of the lens. b) Measure & record the image height and object height, then calculate the magnification using equations (1) and (2). Compare these magnifications. • For the case(s) with VIRTUAL image ...
... a) Calculate the experimental focal length from equation (3) and compare it to the actual focal length of the lens. b) Measure & record the image height and object height, then calculate the magnification using equations (1) and (2). Compare these magnifications. • For the case(s) with VIRTUAL image ...
PPT
... equal components in horizontal and vertical directions. Therefore running the light through a polarizer will cut the intensity in half: I=I0/2 When polarized light hits a polarizing sheet, only the component of the field aligned with the sheet will get through. ...
... equal components in horizontal and vertical directions. Therefore running the light through a polarizer will cut the intensity in half: I=I0/2 When polarized light hits a polarizing sheet, only the component of the field aligned with the sheet will get through. ...
Business Unit Fiber Optics Business Unit Fiber Optics Fiberoptic
... In this example, the output NA will be 0.0022 or, since NA = Sin ß, where ß in the half angle in degrees, we get ß = 0.13 degrees. We may convert this to radians to get 2.2mRad divergence. Again, this represents the half angle. You will notice that since the output beam diameter is 100X the fiber di ...
... In this example, the output NA will be 0.0022 or, since NA = Sin ß, where ß in the half angle in degrees, we get ß = 0.13 degrees. We may convert this to radians to get 2.2mRad divergence. Again, this represents the half angle. You will notice that since the output beam diameter is 100X the fiber di ...
3-D wave structuring and applications
... •While for long-distance communication light has an unquestionable advantage over any other means of communication, this is not the case for conventional computing scenarios where propagation and diffraction effects play an important role. •High spatial parallelism and spatial bandwidth. •Not compat ...
... •While for long-distance communication light has an unquestionable advantage over any other means of communication, this is not the case for conventional computing scenarios where propagation and diffraction effects play an important role. •High spatial parallelism and spatial bandwidth. •Not compat ...
Fiber Optic Communications - New Mexico State University
... – Scattering is the spreading apart of light caused by interaction with matter. – Rayleigh scattering, or molecular scattering, is caused by small particles of matter (less than or equal to 1/10 wavelength) interacting with light. – Mie scattering is due to interaction with matter larger than 1/10 w ...
... – Scattering is the spreading apart of light caused by interaction with matter. – Rayleigh scattering, or molecular scattering, is caused by small particles of matter (less than or equal to 1/10 wavelength) interacting with light. – Mie scattering is due to interaction with matter larger than 1/10 w ...
Part 1
... The sign between kx and t determines the direction the wave travels along the x-axis. + wave travels to left (in the direction of decreasing x) - wave travels to right (in the direction of increasing x) The phase angle shifts the cosine or sine function left or right. This can be used to match ...
... The sign between kx and t determines the direction the wave travels along the x-axis. + wave travels to left (in the direction of decreasing x) - wave travels to right (in the direction of increasing x) The phase angle shifts the cosine or sine function left or right. This can be used to match ...
Problem Sheet
... 4. Use Fermat’s principle to show that a thin lens with thickness given by w = w0 − αy 2 , where y is the distance from the axis, will focus paraxial rays from an object on the axis, and find the focal length as a function of α and the refractive index n. [Hint: the best way to interpret“paraxial” i ...
... 4. Use Fermat’s principle to show that a thin lens with thickness given by w = w0 − αy 2 , where y is the distance from the axis, will focus paraxial rays from an object on the axis, and find the focal length as a function of α and the refractive index n. [Hint: the best way to interpret“paraxial” i ...
Optical Lenses part 2
... A lens is a curved transparent material that is smooth and regularly shaped so that when light strikes it, the light refracts in a predictable and useful way. Made of transparent glass or very hard plastic ...
... A lens is a curved transparent material that is smooth and regularly shaped so that when light strikes it, the light refracts in a predictable and useful way. Made of transparent glass or very hard plastic ...
Advanced Optics Lab at San Jose State University Ramen
... A variable slit is provided to the students. They are supposed to select a doublet lens of the proper focal length from a catalog such that for a typical source the lens is substantially illuminated. This in turn will illuminate a substantial part of the grating which will result in higher resolutio ...
... A variable slit is provided to the students. They are supposed to select a doublet lens of the proper focal length from a catalog such that for a typical source the lens is substantially illuminated. This in turn will illuminate a substantial part of the grating which will result in higher resolutio ...
9-26 Geometrical Optics
... The optical axis connects the center of the radius of curvature of the two surfaces (i.e. it is the axis of symmetry of the lens) The focal points are one focal length away from the center of the lens on the optical axis The focal planes are normal to the optical axis and contain the focal points ...
... The optical axis connects the center of the radius of curvature of the two surfaces (i.e. it is the axis of symmetry of the lens) The focal points are one focal length away from the center of the lens on the optical axis The focal planes are normal to the optical axis and contain the focal points ...
Plane mirrors
... 1. The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. II. Mirrors 1. There are 3 types of mirrors: Plane, concave, and convex. A. Plane Mirrors: 1. Plane mirrors- flat sheet of glass that has a smooth, silvercolored coating on one side. When light strikes a mirror, the coating reflects the light ...
... 1. The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. II. Mirrors 1. There are 3 types of mirrors: Plane, concave, and convex. A. Plane Mirrors: 1. Plane mirrors- flat sheet of glass that has a smooth, silvercolored coating on one side. When light strikes a mirror, the coating reflects the light ...
Quantum mechanical properties of Bessel modes and their effect on
... • Bessel EM modes are studied within the general framework of quantum optics. The basic dynamical operators are identified and their algebraic properties are studied. • As a mean to measure these dynamical properties, the transition probability for the emission of a Bessel photon by an atomic system ...
... • Bessel EM modes are studied within the general framework of quantum optics. The basic dynamical operators are identified and their algebraic properties are studied. • As a mean to measure these dynamical properties, the transition probability for the emission of a Bessel photon by an atomic system ...
mirrors and lenses - Appoquinimink High School
... where the index of refraction is less (water into air for example), the light bends away from the normal. At a particular incident angle, the angle of refraction will be 90 degrees. This is called the critical angle. ...
... where the index of refraction is less (water into air for example), the light bends away from the normal. At a particular incident angle, the angle of refraction will be 90 degrees. This is called the critical angle. ...
Fraunhofer diffraction from gratings In this exercise we use a two
... means a convex lens. We will use a lens with f 150 mm and we will search for the sharp image for the following three values of s: 1.5 f, 2.0 f and 3.0 f. Furthermore we will demonstrate that the image formed by the first lens acts as the object of the next lens, or more generally, the image forme ...
... means a convex lens. We will use a lens with f 150 mm and we will search for the sharp image for the following three values of s: 1.5 f, 2.0 f and 3.0 f. Furthermore we will demonstrate that the image formed by the first lens acts as the object of the next lens, or more generally, the image forme ...
Optical Telescopes
... Optical Telescopes Introduction The night sky always attracted people by its charming mystery. Observers had been using naked eyes for their explorations for many centuries. Obviously, they could not achieve a lot due to eyesight limitations. It cannot be estimated, how important the invention of te ...
... Optical Telescopes Introduction The night sky always attracted people by its charming mystery. Observers had been using naked eyes for their explorations for many centuries. Obviously, they could not achieve a lot due to eyesight limitations. It cannot be estimated, how important the invention of te ...
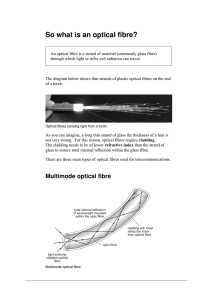
Soliton Propagation in Optical Fibers
... Bell intend to connect Boston and Cambridge...with a line of sunbeams hung on telegraph posts, and, if so, what diameter are the sunbeams to be...?...will it be necessary to insulate them against the weather...?...until (the public) sees a man going through the streets with a coil of No. 12 sunbeams ...
... Bell intend to connect Boston and Cambridge...with a line of sunbeams hung on telegraph posts, and, if so, what diameter are the sunbeams to be...?...will it be necessary to insulate them against the weather...?...until (the public) sees a man going through the streets with a coil of No. 12 sunbeams ...
Advantages of Infinity-Corrected Optics in FT
... Another reality of optics is the inability to grind and polish a perfect powered mirror. Aspherical mirrors are particularly difficult, and are essential to traditional FT-IR microscope designs. When placed in a complex optical system, the fluctuations and aberrations due to small flaws are magnifie ...
... Another reality of optics is the inability to grind and polish a perfect powered mirror. Aspherical mirrors are particularly difficult, and are essential to traditional FT-IR microscope designs. When placed in a complex optical system, the fluctuations and aberrations due to small flaws are magnifie ...
Nanoscopy with focused light
... Optical microscopy: the resolution revolution Stefan W. Hell Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Göttingen German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg [email protected] ...
... Optical microscopy: the resolution revolution Stefan W. Hell Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Göttingen German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg [email protected] ...
lab9 - University of Puget Sound
... What happens to a well-focused image when a portion of the lens is blocked? Does the left side of the image disappear when the left half of the lens is covered? Or the right half, or what? Explain your observations. Describe what happens when the object distance is less than the focal length. Can yo ...
... What happens to a well-focused image when a portion of the lens is blocked? Does the left side of the image disappear when the left half of the lens is covered? Or the right half, or what? Explain your observations. Describe what happens when the object distance is less than the focal length. Can yo ...