3.0Mb PDF - David Kleinfeld
... Represent each interface or transition by an appropriate ABCD, or transfer matrix. Then whole optical systems are reduced to a single matrix by multiplying through matrices for each component. We recall that matrix algebra involves ...
... Represent each interface or transition by an appropriate ABCD, or transfer matrix. Then whole optical systems are reduced to a single matrix by multiplying through matrices for each component. We recall that matrix algebra involves ...
Optics Studio Manual - Department of Physics
... interference and diffraction were all well understood and used before the electromagnetic theory of light was espoused by Maxwell. It is important that you view optics as phenomena that can be understood and applied as such to numerous applications. Ultimately, with other courses in the theory of op ...
... interference and diffraction were all well understood and used before the electromagnetic theory of light was espoused by Maxwell. It is important that you view optics as phenomena that can be understood and applied as such to numerous applications. Ultimately, with other courses in the theory of op ...
Lecture 25: Optical Instruments
... Resolution of Single-Slit and Circular Apertures Resolution of single-slit aperture The ability of an optical system such as the eye, a microscope, or a telescope to distinguish between closely spaced objects is limited because of wave nature of light. - Light from two independent sources which a ...
... Resolution of Single-Slit and Circular Apertures Resolution of single-slit aperture The ability of an optical system such as the eye, a microscope, or a telescope to distinguish between closely spaced objects is limited because of wave nature of light. - Light from two independent sources which a ...
A History of Imaging
... The first practical optical instrument—namely spectacles—appeared in 1270 as well, in Florence, Italy. Interestingly, spectacles do not represent a development in optics as much they do an advance in packaging. As evidenced by the writings of Bacon, Europeans were already aware of a lens’s ability to ...
... The first practical optical instrument—namely spectacles—appeared in 1270 as well, in Florence, Italy. Interestingly, spectacles do not represent a development in optics as much they do an advance in packaging. As evidenced by the writings of Bacon, Europeans were already aware of a lens’s ability to ...
DG Papazoglou et al.
... Optical aberrations can be envisioned as a way to impose polynomial phase distributions on plane wave! Coma aberration Cubic phase ! ...
... Optical aberrations can be envisioned as a way to impose polynomial phase distributions on plane wave! Coma aberration Cubic phase ! ...
Week7-animations
... Note: Incoming wave can be thought of as a sum of plane waves. Each plane wave comes to focus at a different point in the focal plane. Each point in the focal plane corresponds to a unique x and y combination. ...
... Note: Incoming wave can be thought of as a sum of plane waves. Each plane wave comes to focus at a different point in the focal plane. Each point in the focal plane corresponds to a unique x and y combination. ...
Short-pulse limits in optical instrumentation design for the S
... or by "slicing" out reduced cross sections of the LCLS photon pulse; 7) the development of a low-loss beam length dilator (to minimize the relative importance of edge effects without discarding most of the pulse photons) would be desirable. We can conclude our discussion by noting that a general ana ...
... or by "slicing" out reduced cross sections of the LCLS photon pulse; 7) the development of a low-loss beam length dilator (to minimize the relative importance of edge effects without discarding most of the pulse photons) would be desirable. We can conclude our discussion by noting that a general ana ...
Light Rays
... Light from the sky is gradually refracted more towards the horizontal as the air near the ground has a lower refractive index (optically less dense). Total internal reflection takes place when it meets a layer of air at an angle greater than the critical angle. The image of the sky is then formed on ...
... Light from the sky is gradually refracted more towards the horizontal as the air near the ground has a lower refractive index (optically less dense). Total internal reflection takes place when it meets a layer of air at an angle greater than the critical angle. The image of the sky is then formed on ...
All Facts for Choosing LED Optics Correctly
... Quite often, a request for a specific light pattern can easily be achieved by using several different standard lenses. A simple example of this is a normal car head lamp: there needs to be one specific solution for the low-beam light, while the high beam light can be achieved by using another optica ...
... Quite often, a request for a specific light pattern can easily be achieved by using several different standard lenses. A simple example of this is a normal car head lamp: there needs to be one specific solution for the low-beam light, while the high beam light can be achieved by using another optica ...
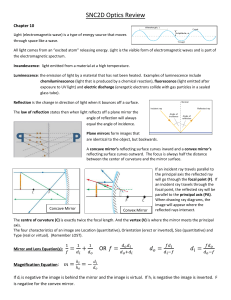
SNC2D Optics Review
... Partial reflection and refraction occurs when an incidence ray strikes a new medium and some of the light rays are reflected and some of the light rays are refracted. Examples: light reflecting and refracting off of surface of the water, rear-view mirrors The amount of reflection depends on 1. The t ...
... Partial reflection and refraction occurs when an incidence ray strikes a new medium and some of the light rays are reflected and some of the light rays are refracted. Examples: light reflecting and refracting off of surface of the water, rear-view mirrors The amount of reflection depends on 1. The t ...
N15_Geom_Optics - University of Arizona
... Dispersion, the variation of the index of refraction with frequency in transparent materials, causes problems with the focal properties of lenses. As we saw, in prisms, blue light bends more than red light. So the same effect must happen in lenses—where one assumes that ray paths are independent of ...
... Dispersion, the variation of the index of refraction with frequency in transparent materials, causes problems with the focal properties of lenses. As we saw, in prisms, blue light bends more than red light. So the same effect must happen in lenses—where one assumes that ray paths are independent of ...
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS ADVANCED PLACEMENT TEST (SAMPLE)
... radio waves of wavelength 75 cm, instead of visible light, to form images. Compute the diffraction-limited feature size that that can be resolved according to the Rayleigh criteria ...
... radio waves of wavelength 75 cm, instead of visible light, to form images. Compute the diffraction-limited feature size that that can be resolved according to the Rayleigh criteria ...
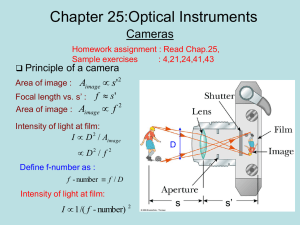
Chapter 25
... The ability of an optical system to distinguish between closely spaced objects is limited due to the wave nature of light If two sources of light are close together, they can be treated as noncoherent sources Because of diffraction, the images consist of bright central regions flanked by weaker brig ...
... The ability of an optical system to distinguish between closely spaced objects is limited due to the wave nature of light If two sources of light are close together, they can be treated as noncoherent sources Because of diffraction, the images consist of bright central regions flanked by weaker brig ...
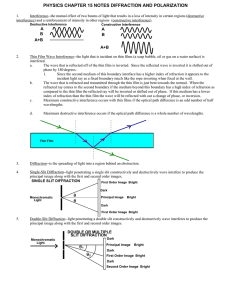
PHYSICS CHAPTER 15 NOTES DIFFRACTION AND
... Since the second medium of this boundary interface has a higher index of refraction it appears to the incident light ray as a fixed boundary much like the rope inverting when fixed at the wall. b. The wave that is refracted and transmitted through the thin film is just bent towards the normal. When ...
... Since the second medium of this boundary interface has a higher index of refraction it appears to the incident light ray as a fixed boundary much like the rope inverting when fixed at the wall. b. The wave that is refracted and transmitted through the thin film is just bent towards the normal. When ...
Calculating Vergences - University of Queensland
... Calculating Image Locations Consider the situation where a lens is used to image an object. For example, you are taking a photograph of a friend. Your friend is the source of scattered light, the lens in your camera is the optical element with a power P, and the film in The University of Queensland ...
... Calculating Image Locations Consider the situation where a lens is used to image an object. For example, you are taking a photograph of a friend. Your friend is the source of scattered light, the lens in your camera is the optical element with a power P, and the film in The University of Queensland ...
GEOMETRIC OPTICS I. What is GEOMTERIC OPTICS In geometric
... focal point-the point on the axis of a lens or mirror to which parallel rays of light converge or from which they appear to diverge after refraction or reflection radius of curvature-a point beyond the focal point that indicates how curved a lens or mirror is virtual image-an optical image from whic ...
... focal point-the point on the axis of a lens or mirror to which parallel rays of light converge or from which they appear to diverge after refraction or reflection radius of curvature-a point beyond the focal point that indicates how curved a lens or mirror is virtual image-an optical image from whic ...
Ray Diagram PRELAB LAB
... A. Set up the lens apparatus as shown by your instructor. Using focal length of your lens using an object that is very far away – across the street. B. Place the object light at a distance further than the focal length and move the screen until you bring the image into focus. Record the image and ob ...
... A. Set up the lens apparatus as shown by your instructor. Using focal length of your lens using an object that is very far away – across the street. B. Place the object light at a distance further than the focal length and move the screen until you bring the image into focus. Record the image and ob ...
amplitude transfer function
... location–dependent: typically we get more blur near the edges of the field (narrower MTF ⇔broader PSF) • This, in addition, means that real–life optical systems are not shift invariant either! • ⇒ the concept of MTF is approximate, near the region where the system is approximately shift invariant (r ...
... location–dependent: typically we get more blur near the edges of the field (narrower MTF ⇔broader PSF) • This, in addition, means that real–life optical systems are not shift invariant either! • ⇒ the concept of MTF is approximate, near the region where the system is approximately shift invariant (r ...
Microscopes
... • Considered the simplest approach • All transmitted light microscopes in use are designed for Kohler illumination ...
... • Considered the simplest approach • All transmitted light microscopes in use are designed for Kohler illumination ...
Geometric Optics using the Vergence Method
... Calculating Image Locations Consider the situation where a lens is used to image an object. For example, you are taking a photograph of a friend. Your friend is the source of scattered light, the lens in your camera is the optical element with a power P, and the film in The University of Queensland ...
... Calculating Image Locations Consider the situation where a lens is used to image an object. For example, you are taking a photograph of a friend. Your friend is the source of scattered light, the lens in your camera is the optical element with a power P, and the film in The University of Queensland ...