lecture 31 - magnifier, telescope
... If intermediate image were formed exactly at the focal point of the eyepiece, final image would be at . As it is, it will just be very far away. Regardless of how far away it is, though, the angle is given by the blue ray. ...
... If intermediate image were formed exactly at the focal point of the eyepiece, final image would be at . As it is, it will just be very far away. Regardless of how far away it is, though, the angle is given by the blue ray. ...
Ultrafast Optics: Tools and Techniques
... science behind ultrafast optics to probe realms that are unseen to the common eye. They employ a variety of techniques and ideas to probe tiny structures on thin films, observe the rotation and vibration of molecules, and generate laser-like beams of X-rays and ultraviolet light that can be manipula ...
... science behind ultrafast optics to probe realms that are unseen to the common eye. They employ a variety of techniques and ideas to probe tiny structures on thin films, observe the rotation and vibration of molecules, and generate laser-like beams of X-rays and ultraviolet light that can be manipula ...
Frequency Domain Optical Coherence Tomography (FDOCT)
... IMSURE Summer Research Fellow At Beckman Laser Institute University of California at Irvine Irvine, CA 92612 Email: [email protected] Faculty mentor: Prof. Zhongping Chen Lab mentor: Jun Zhang ...
... IMSURE Summer Research Fellow At Beckman Laser Institute University of California at Irvine Irvine, CA 92612 Email: [email protected] Faculty mentor: Prof. Zhongping Chen Lab mentor: Jun Zhang ...
Optics and Human Vision
... Let S1 be the distance from the lens to the target Let S2 be the distance from the lens to the film The focal length, f, is a measure of how strongly a lens converges light The magnification factor, m, is another measure. ...
... Let S1 be the distance from the lens to the target Let S2 be the distance from the lens to the film The focal length, f, is a measure of how strongly a lens converges light The magnification factor, m, is another measure. ...
Chapter 34 – Geometric Optics and Optical Instruments
... A glass rod 40 cm long and index 1.50 has one end that is convex of radius 20 cm and the other end has a convex surface of radius 30 cm. An object is placed 100 cm in front of the 20 cm convex surface. Where, what size, and what orientation is the final image? ...
... A glass rod 40 cm long and index 1.50 has one end that is convex of radius 20 cm and the other end has a convex surface of radius 30 cm. An object is placed 100 cm in front of the 20 cm convex surface. Where, what size, and what orientation is the final image? ...
ppt
... Johannes Kofler Institute for Applied Physics Johannes Kepler University Linz Diploma Examination November 18th, 2004 ...
... Johannes Kofler Institute for Applied Physics Johannes Kepler University Linz Diploma Examination November 18th, 2004 ...
Telescopes
... through or reflects off of Eye-piece- lens or mirror light passes through or reflects off of before entering the eye Optical Tube- is the chamber light passes through between lenses/mirrors Secondary Mirror-second mirror light reflects off of before being sent to eye-piece in some reflecting t ...
... through or reflects off of Eye-piece- lens or mirror light passes through or reflects off of before entering the eye Optical Tube- is the chamber light passes through between lenses/mirrors Secondary Mirror-second mirror light reflects off of before being sent to eye-piece in some reflecting t ...
The present work gives recommendations for rational - Dimka
... Scheme assembling and achromat optimization results The analysis of different vendors’ microobjective series of a given class [9] gave the following default values of their basic optical characteristics: the back focal length f 3,7 mm; relative aperture – 1:2,4; field angle in object space – 2 ...
... Scheme assembling and achromat optimization results The analysis of different vendors’ microobjective series of a given class [9] gave the following default values of their basic optical characteristics: the back focal length f 3,7 mm; relative aperture – 1:2,4; field angle in object space – 2 ...
Convolution in Imaging and the Optical Transfer Function Process
... the apparatus and collected by a carefully placed lens. The lens then creates a light column, which is then split by what is called a beam splitter. A beam splitter is an optical device that splits a light beam into two (it is most commonly made from two triangular glass prisms – See fig. 3). 50% of ...
... the apparatus and collected by a carefully placed lens. The lens then creates a light column, which is then split by what is called a beam splitter. A beam splitter is an optical device that splits a light beam into two (it is most commonly made from two triangular glass prisms – See fig. 3). 50% of ...
Chapter 25
... Largest in the world are 10 m diameter Keck telescopes on Mauna Kea in Hawaii Largest single mirror in US is 5 m diameter on Mount Palomar in California ...
... Largest in the world are 10 m diameter Keck telescopes on Mauna Kea in Hawaii Largest single mirror in US is 5 m diameter on Mount Palomar in California ...
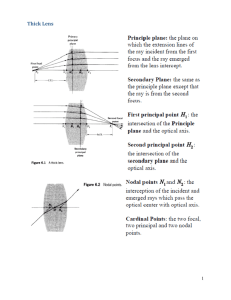
Thick Lens 1
... since there are no optical elements located in front of it. The (real) image of lens 1, as seen through lens 2, is the exit pupil. All the light from the object gathered by the optical system passes through the exit pupil. In an optical system designed for visual observations, it is desirable to hav ...
... since there are no optical elements located in front of it. The (real) image of lens 1, as seen through lens 2, is the exit pupil. All the light from the object gathered by the optical system passes through the exit pupil. In an optical system designed for visual observations, it is desirable to hav ...
Microscopes:
... magnification or greater (usually employing an oil immersion lens). Phase –contrast. Several different forms of phase-contrast are available. Conventional phase is advantageous for looking at live semen, as well as semen “fixed” in an appropriate liquid fixative (e.g. Formal-saline or PBS-Gluteralde ...
... magnification or greater (usually employing an oil immersion lens). Phase –contrast. Several different forms of phase-contrast are available. Conventional phase is advantageous for looking at live semen, as well as semen “fixed” in an appropriate liquid fixative (e.g. Formal-saline or PBS-Gluteralde ...
Notes on optical fibres and fibre bundles
... that the students who are not too familiar with optics will find this note useful and that the interested reader will be spurred on to search elsewhere for further details. The technology of fibre optics, is a relatively simple and old technology. Guiding of light by refraction, the principle that m ...
... that the students who are not too familiar with optics will find this note useful and that the interested reader will be spurred on to search elsewhere for further details. The technology of fibre optics, is a relatively simple and old technology. Guiding of light by refraction, the principle that m ...
LM Ch 4: Optics
... 1830’s, the solution to chromatic aberrations was found by cementing two lenses made of different glasses (one double convex and one plano concave) together into an Achromatic Doublet to make a compound lens (see Appendix A for more details). Today, compound lens consists of many lens elements as sh ...
... 1830’s, the solution to chromatic aberrations was found by cementing two lenses made of different glasses (one double convex and one plano concave) together into an Achromatic Doublet to make a compound lens (see Appendix A for more details). Today, compound lens consists of many lens elements as sh ...
Light microscopy
... 5. By noting the length of an unknown structure in graticule divisions you can then convert this into absolute units of length, e.g. µm. 6. Each objective lens needs to be calibrated in the same way. Once calibrated objects can be measured in EPUs. EPUs are converted into absolute measurement using ...
... 5. By noting the length of an unknown structure in graticule divisions you can then convert this into absolute units of length, e.g. µm. 6. Each objective lens needs to be calibrated in the same way. Once calibrated objects can be measured in EPUs. EPUs are converted into absolute measurement using ...
How to turn your microscope into a phase contrast microscope
... differences. It was invented by Frits Zernike, a revolutionary invention that earned him the Nobel Prize in 1953. He achieved that the light variations seen, accurately represent phase shifts. Here, I ask a simpler question: if I just want phase shifts to turn into intensity differences, what is the ...
... differences. It was invented by Frits Zernike, a revolutionary invention that earned him the Nobel Prize in 1953. He achieved that the light variations seen, accurately represent phase shifts. Here, I ask a simpler question: if I just want phase shifts to turn into intensity differences, what is the ...