PowerPoint Presentation - Tip-tilt mirror and sensor configuration
... when source, aperture, and detector are all very far apart (or when lenses are used to convert spherical waves into plane waves) ...
... when source, aperture, and detector are all very far apart (or when lenses are used to convert spherical waves into plane waves) ...
How does a confocal microscope work
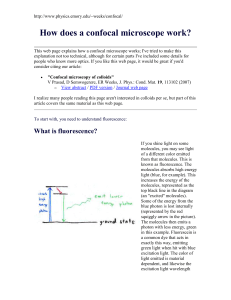
... Imagine we have some lenses inside the microscope, that focus light from the focal point of one lens to another point. This is represented by the blue rays of light in the above picture. The red rays of light represent light from another point in the sample, which is not at the focal point of the le ...
... Imagine we have some lenses inside the microscope, that focus light from the focal point of one lens to another point. This is represented by the blue rays of light in the above picture. The red rays of light represent light from another point in the sample, which is not at the focal point of the le ...
Breakup and Fusion of Self-Guided Femtosecond Light Pulses in Air
... and theoretically, the breakup of beams with 3 mm waist and display evidence of their ability to merge into a single light guide. The onset of small-scale filamentation preceding the ionization is here thoroughly investigated. For clarity, the beam distortions caused by modulational instability will ...
... and theoretically, the breakup of beams with 3 mm waist and display evidence of their ability to merge into a single light guide. The onset of small-scale filamentation preceding the ionization is here thoroughly investigated. For clarity, the beam distortions caused by modulational instability will ...
Surface profile measurement of aspheric optics using
... between light reflected from the aspheric surface and a known reference surface (usually the rear surface) while the probe scans the contour of the test optic. The phase difference between the test and reference surfaces is deduced from the measured intensity and the deviation of the aspheric surfac ...
... between light reflected from the aspheric surface and a known reference surface (usually the rear surface) while the probe scans the contour of the test optic. The phase difference between the test and reference surfaces is deduced from the measured intensity and the deviation of the aspheric surfac ...
Synthesis of highly focused fields with circular
... requirements of a specific problem [10]. Interestingly, several authors described inverse methods to find the pupil function from a predetermined field distribution in the focal area [11, 12]. Light shaping can be accomplished by using an optical setup able to generate beams with arbitrary polariza ...
... requirements of a specific problem [10]. Interestingly, several authors described inverse methods to find the pupil function from a predetermined field distribution in the focal area [11, 12]. Light shaping can be accomplished by using an optical setup able to generate beams with arbitrary polariza ...
3D differential interference contrast microscopy using synthetic
... original passband defined by the NA. This means that the sampling frequency has increased by about a factor of two in the scattering plane compared to the zero-degree illumination case. The actual increase is a factor of 1.8 in Fig. 2(h). When adding the set of angular images, it is important to syn ...
... original passband defined by the NA. This means that the sampling frequency has increased by about a factor of two in the scattering plane compared to the zero-degree illumination case. The actual increase is a factor of 1.8 in Fig. 2(h). When adding the set of angular images, it is important to syn ...
8. Beam splitters
... 8.1. Beam splitter plates Plate dividers are thin plane-parallel or edge plates made of optical glass, quartz or single-axis crystals (e.g. CaF2) coated with thin-film layers system. Depending on application it can be either metallic layer or dielectric coating. However one should remember that suc ...
... 8.1. Beam splitter plates Plate dividers are thin plane-parallel or edge plates made of optical glass, quartz or single-axis crystals (e.g. CaF2) coated with thin-film layers system. Depending on application it can be either metallic layer or dielectric coating. However one should remember that suc ...
Airy disk
In optics, the Airy disk (or Airy disc) and Airy pattern are descriptions of the best focused spot of light that a perfect lens with a circular aperture can make, limited by the diffraction of light. The Airy disk is of importance in physics, optics, and astronomy.The diffraction pattern resulting from a uniformly-illuminated circular aperture has a bright region in the center, known as the Airy disk which together with the series of concentric bright rings around is called the Airy pattern. Both are named after George Biddell Airy. The disk and rings phenomenon had been known prior to Airy; John Herschel described the appearance of a bright star seen through a telescope under high magnification for an 1828 article on light for the Encyclopedia Metropolitana:...the star is then seen (in favourable circumstances of tranquil atmosphere, uniform temperature, &c.) as a perfectly round, well-defined planetary disc, surrounded by two, three, or more alternately dark and bright rings, which, if examined attentively, are seen to be slightly coloured at their borders. They succeed each other nearly at equal intervals round the central disc....However, Airy wrote the first full theoretical treatment explaining the phenomenon (his 1835 ""On the Diffraction of an Object-glass with Circular Aperture"").Mathematically, the diffraction pattern is characterized by the wavelength of light illuminating the circular aperture, and the aperture's size. The appearance of the diffraction pattern is additionally characterized by the sensitivity of the eye or other detector used to observe the pattern.The most important application of this concept is in cameras and telescopes. Owing to diffraction, the smallest point to which a lens or mirror can focus a beam of light is the size of the Airy disk. Even if one were able to make a perfect lens, there is still a limit to the resolution of an image created by this lens. An optical system in which the resolution is no longer limited by imperfections in the lenses but only by diffraction is said to be diffraction limited.