The Research of Near-Infrared Electro-Optics
... (2) The light source and lens is fine tuned until the reflected beam from the plane mirror being focused on the position of the light source. (3) The photodiode is also calibrated and fine tunes as in step 1 & 2, but to achieve maximum signal receipt. plane mirror ...
... (2) The light source and lens is fine tuned until the reflected beam from the plane mirror being focused on the position of the light source. (3) The photodiode is also calibrated and fine tunes as in step 1 & 2, but to achieve maximum signal receipt. plane mirror ...
Experiment 15
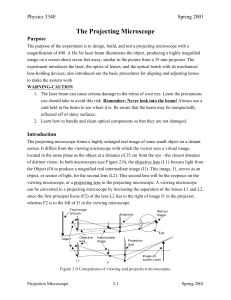
... between the given focal length and this value? (b) What value did you determine for the converging lens focal length from the 1/s vs. 1/s’ graph in Part A? What is the percentage difference between the given focal length and this value? 3. What happens to the image if half of the converging lens is ...
... between the given focal length and this value? (b) What value did you determine for the converging lens focal length from the 1/s vs. 1/s’ graph in Part A? What is the percentage difference between the given focal length and this value? 3. What happens to the image if half of the converging lens is ...
PILE15_1.20040629140..
... focal plane – a plane through the principal focus and is perpendicular to the principal axis. Simulation: Parallel rays through convex lens ...
... focal plane – a plane through the principal focus and is perpendicular to the principal axis. Simulation: Parallel rays through convex lens ...
IMPORTANT FEATURES FOR A RIGHT - pi
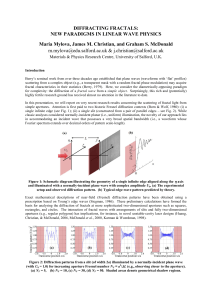
... The example c) in Fig. 1 corresponds to very important for practice case of creating a small laser spot with uniform intensity profile just in focal plane of a lens. Realizing this approach requires solving of the inverse problem – which intensity distribution should be at the entrance of a lens in ...
... The example c) in Fig. 1 corresponds to very important for practice case of creating a small laser spot with uniform intensity profile just in focal plane of a lens. Realizing this approach requires solving of the inverse problem – which intensity distribution should be at the entrance of a lens in ...
Lecture 14: Lenses
... focal length f , then an image of the object will be focussed in the lens/mirror at a distance v from it ...
... focal length f , then an image of the object will be focussed in the lens/mirror at a distance v from it ...
Tech Notes Wavelength 2012 | www.ll.mit.edu
... • Compact size • Wavelength-versatility—may be important depending on the specific welding/cutting details (both the materials and the gas environment surrounding the beam) The WBC technology combines high brightness, efficiency, and reliability with the power to perform the functions of current ind ...
... • Compact size • Wavelength-versatility—may be important depending on the specific welding/cutting details (both the materials and the gas environment surrounding the beam) The WBC technology combines high brightness, efficiency, and reliability with the power to perform the functions of current ind ...
Transmission Electron Microscopy
... HRTEM images formation is based on the interference between two or more diffracted beams from the electron beam after the interaction with a thin sample. Crystalline materials present well defined diffraction angles, as described by the Bragg’s law, and their interference generates a periodic patter ...
... HRTEM images formation is based on the interference between two or more diffracted beams from the electron beam after the interaction with a thin sample. Crystalline materials present well defined diffraction angles, as described by the Bragg’s law, and their interference generates a periodic patter ...
Diffraction of light by a single slit and gratings
... Physical Lab Exercise for Engineering Students ...
... Physical Lab Exercise for Engineering Students ...
Tabletop nanometer extreme ultraviolet imaging in an
... (SEM) images, and also removes all negative effects of nonuniform illumination of the sample or imperfect knowledge of the sample position as it is scanned [17]. The result is a general and extensible imaging technique that can provide a comprehensive and definitive characterization of how light at ...
... (SEM) images, and also removes all negative effects of nonuniform illumination of the sample or imperfect knowledge of the sample position as it is scanned [17]. The result is a general and extensible imaging technique that can provide a comprehensive and definitive characterization of how light at ...
00 Fourier optics – 4f Arrangement – Filtering and reconstruction
... clamp and fix it onto the optical plate using a right-angle clamp to connect it to a support rod clamped into a magnetic base. Now position the sonic transducer with its surface plane parallel to the water’s surface such that it is immersed in the liquid by about 5 mm without bubble formation. (Caut ...
... clamp and fix it onto the optical plate using a right-angle clamp to connect it to a support rod clamped into a magnetic base. Now position the sonic transducer with its surface plane parallel to the water’s surface such that it is immersed in the liquid by about 5 mm without bubble formation. (Caut ...
Airy disk
In optics, the Airy disk (or Airy disc) and Airy pattern are descriptions of the best focused spot of light that a perfect lens with a circular aperture can make, limited by the diffraction of light. The Airy disk is of importance in physics, optics, and astronomy.The diffraction pattern resulting from a uniformly-illuminated circular aperture has a bright region in the center, known as the Airy disk which together with the series of concentric bright rings around is called the Airy pattern. Both are named after George Biddell Airy. The disk and rings phenomenon had been known prior to Airy; John Herschel described the appearance of a bright star seen through a telescope under high magnification for an 1828 article on light for the Encyclopedia Metropolitana:...the star is then seen (in favourable circumstances of tranquil atmosphere, uniform temperature, &c.) as a perfectly round, well-defined planetary disc, surrounded by two, three, or more alternately dark and bright rings, which, if examined attentively, are seen to be slightly coloured at their borders. They succeed each other nearly at equal intervals round the central disc....However, Airy wrote the first full theoretical treatment explaining the phenomenon (his 1835 ""On the Diffraction of an Object-glass with Circular Aperture"").Mathematically, the diffraction pattern is characterized by the wavelength of light illuminating the circular aperture, and the aperture's size. The appearance of the diffraction pattern is additionally characterized by the sensitivity of the eye or other detector used to observe the pattern.The most important application of this concept is in cameras and telescopes. Owing to diffraction, the smallest point to which a lens or mirror can focus a beam of light is the size of the Airy disk. Even if one were able to make a perfect lens, there is still a limit to the resolution of an image created by this lens. An optical system in which the resolution is no longer limited by imperfections in the lenses but only by diffraction is said to be diffraction limited.