Microscopy Tutorial - Fred Hutch Shared Resources
... epifluorescence), and by the wavelength of light, but other optical components, as well as the imaging device, may alter the final resolution. It is important to note that resolution is not the ability to see small objects, but rather to separate very close objects. The ability to see small objects ...
... epifluorescence), and by the wavelength of light, but other optical components, as well as the imaging device, may alter the final resolution. It is important to note that resolution is not the ability to see small objects, but rather to separate very close objects. The ability to see small objects ...
Structural, growth and characterizations of NLO crystal
... In order to reveal the properties of the crystal, the TGCN single crystals were subjected to various tests. Single crystal X-ray diffraction studies were carried out using a Bruker AXS Kappa APEX II single crystal CCD diffractometer coupled with graphite-monochromated MoKα (λ= 0.7107Å) radiation. Th ...
... In order to reveal the properties of the crystal, the TGCN single crystals were subjected to various tests. Single crystal X-ray diffraction studies were carried out using a Bruker AXS Kappa APEX II single crystal CCD diffractometer coupled with graphite-monochromated MoKα (λ= 0.7107Å) radiation. Th ...
Theory of confocal fluorescence imaging in the
... where dx ¼ nxh and dy ¼ nyh are the lattice distances of the grid. The grid can have many different shapes, the simplest being square, but pseudohexagonal grids or line patterns are also possible and in some cases preferable. In the second approach, all SLM elements are ideally modulated in a comple ...
... where dx ¼ nxh and dy ¼ nyh are the lattice distances of the grid. The grid can have many different shapes, the simplest being square, but pseudohexagonal grids or line patterns are also possible and in some cases preferable. In the second approach, all SLM elements are ideally modulated in a comple ...
Spatially resolved measurement of femtosecond
... Femtosecond laser direct writing (FLDW) has become a common tool to fabricate three-dimensional photonic devices in transparent materials [1,2]. Recent investigations show its potential for creating volumetric diffractive optical elements (DOEs) [3–5] capable of multiplexing spatial and spectral inf ...
... Femtosecond laser direct writing (FLDW) has become a common tool to fabricate three-dimensional photonic devices in transparent materials [1,2]. Recent investigations show its potential for creating volumetric diffractive optical elements (DOEs) [3–5] capable of multiplexing spatial and spectral inf ...
Nanowire Grid Polarizers for Mid- and Long-Wavelength
... applications ranging from imaging and displays to communications and scientific instrumentation. The WGP typically consists of an array of metallic lines with sub-wavelength pitch supported by a transparent substrate. Wire grid structures are known to be effective as infrared polarizers with short o ...
... applications ranging from imaging and displays to communications and scientific instrumentation. The WGP typically consists of an array of metallic lines with sub-wavelength pitch supported by a transparent substrate. Wire grid structures are known to be effective as infrared polarizers with short o ...
Fiberoptic Sample Holder (FOSH): Characteristics and Uses APPLICATION NOTE 1056-201
... The sample-holder section of the FOSH consists of a spring-loaded slide assembly of nested quartz tubes. The sample-holder components are almost entirely quartz, which minimizes the magnetic background signal from the sample holder. Samples are mounted in a small quartz bucket that has a quartz lid ...
... The sample-holder section of the FOSH consists of a spring-loaded slide assembly of nested quartz tubes. The sample-holder components are almost entirely quartz, which minimizes the magnetic background signal from the sample holder. Samples are mounted in a small quartz bucket that has a quartz lid ...
2. - ACMAC
... Excitation along an area (vs. line definition of transverse phase in free-space) Short plasmon propagation and measurement distance (<100 microns), thus requiring fast acceleration (=non-paraxial conditions) Flexible beam shapers (e.g. Spatial Light Modulators) do not exist ...
... Excitation along an area (vs. line definition of transverse phase in free-space) Short plasmon propagation and measurement distance (<100 microns), thus requiring fast acceleration (=non-paraxial conditions) Flexible beam shapers (e.g. Spatial Light Modulators) do not exist ...
TEP 2.6.11-00 Fourier optics – 2f Arrangement TEP 2.6.11
... (a) Plane wave As a first partial experiment observe the plane wave itself (the light spot), i. e. no diffracting structures are placed in the object plane. Sketch your observation in the Fourier plane SC. According to the theory, a point should appear in the Fourier plane SC behind the lens. This i ...
... (a) Plane wave As a first partial experiment observe the plane wave itself (the light spot), i. e. no diffracting structures are placed in the object plane. Sketch your observation in the Fourier plane SC. According to the theory, a point should appear in the Fourier plane SC behind the lens. This i ...
Wave Optics Module Model Library
... where w = 3500 nm is the beam waist, and the y = 0 line is the centerline of the beam. Use this expression in a Port boundary condition on the left side to model the incident beam. Model all the other domain boundaries using Scattering Boundary Conditions. These conditions are appropriate when they ...
... where w = 3500 nm is the beam waist, and the y = 0 line is the centerline of the beam. Use this expression in a Port boundary condition on the left side to model the incident beam. Model all the other domain boundaries using Scattering Boundary Conditions. These conditions are appropriate when they ...
observing sunspots using a pinhole camera
... The resulting solar image was 24.1 centimeters in diameter. Noting several sunspots visible, I proceeded to trace their images onto the screen (This is much more difficult than it sounds since the Sun is a fast moving target, particularly at this projection size and no tracking involved. Several att ...
... The resulting solar image was 24.1 centimeters in diameter. Noting several sunspots visible, I proceeded to trace their images onto the screen (This is much more difficult than it sounds since the Sun is a fast moving target, particularly at this projection size and no tracking involved. Several att ...
Bistable localized emission states in a 200 μm broad
... Small-area bistable lasing spots, indicators of cavity solitons, can be created at different positions within the aperture of a broad-area VCSEL with frequencyselective feedback. These spots can be switched on and off with an incoherent injected field. ...
... Small-area bistable lasing spots, indicators of cavity solitons, can be created at different positions within the aperture of a broad-area VCSEL with frequencyselective feedback. These spots can be switched on and off with an incoherent injected field. ...
The Onset of Matter-Wave Amplification in a Superradiant Bose
... experiments clarify the nature of bosonic stimulation in the four-wave mixing of light and atoms. Superradiance is the collective emission of light from an ensemble of excited atoms and involves the spontaneous buildup of coherence in a macroscopic ensemble of atoms. Dicke, in his seminal work (1), ...
... experiments clarify the nature of bosonic stimulation in the four-wave mixing of light and atoms. Superradiance is the collective emission of light from an ensemble of excited atoms and involves the spontaneous buildup of coherence in a macroscopic ensemble of atoms. Dicke, in his seminal work (1), ...
IMPORTANT FEATURES FOR A RIGHT - pi
... book2, here we mention some basic features that will be important for further considerations. The Huygens-Fresnel Principle is the corner stone of the diffraction theory. According to that principle each point of a wave front can be considered as a center of a secondary spherical wavelet and by the ...
... book2, here we mention some basic features that will be important for further considerations. The Huygens-Fresnel Principle is the corner stone of the diffraction theory. According to that principle each point of a wave front can be considered as a center of a secondary spherical wavelet and by the ...
High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy
... focus setting and on the sample thickness ‐ Image interpretation often requires simulations ‐ Fringes in vacuum: image delocalization ‐ The images provide the correct symmetry HRTEM; Rolf Erni 2013 ...
... focus setting and on the sample thickness ‐ Image interpretation often requires simulations ‐ Fringes in vacuum: image delocalization ‐ The images provide the correct symmetry HRTEM; Rolf Erni 2013 ...
Slides
... Spectral property is the same as that of a single electron Dw/w=1/Nu Temporal phase space area Wz ~(Dw/w) Dzel ...
... Spectral property is the same as that of a single electron Dw/w=1/Nu Temporal phase space area Wz ~(Dw/w) Dzel ...
Interference with monochromatic light
... source is laterally extended, the same point x, y on the screen is attained by many light rays, all with different ϑ. It is obvious that the contrast in the interference pattern then must decrease. Loss of contrast will also be stated, if the light is no longer monochromatic, because again the phase ...
... source is laterally extended, the same point x, y on the screen is attained by many light rays, all with different ϑ. It is obvious that the contrast in the interference pattern then must decrease. Loss of contrast will also be stated, if the light is no longer monochromatic, because again the phase ...
Introduction Geological setting and host rocks
... 2. The formation namely of phillipsite/harmotome-Na (not-K) can be explained with the abundant presence of celadonite in the host rocks („exhaustion” of all potassium), while the lack of magnesium and iron in the harmotomes – with abundant formation of smectite. 3. The harmotomes from p. 392 have co ...
... 2. The formation namely of phillipsite/harmotome-Na (not-K) can be explained with the abundant presence of celadonite in the host rocks („exhaustion” of all potassium), while the lack of magnesium and iron in the harmotomes – with abundant formation of smectite. 3. The harmotomes from p. 392 have co ...
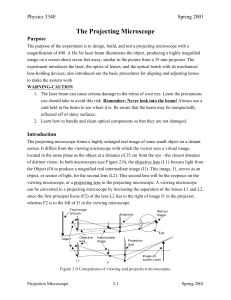
The Projecting Microscope
... located in the same plane as the object at a distance of 25 cm from the eye - the closest distance of distinct vision. In both microscopes (see Figure 2.0), the objective lens (L1) focuses light from the Object (O) to produce a magnified real intermediate image (I1). This image, I1, serves as an obj ...
... located in the same plane as the object at a distance of 25 cm from the eye - the closest distance of distinct vision. In both microscopes (see Figure 2.0), the objective lens (L1) focuses light from the Object (O) to produce a magnified real intermediate image (I1). This image, I1, serves as an obj ...
Quadriwave lateral shearing interferometry
... to measure the volume of erythrocytes under a range of osmotic conditions [17]. This technique needs multiple measurements (at least 3) in different shifted planes and the shift values need to be precise in order to obtain quantitative measurements. In this paper, we propose a new application in pha ...
... to measure the volume of erythrocytes under a range of osmotic conditions [17]. This technique needs multiple measurements (at least 3) in different shifted planes and the shift values need to be precise in order to obtain quantitative measurements. In this paper, we propose a new application in pha ...
Measurement of the Number of Atoms in a Magneto
... is done to reduce the linewidth of the laser. In an external cavity laser, the beam exiting the laser diode hits a grating at an angle. The first order beam is reflected back into the laser diode while the zeroth order beam is used in the experiment. Thus, mainly the wavelength that is back-reflecte ...
... is done to reduce the linewidth of the laser. In an external cavity laser, the beam exiting the laser diode hits a grating at an angle. The first order beam is reflected back into the laser diode while the zeroth order beam is used in the experiment. Thus, mainly the wavelength that is back-reflecte ...
Superprism phenomena in planar photonic crystals
... Fig. 4. (a) Photonic band structure (TE-polarized) for the PhCs used in this demonstration. A plane-wave expansion method was used. The dashed horizontal line corresponds to one of the frequencies we used in the experiment. (b) The iso-frequency contours for the first band (TE-polarized). The method ...
... Fig. 4. (a) Photonic band structure (TE-polarized) for the PhCs used in this demonstration. A plane-wave expansion method was used. The dashed horizontal line corresponds to one of the frequencies we used in the experiment. (b) The iso-frequency contours for the first band (TE-polarized). The method ...
Observation of optical polarization Möbius strips
... three half-twists. We show the corresponding theoretically calculated and experimentally observed Möbius strips with 3/2-twists for a Poincaré beam with q = –1/2 under tight focusing in Fig. 3, A and B, respectively. A Möbius strip of 5/2-twists is created and also observed by replacing the q-plate ...
... three half-twists. We show the corresponding theoretically calculated and experimentally observed Möbius strips with 3/2-twists for a Poincaré beam with q = –1/2 under tight focusing in Fig. 3, A and B, respectively. A Möbius strip of 5/2-twists is created and also observed by replacing the q-plate ...
Composite Optical Vortices Formed by Collinear Laguerre-Gauss Beams
... seen in Fig. 1, which displays in row (a) the intensity profile of the beam, and in row (b) the phase of the field. In both types of images we have deliberately discretized the gray scale to appreciate better the intensity and phase contours. One step in the gray scale corresponds to one tenth of the ...
... seen in Fig. 1, which displays in row (a) the intensity profile of the beam, and in row (b) the phase of the field. In both types of images we have deliberately discretized the gray scale to appreciate better the intensity and phase contours. One step in the gray scale corresponds to one tenth of the ...
Planar second-harmonic generation with noncollinear pumps in
... in the X-Y (a-b) plane. In this way, an infinite number of reciprocal vectors is available to realize different types of the phase matching conditions. It has been demonstrated recently that depending on geometry of interaction the second-harmonic (SH) radiation can be generated either in the form o ...
... in the X-Y (a-b) plane. In this way, an infinite number of reciprocal vectors is available to realize different types of the phase matching conditions. It has been demonstrated recently that depending on geometry of interaction the second-harmonic (SH) radiation can be generated either in the form o ...
Enhancement of image quality and imaging depth with Airy light
... high-resolution, single-photon excitation LSM, as these beam types overcome diffraction and can maintain a constant beam profile over longer longitudinal distances than a Gaussian beam. The lower peak intensity used in Airy LSM further reduces photodamage in the sample [9]. Bessel beam-based LSM has ...
... high-resolution, single-photon excitation LSM, as these beam types overcome diffraction and can maintain a constant beam profile over longer longitudinal distances than a Gaussian beam. The lower peak intensity used in Airy LSM further reduces photodamage in the sample [9]. Bessel beam-based LSM has ...