![[PDF]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008791769_1-3b8e6dd90a51b8e04844f5b8abb259ea-300x300.png)
prezantacia aj
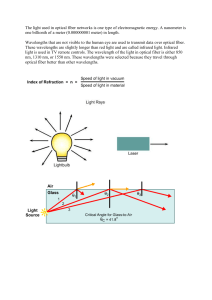
... The light used in optical fiber networks is one type of electromagnetic energy. A nanometer is one billionth of a meter (0.000000001 meter) in length. Wavelengths that are not visible to the human eye are used to transmit data over optical fiber. These wavelengths are slightly longer than red light ...
... The light used in optical fiber networks is one type of electromagnetic energy. A nanometer is one billionth of a meter (0.000000001 meter) in length. Wavelengths that are not visible to the human eye are used to transmit data over optical fiber. These wavelengths are slightly longer than red light ...
Semiperiodicity versus periodicity for ultra broadband optical
... probability as a result of the strong field enhancement.7 It has been shown that this technique can boost optical absorption by 26%.8 One important aspect in solar cell design is its adherence to the very large bandwidth of the solar illumination spectrum. In the context of the actual plasmonic back ...
... probability as a result of the strong field enhancement.7 It has been shown that this technique can boost optical absorption by 26%.8 One important aspect in solar cell design is its adherence to the very large bandwidth of the solar illumination spectrum. In the context of the actual plasmonic back ...
Sample Pages
... much lower propagation losses, so that its power remains nearly constant, unless the fiber is very long. The high loss for cladding modes is convenient, e.g., when checking how efficiently light is launched into the fiber core, or when measuring the propagation losses of the fiber core. Residual lig ...
... much lower propagation losses, so that its power remains nearly constant, unless the fiber is very long. The high loss for cladding modes is convenient, e.g., when checking how efficiently light is launched into the fiber core, or when measuring the propagation losses of the fiber core. Residual lig ...
Manipulating Light with a Magnetic Field - lpmmc
... atoms, but looking only at charge distributions on scales large compared to the atomic scale. Microscopic charges and currents are described by the polarization density vector P and the magnetization M . It is important to realize that this description is only approximate. Cases are known for which ...
... atoms, but looking only at charge distributions on scales large compared to the atomic scale. Microscopic charges and currents are described by the polarization density vector P and the magnetization M . It is important to realize that this description is only approximate. Cases are known for which ...
Quenching of Giant Hysteresis Effects in La Y H Switchable Mirrors
... Since the discovery that thin YHx and LaHx films show dramatic changes in their optical properties near their metal-insulator (MI) transition when the hydrogento-metal ratio x increases from 2 to 3 [1], these materials have attracted a lot of interest because of their technological potential [2–4] a ...
... Since the discovery that thin YHx and LaHx films show dramatic changes in their optical properties near their metal-insulator (MI) transition when the hydrogento-metal ratio x increases from 2 to 3 [1], these materials have attracted a lot of interest because of their technological potential [2–4] a ...
Laser Spectroscopy B3 - Imperial College London
... through the rubidium cell as depicted in the initial setup diagram. If the laser is correctly tuned then the beams passing through the cell will appear as bright glowing lines on the camera, similar to those shown in FIG. 1(b). Because atoms can only absorb photons with very specific energies, and t ...
... through the rubidium cell as depicted in the initial setup diagram. If the laser is correctly tuned then the beams passing through the cell will appear as bright glowing lines on the camera, similar to those shown in FIG. 1(b). Because atoms can only absorb photons with very specific energies, and t ...
EXPERIMENT 28 Intrinsic Viscosity: Chain Linkage in Polyvinyl
... At this point, two " initial" solutions have be n prepared: 100 mL of each of two aqueous polymer solutions of the same concentration (~ 0.9 g/100 mL), one cleaved with periodate and one uncleaved. To obtain a second concentration of each material, pipette 50 mL of the " initial" solution into a 100 ...
... At this point, two " initial" solutions have be n prepared: 100 mL of each of two aqueous polymer solutions of the same concentration (~ 0.9 g/100 mL), one cleaved with periodate and one uncleaved. To obtain a second concentration of each material, pipette 50 mL of the " initial" solution into a 100 ...
Unit 2: Atoms, Ions and Ionic Compounds
... compared to the initial concentration of the weak base. Check the validity of previous assumption. Calculate the [OH-] concentration and pOH Use pOH to calculate pH. ...
... compared to the initial concentration of the weak base. Check the validity of previous assumption. Calculate the [OH-] concentration and pOH Use pOH to calculate pH. ...
54_1.PDF
... the gas jet. Stainless steel collimators of adequate apertures for the different opening cones of the electron beam ensured that the beam halo was accounted for. To obtain the angular divergence of electrons as a function of their position within the beam envelope, the well known "pepper pot" techni ...
... the gas jet. Stainless steel collimators of adequate apertures for the different opening cones of the electron beam ensured that the beam halo was accounted for. To obtain the angular divergence of electrons as a function of their position within the beam envelope, the well known "pepper pot" techni ...
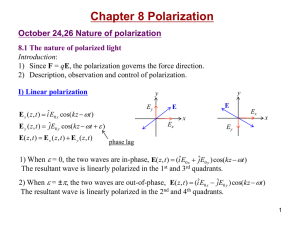
Chapter 8
... Less expensive, but sensitive to wavelength, incident angle and temperature. d d. d ...
... Less expensive, but sensitive to wavelength, incident angle and temperature. d d. d ...
Chiral specific electron vortex beam spectroscopy
... We can now address the physical meaning of the double summation over p and p0 in Eq. (13) and the implications of this for the chiral-specific spectroscopy of atoms located away from the vortex beam axis. The off-axis case is illustrated in Fig. (1)(b). It can be seen that the features uncovered abo ...
... We can now address the physical meaning of the double summation over p and p0 in Eq. (13) and the implications of this for the chiral-specific spectroscopy of atoms located away from the vortex beam axis. The off-axis case is illustrated in Fig. (1)(b). It can be seen that the features uncovered abo ...
The color of shock waves in photonic crystals Abstract Evan J. Reed,
... Manipulation of light using technologies that do not require electronics is the only feasible way to retain information about phase coherence and/or quantum information. These properties are required for many all-optical signal processing schemes and all quantum information processing and transport ...
... Manipulation of light using technologies that do not require electronics is the only feasible way to retain information about phase coherence and/or quantum information. These properties are required for many all-optical signal processing schemes and all quantum information processing and transport ...
An optical cloak made of dielectrics LETTERS *
... (Si) slab waveguide where the cloak region is obtained by varying the effective index of refraction in a two-dimensional (2D) space. This index profile is designed using quasi-conformal mapping and realized by fabricating a 2D sub-wavelength hole lattice with varying density23 (see Supplementary Inf ...
... (Si) slab waveguide where the cloak region is obtained by varying the effective index of refraction in a two-dimensional (2D) space. This index profile is designed using quasi-conformal mapping and realized by fabricating a 2D sub-wavelength hole lattice with varying density23 (see Supplementary Inf ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.