
PDF
... emergence of a scattering maximum, suggesting the development of ion-rich microdomains or clusters. Although the noise level of the invariant data is rather high, the observed transition is nonetheless important, since it is clearly indicative of the development of microphase separation at the trans ...
... emergence of a scattering maximum, suggesting the development of ion-rich microdomains or clusters. Although the noise level of the invariant data is rather high, the observed transition is nonetheless important, since it is clearly indicative of the development of microphase separation at the trans ...
Resins for Optics
... 1-1. Brief Description of the Refractive Index The refractive index shows the optical density of a material and it is generally represented by “n”. In other words, the refractive index is the resistance under which light passes through a material. A greater resistance results in an increased refract ...
... 1-1. Brief Description of the Refractive Index The refractive index shows the optical density of a material and it is generally represented by “n”. In other words, the refractive index is the resistance under which light passes through a material. A greater resistance results in an increased refract ...
AP Chemistry
... saturated AgCrO4 solution by spectrophotometry, calculate Ksp for AgCrO4 and compare it to the expected value. Fill three cuvette tubes with the K2CrO4 standards. Set the spectrophotometer to 375 nm and measure absorbance. a. Calculate the CrO42- concentration for each standard and record its absorb ...
... saturated AgCrO4 solution by spectrophotometry, calculate Ksp for AgCrO4 and compare it to the expected value. Fill three cuvette tubes with the K2CrO4 standards. Set the spectrophotometer to 375 nm and measure absorbance. a. Calculate the CrO42- concentration for each standard and record its absorb ...
Analyzing optical spectra by computer simulation
... may be many local minima in addition to the wanted global minimum of the fit deviation. Although there are minimization algorithms which may escape from local minima, they are usually very slow and their application is not recommended for spectrum fitting. It is more efficient in most cases to reduc ...
... may be many local minima in addition to the wanted global minimum of the fit deviation. Although there are minimization algorithms which may escape from local minima, they are usually very slow and their application is not recommended for spectrum fitting. It is more efficient in most cases to reduc ...
Laser Doppler Flowmetry - a Theoretical Framework
... part, respectively, since those signals are usually processed completely separately. Looking at expression 4.7, one can realize that the signal to noise ratio of the iac signal decreases when the number of speckle areas, ns, increases, arguing that the detector should contain as few speckle areas as ...
... part, respectively, since those signals are usually processed completely separately. Looking at expression 4.7, one can realize that the signal to noise ratio of the iac signal decreases when the number of speckle areas, ns, increases, arguing that the detector should contain as few speckle areas as ...
Base units of the SI, fundamental constants and
... c vt This equation has been solved to yield the modal content of real laser beams and diffraction corrections have been studied in great detail by generations of opticians. The propagation of light pulses is also very well described and understood in laser and microwave links. It is true that ultra- ...
... c vt This equation has been solved to yield the modal content of real laser beams and diffraction corrections have been studied in great detail by generations of opticians. The propagation of light pulses is also very well described and understood in laser and microwave links. It is true that ultra- ...
Other photon-lithographies
... from the same source location Y (so no need of spatial coherence). In addition, the laser source doesn’t need to be monochromatic (very narrow l), so the name “achromatic”. ...
... from the same source location Y (so no need of spatial coherence). In addition, the laser source doesn’t need to be monochromatic (very narrow l), so the name “achromatic”. ...
Wave Optics Module Model Library
... Use this expression in a Port boundary condition on the left side to model the incident beam. Model all the other domain boundaries using Scattering Boundary Conditions. These conditions are appropriate when they are placed several wavelengths away from any scattering objects and the wave is known t ...
... Use this expression in a Port boundary condition on the left side to model the incident beam. Model all the other domain boundaries using Scattering Boundary Conditions. These conditions are appropriate when they are placed several wavelengths away from any scattering objects and the wave is known t ...
Confocal Microscopy - Emory Physics
... to drop to a lower energy level (the second black line). If the surrounding molecules are not able to accept the larger energy difference needed to further lower the molecule to its ground state, it may undergo spontaneous emission, thereby losing the remaining energy, by emitting light of a longer ...
... to drop to a lower energy level (the second black line). If the surrounding molecules are not able to accept the larger energy difference needed to further lower the molecule to its ground state, it may undergo spontaneous emission, thereby losing the remaining energy, by emitting light of a longer ...
NRC Publications Archive Archives des publications du CNRC
... As shown in Appendix A, D rel can be interpreted as a factor which expresses how many times quicker the visibility in an enclosure will be reduced to a certain level. if, under testing conditions, smoke is produced by the test specimen instead of by the reference wood. The relative time required to ...
... As shown in Appendix A, D rel can be interpreted as a factor which expresses how many times quicker the visibility in an enclosure will be reduced to a certain level. if, under testing conditions, smoke is produced by the test specimen instead of by the reference wood. The relative time required to ...
Influence of Protonation State on the Excited State Dynamics of a
... MLCT states in the case of RuH and RuH2 to mainly IL states for Ru. The IL states, which dominate the electronic properties of Ru in the visible spectral range, were mainly associated with the pyrene moiety. 3.2. Femtosecond Transient Absorption Spectroscopy. After having discussed the ground-state ...
... MLCT states in the case of RuH and RuH2 to mainly IL states for Ru. The IL states, which dominate the electronic properties of Ru in the visible spectral range, were mainly associated with the pyrene moiety. 3.2. Femtosecond Transient Absorption Spectroscopy. After having discussed the ground-state ...
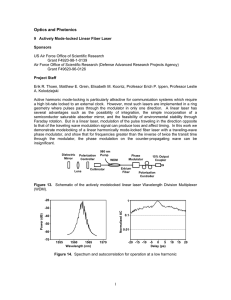
E. Ippen
... In contrast to the case of AM, timing is not restored directly by PM. Mistimed pulses first experience a shift in frequency that converts to retiming through group-velocity dispersion (GVD). Upon successive round trips, the accumulated frequency shifts are damped out by filtering. Two typical traces ...
... In contrast to the case of AM, timing is not restored directly by PM. Mistimed pulses first experience a shift in frequency that converts to retiming through group-velocity dispersion (GVD). Upon successive round trips, the accumulated frequency shifts are damped out by filtering. Two typical traces ...
——— Our CVD diamond has an extremely broad
... only possible with a multitude of different windows each spanning a small wavelength range. So with CVD diamond, instead of many different components, only one is required. ...
... only possible with a multitude of different windows each spanning a small wavelength range. So with CVD diamond, instead of many different components, only one is required. ...
Cathodoluminescence in the scanning transmission electron
... on luminescence properties. For example, some dislocations can act as non-radiative centres, quenching the emission of the object of interest, but others can be radiative. Colour centres can be highly absorbing and/or emitting, dominating the optical properties of the host matrix in the visible rang ...
... on luminescence properties. For example, some dislocations can act as non-radiative centres, quenching the emission of the object of interest, but others can be radiative. Colour centres can be highly absorbing and/or emitting, dominating the optical properties of the host matrix in the visible rang ...
Reports for the two projects on Bisosensors have been combined
... measurable shift of the resonator’s resonance frequency. Several approaches for THz biosensors applying this feature are currently investigated [e.g. 3,4,5], aiming at a high sensitivity since the amount of probe material is very low. The smaller the required amount of material and the larger the fr ...
... measurable shift of the resonator’s resonance frequency. Several approaches for THz biosensors applying this feature are currently investigated [e.g. 3,4,5], aiming at a high sensitivity since the amount of probe material is very low. The smaller the required amount of material and the larger the fr ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... The Common Ion Effect explains why there is a reduction in the solubility of a salt due to the presence of a common ion. Example: Think about the solubility of CaF2(s) in NaF(aq)…. The CaF2(s) can’t breakdown as easily because there is already F- ions in solution. ...
... The Common Ion Effect explains why there is a reduction in the solubility of a salt due to the presence of a common ion. Example: Think about the solubility of CaF2(s) in NaF(aq)…. The CaF2(s) can’t breakdown as easily because there is already F- ions in solution. ...
17 - Wiley
... structures show that the phenolate anion can distribute its negative charge around the benzene ring, increasing its stability compared with that of the localized O– that results from removal of a proton from ethanol. That is why phenol is a weak acid, whereas alcohols such as ethanol are not acidic. ...
... structures show that the phenolate anion can distribute its negative charge around the benzene ring, increasing its stability compared with that of the localized O– that results from removal of a proton from ethanol. That is why phenol is a weak acid, whereas alcohols such as ethanol are not acidic. ...
Bulgarian Chemical Communications, Volume 41, Number 4 (pp
... The degradation of diazo dyes Brilliant Yellow (BY) and Bismark Brown (BB) was investigated by the photoFenton-like process Fe2+/ammonium persulphate (APS)/UV in acidic pH medium. The influence of various reaction parameters like pH, concentration of Fe2+ ions/APS, structure of the dye and effect of ...
... The degradation of diazo dyes Brilliant Yellow (BY) and Bismark Brown (BB) was investigated by the photoFenton-like process Fe2+/ammonium persulphate (APS)/UV in acidic pH medium. The influence of various reaction parameters like pH, concentration of Fe2+ ions/APS, structure of the dye and effect of ...
prezantacia aj
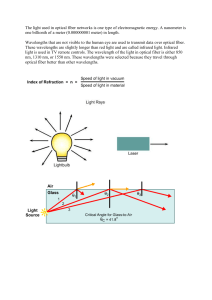
... The light used in optical fiber networks is one type of electromagnetic energy. A nanometer is one billionth of a meter (0.000000001 meter) in length. Wavelengths that are not visible to the human eye are used to transmit data over optical fiber. These wavelengths are slightly longer than red light ...
... The light used in optical fiber networks is one type of electromagnetic energy. A nanometer is one billionth of a meter (0.000000001 meter) in length. Wavelengths that are not visible to the human eye are used to transmit data over optical fiber. These wavelengths are slightly longer than red light ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.



















![[PDF]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008791769_1-3b8e6dd90a51b8e04844f5b8abb259ea-300x300.png)