Conjugate Acids and Bases
... Many reactions never result in complete conversion of reactants to products. They proceed to a state of chemical equilibrium in which the ratio of concentrations of reactants and products is constant. Equilibrium-constant expressions are algebraic equations that describe the concentration relationsh ...
... Many reactions never result in complete conversion of reactants to products. They proceed to a state of chemical equilibrium in which the ratio of concentrations of reactants and products is constant. Equilibrium-constant expressions are algebraic equations that describe the concentration relationsh ...
the Workshop Document (3)
... transducer response is very low and the measurements are noisy. Since both transducers are aimed at the center point of the pedestal, the grating should be placed there also. Measurements of the diffracted amplitude can then be made at various angles and various frequencies. To compare amplitudes at ...
... transducer response is very low and the measurements are noisy. Since both transducers are aimed at the center point of the pedestal, the grating should be placed there also. Measurements of the diffracted amplitude can then be made at various angles and various frequencies. To compare amplitudes at ...
Lunau K (2000) - Behaviour and Ecology at Nottingham
... reaction, since the flies are insensitive to red light (redblind). Comparative studies of the spectral reflection of pollen show that these signal features of pollen in melittophile flowers with visibly presented pollen are more commonly present than in melittophile flowers with concealed pollen (Da ...
... reaction, since the flies are insensitive to red light (redblind). Comparative studies of the spectral reflection of pollen show that these signal features of pollen in melittophile flowers with visibly presented pollen are more commonly present than in melittophile flowers with concealed pollen (Da ...
1333.PDF
... pulse can allow recording of time dependent species concentrations, and therefore kinetics. Two types of femtosecond (fs) time-resolved interferometry are used. Both utilize a MachZehnder interferometer with the sample in one arm and a time delay in the reference arm. For spectral interferometry (sp ...
... pulse can allow recording of time dependent species concentrations, and therefore kinetics. Two types of femtosecond (fs) time-resolved interferometry are used. Both utilize a MachZehnder interferometer with the sample in one arm and a time delay in the reference arm. For spectral interferometry (sp ...
Final Exam - Dawson College
... c. If the actual vapor pressure measured is 15.2 mm Hg, will the boiling point of this solution be higher or lower than the one expected from Raoult’s law? Explain. ...
... c. If the actual vapor pressure measured is 15.2 mm Hg, will the boiling point of this solution be higher or lower than the one expected from Raoult’s law? Explain. ...
Generation of relativistic intensity pulses at a kilohertz
... (Spectra-Physics Lasers, Evolution X), which can generate 10-W average power at a 1-kHz repetition rate. More than 1 mJ of pulse energy can be obtained for a pump energy of 9.5 mJ. This amplifier design is easy to align because of its simplicity. Furthermore, there are only two mirror ref lections f ...
... (Spectra-Physics Lasers, Evolution X), which can generate 10-W average power at a 1-kHz repetition rate. More than 1 mJ of pulse energy can be obtained for a pump energy of 9.5 mJ. This amplifier design is easy to align because of its simplicity. Furthermore, there are only two mirror ref lections f ...
Controllable Optical Phase Shift Over One Radian from a Single
... using a double-needle radio-frequency (RF) quadrupole Paul trap operating at a drive frequency of 40 MHz. Laser light at 369.5 nm, near resonance with a strong transition of the ion, is weakly focused onto the ion to provide an illumination field with power of ∼ 5 nW and spot diameter of 5 µm (full- ...
... using a double-needle radio-frequency (RF) quadrupole Paul trap operating at a drive frequency of 40 MHz. Laser light at 369.5 nm, near resonance with a strong transition of the ion, is weakly focused onto the ion to provide an illumination field with power of ∼ 5 nW and spot diameter of 5 µm (full- ...
optical fibre communication
... are called SPLICING. Temporary joints made by two fibres are called as CONNECTORS. Special device named COUPLERS are needed to join 3 or more fibres. Losses in transferring signals in copper can be neglected but it is not so with fibres. Hence it should account for the losses deriving from coupling ...
... are called SPLICING. Temporary joints made by two fibres are called as CONNECTORS. Special device named COUPLERS are needed to join 3 or more fibres. Losses in transferring signals in copper can be neglected but it is not so with fibres. Hence it should account for the losses deriving from coupling ...
Interferometer design for writing Bragg gratings in optical fibers
... positions of the components are critical, particularly the stability of these components. Exposure of the target to make a grating structure takes approximately 300 seconds, during which time, the components should remain stable relative to each other to within a few nm. Analysis of this geometry re ...
... positions of the components are critical, particularly the stability of these components. Exposure of the target to make a grating structure takes approximately 300 seconds, during which time, the components should remain stable relative to each other to within a few nm. Analysis of this geometry re ...
Surface Plasmon Interference Nanolithography
... A new nanophotolithography technique based on the interference of surface plasmon waves is proposed and demonstrated by using computer simulations. The wavelengths of the surface plasmon waves at metal and dielectric interfaces can reach the nanometer scale while their frequencies remain in the opti ...
... A new nanophotolithography technique based on the interference of surface plasmon waves is proposed and demonstrated by using computer simulations. The wavelengths of the surface plasmon waves at metal and dielectric interfaces can reach the nanometer scale while their frequencies remain in the opti ...
Vacuum Ultraviolet Spectroscopy and Photochemistry of Zinc
... dashed vertical line in Figure 1, a blue shift of the band occurs from the 213.9 nm gas phase position17 of the atomic transition. Two other major characteristics of the atomic absorption profile recorded in solid D2 are the large bandwidth (∼2050 cm−1) and the pronounced 3-fold splitting with resolv ...
... dashed vertical line in Figure 1, a blue shift of the band occurs from the 213.9 nm gas phase position17 of the atomic transition. Two other major characteristics of the atomic absorption profile recorded in solid D2 are the large bandwidth (∼2050 cm−1) and the pronounced 3-fold splitting with resolv ...
Deposition and Characterization of Dielectric Distributed Bragg
... The Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser (VCSEL) is a laser well suited for data centre applications due to its low cost, high speeds, good fiber coupling, and low threshold current The current standard wavelength for short-haul is 850 nm, however switching to 980 nm can improve transmission dista ...
... The Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser (VCSEL) is a laser well suited for data centre applications due to its low cost, high speeds, good fiber coupling, and low threshold current The current standard wavelength for short-haul is 850 nm, however switching to 980 nm can improve transmission dista ...
Photonic crystal cavities in silicon dioxide
... Next, we use the perturbation design suggested by previous references and introduce a parabolic relationship between the lattice constant and the x-coordinate, thus forming an optical potential well.13 In particular, we choose a minimum effective lattice constant of 0.90a at the center of the potent ...
... Next, we use the perturbation design suggested by previous references and introduce a parabolic relationship between the lattice constant and the x-coordinate, thus forming an optical potential well.13 In particular, we choose a minimum effective lattice constant of 0.90a at the center of the potent ...
Chemical sensors based on quantum cascade lasers
... realized only for selected devices. One of the limiting factors is a mismatch between the active region peak-gain and the DFB structure mode, due to their different temperature dependence [22]. Another limitation for current-tuning of a CW laser is that at a certain current level higher order transv ...
... realized only for selected devices. One of the limiting factors is a mismatch between the active region peak-gain and the DFB structure mode, due to their different temperature dependence [22]. Another limitation for current-tuning of a CW laser is that at a certain current level higher order transv ...
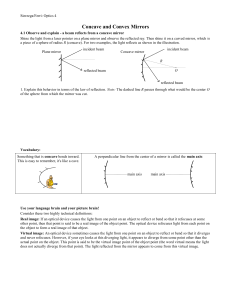
Concave and Convex Mirrors
... Real image: If an optical device causes the light from one point on an object to reflect or bend so that it refocuses at some other point, then that point is said to be a real image of the object point. The optical device refocuses light from each point on the object to form a real image of that obj ...
... Real image: If an optical device causes the light from one point on an object to reflect or bend so that it refocuses at some other point, then that point is said to be a real image of the object point. The optical device refocuses light from each point on the object to form a real image of that obj ...
Light consists of electromagnetic waves that have oscillating electric
... We will denote the propagation direction of a plane wave by the wave vector k. In real optical systems, such (infinitely spread) plane waves do not exist because of the finite size of the optical elements. Non-planar optical components cause further deviations of the wave from planarity so the wave ...
... We will denote the propagation direction of a plane wave by the wave vector k. In real optical systems, such (infinitely spread) plane waves do not exist because of the finite size of the optical elements. Non-planar optical components cause further deviations of the wave from planarity so the wave ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.