Birefringence dispersion in fused silica for DUV lithography
... stepper systems have been two of the driving forces towards production of integrated circuits with smaller feature sizes. Fused silica lens elements in current lithography tools possess high internal transmission, high index homogeneity, low induced absorption and low birefringence. While absorption ...
... stepper systems have been two of the driving forces towards production of integrated circuits with smaller feature sizes. Fused silica lens elements in current lithography tools possess high internal transmission, high index homogeneity, low induced absorption and low birefringence. While absorption ...
Light Rays
... All points on a given wave front are taken as point sources for the production of spherical secondary waves, called wavelets, that propagate outward through a medium with speeds characteristic of waves in that medium. After some time interval has passed, the new position of the wave front is the sur ...
... All points on a given wave front are taken as point sources for the production of spherical secondary waves, called wavelets, that propagate outward through a medium with speeds characteristic of waves in that medium. After some time interval has passed, the new position of the wave front is the sur ...
Waves and Radiation
... In this case the light rays are slowed down by the water and are _____, causing the pen to look odd. The two mediums in this example are ______ and _______. Words – speed up, water, air, bent, medium ...
... In this case the light rays are slowed down by the water and are _____, causing the pen to look odd. The two mediums in this example are ______ and _______. Words – speed up, water, air, bent, medium ...
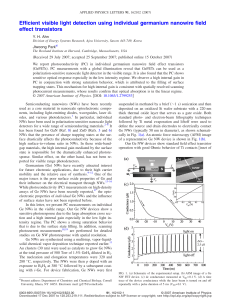
Efficient visible light detection using individual germanium nanowire
... arrays of Ge NWs have been recently reported,17 the optoelectronic properties of individual Ge NWs and the influence of surface states have not been reported before. In this letter, we present PC measurements on individual Ge NWs in the visible range. Our Ge NW devices show a sensitive photoresponse ...
... arrays of Ge NWs have been recently reported,17 the optoelectronic properties of individual Ge NWs and the influence of surface states have not been reported before. In this letter, we present PC measurements on individual Ge NWs in the visible range. Our Ge NW devices show a sensitive photoresponse ...
Spring 2014 Chemistry Review
... 20) What properties of metals are explained by metallic bonding theory? What major difference in metals allows this to happen? 21) Define and give an example of an alloy. ...
... 20) What properties of metals are explained by metallic bonding theory? What major difference in metals allows this to happen? 21) Define and give an example of an alloy. ...
chapter 7
... electrons, they have much shorter "wavelength" than the electrons. Hence, the proton microscope achieves an even higher resolution compared to that of the electron microscope. 4. Electron X-ray microanalyzer. The purpose of this instrument is to provide information on the elemental composition of th ...
... electrons, they have much shorter "wavelength" than the electrons. Hence, the proton microscope achieves an even higher resolution compared to that of the electron microscope. 4. Electron X-ray microanalyzer. The purpose of this instrument is to provide information on the elemental composition of th ...
9-5 Huygens principle
... effective distance traveled by a light ray (if it travels through a dense material of index n the effective distance is n times greater than the actual distance) Small variations in the path taken by a light ray must not affect the optical path length d(OPL)=0 for the path taken by a light ray (noti ...
... effective distance traveled by a light ray (if it travels through a dense material of index n the effective distance is n times greater than the actual distance) Small variations in the path taken by a light ray must not affect the optical path length d(OPL)=0 for the path taken by a light ray (noti ...
Photoelectric Effect
... kinetic energy depend on the wavelength and intensity of the light striking the surface, and account for this dependence in terms of a photon model of light. (4) Sketch or identify a graph of stopping potential versus frequency for a photoelectric-effect experiment, determine from such a graph the t ...
... kinetic energy depend on the wavelength and intensity of the light striking the surface, and account for this dependence in terms of a photon model of light. (4) Sketch or identify a graph of stopping potential versus frequency for a photoelectric-effect experiment, determine from such a graph the t ...
Molecular Luminescence Spectroscopy
... from molecules that have been excited to higher energy levels by absorption of electromagnetic radiation. ...
... from molecules that have been excited to higher energy levels by absorption of electromagnetic radiation. ...
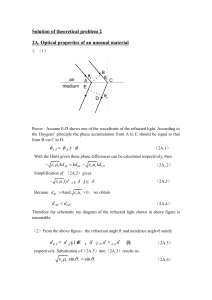
Solution of theoretical problem 2
... light wave accumulated during its propagation in air, the second term shows the phase difference of the light wave accumulated during its propagation in the unusual medium, while the third term accounts for the phase difference of the light wave accumulated due to the two reflections in succession f ...
... light wave accumulated during its propagation in air, the second term shows the phase difference of the light wave accumulated during its propagation in the unusual medium, while the third term accounts for the phase difference of the light wave accumulated due to the two reflections in succession f ...
Hollow Retroreflectors Promote Precision Optical Alignment
... Advances in work materials and coatings are pushing this self-compensating mirror technology beyond traditional uses, such as laser tracking, and further into space-based interferometry, long-path spectroscopy and other emerging applications. by Zvi Bleier, Itai Vishnia and Jack Lipkins, PLX Inc. re ...
... Advances in work materials and coatings are pushing this self-compensating mirror technology beyond traditional uses, such as laser tracking, and further into space-based interferometry, long-path spectroscopy and other emerging applications. by Zvi Bleier, Itai Vishnia and Jack Lipkins, PLX Inc. re ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.