English
... subordination of clauses in sentences with subtle structural problems (E24.d.1) 2. Maintain consistent verb tense and pronoun person on the basis of the preceding clause or sentence (E24.d.2) 1. Ensure that a pronoun agrees with its antecedent when the two occur in separate clauses or sentences (E24 ...
... subordination of clauses in sentences with subtle structural problems (E24.d.1) 2. Maintain consistent verb tense and pronoun person on the basis of the preceding clause or sentence (E24.d.2) 1. Ensure that a pronoun agrees with its antecedent when the two occur in separate clauses or sentences (E24 ...
Phrases, Clauses, and Commas
... Appositive (interrupter) noun or pronoun, often with modifiers, set beside another noun or pronoun to explain it further • My brother’s car, a sporty red hatchback with bucket seats, is the envy of my friends. ...
... Appositive (interrupter) noun or pronoun, often with modifiers, set beside another noun or pronoun to explain it further • My brother’s car, a sporty red hatchback with bucket seats, is the envy of my friends. ...
Haunted by Commas
... Jane went to the store, and her husband Joe stayed at home with the baby. 2. Use a semicolon Jane went to the store; her husband Joe stayed at home with the baby. 3. Make two separate sentences Jane went to the store. Her husband Joe stayed at home with the baby. A comma is not strong enough to join ...
... Jane went to the store, and her husband Joe stayed at home with the baby. 2. Use a semicolon Jane went to the store; her husband Joe stayed at home with the baby. 3. Make two separate sentences Jane went to the store. Her husband Joe stayed at home with the baby. A comma is not strong enough to join ...
Reflexive Pronouns
... 2. Have you yourself seen it? OR Have you seen it yourself? 3. The President himself promised to stop the war. 4. She spoke to me herself. OR She herself spoke to me. ...
... 2. Have you yourself seen it? OR Have you seen it yourself? 3. The President himself promised to stop the war. 4. She spoke to me herself. OR She herself spoke to me. ...
What does an adjective do
... Katie can play the piano. She also studied the guitar. She likes many different kinds of music. The noun, “Katie,” is clear, so the adjective clause just gives more information about her: Katie, who studied the guitar, can also play the piano. Katie, who likes many different kinds of music, can play ...
... Katie can play the piano. She also studied the guitar. She likes many different kinds of music. The noun, “Katie,” is clear, so the adjective clause just gives more information about her: Katie, who studied the guitar, can also play the piano. Katie, who likes many different kinds of music, can play ...
Sentence Types
... that is part of each sentence type. Review what a fragment, a run on and a comma splice is. Practice writing one sentence of each type. Check your sentences with your teacher. ...
... that is part of each sentence type. Review what a fragment, a run on and a comma splice is. Practice writing one sentence of each type. Check your sentences with your teacher. ...
Commas in Compound Sentences, Dependent Clauses, and
... independent clauses are joined together with a coordinating conjunction. Remember, an independent clause is a group of words that can stand alone; in other words, it is a complete sentence. A coordinating conjunction connects equal things. There are seven coordinating conjunctions – and, but, or, fo ...
... independent clauses are joined together with a coordinating conjunction. Remember, an independent clause is a group of words that can stand alone; in other words, it is a complete sentence. A coordinating conjunction connects equal things. There are seven coordinating conjunctions – and, but, or, fo ...
Name Class - d-11 teacher pages
... This creates a _____________ sentence. The first part will be occasion (reason for writing) and the second part will be the position (what you plan to prove or explain.) Other conjunctive adverbs that can be used in this way include the following: ...
... This creates a _____________ sentence. The first part will be occasion (reason for writing) and the second part will be the position (what you plan to prove or explain.) Other conjunctive adverbs that can be used in this way include the following: ...
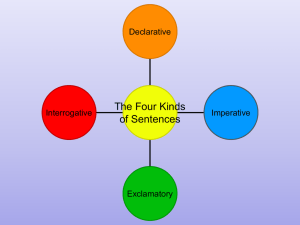
Declarative sentences - Mrs. Paulson`s Class
... Exclamatory Sentence. An exclamatory sentence expresses strong feelings. It ends with an exclamation point. Get out there, and walk the dog! Coming back to this sentence, we notice that it is an imperative sentence that expresses strong feelings . ...
... Exclamatory Sentence. An exclamatory sentence expresses strong feelings. It ends with an exclamation point. Get out there, and walk the dog! Coming back to this sentence, we notice that it is an imperative sentence that expresses strong feelings . ...
Introduction to Rhetorical Analysis AP English
... and see tears welling up in her eyes when she is told that Funtown is closed to colored children, and see ominous clouds of inferiority beginning to form in her little mental sky, and see her beginning to distort her personality by developing an unconscious bitterness toward white people; when you h ...
... and see tears welling up in her eyes when she is told that Funtown is closed to colored children, and see ominous clouds of inferiority beginning to form in her little mental sky, and see her beginning to distort her personality by developing an unconscious bitterness toward white people; when you h ...
TRANSFORMATIONAL- GENERATIVE SYNTAX AND THE TEACHING OF SENTENCE MECHANICS
... tag-question, it is a sentence; if not, it's a fragment. 3 Worth emphasizing here is that students do not need to know how to formulate the TagFormation rule to realize this fact; neither is it necessary for instructors to introduce transformational-generative linguistics as background. Yet, if inst ...
... tag-question, it is a sentence; if not, it's a fragment. 3 Worth emphasizing here is that students do not need to know how to formulate the TagFormation rule to realize this fact; neither is it necessary for instructors to introduce transformational-generative linguistics as background. Yet, if inst ...
A Sentence
... Independent clause: Is a complete sentence and can stand alone. We send a confirmation e-mail for each online order. Dependent clause: Is not a complete sentence and cannot stand alone. It must be joined to an independent clause to make sense. When you call our customer service department, PP 3-18a ...
... Independent clause: Is a complete sentence and can stand alone. We send a confirmation e-mail for each online order. Dependent clause: Is not a complete sentence and cannot stand alone. It must be joined to an independent clause to make sense. When you call our customer service department, PP 3-18a ...
Syntax
... Deep and surface structure Our intuitions tell us that there must be some underlying similarity involving these two superficially different sentences: Charlie broke the window and The window was broken by Charlie. In traditional grammar, the first is called an active sentence, focusing on what Charl ...
... Deep and surface structure Our intuitions tell us that there must be some underlying similarity involving these two superficially different sentences: Charlie broke the window and The window was broken by Charlie. In traditional grammar, the first is called an active sentence, focusing on what Charl ...
QuickGuidetoCommas
... 12. Don't use a comma to separate the subject from the verb. Incorrect: An eighteen-year old in California, is now considered an adult. 13. Don't put a comma between the two verbs or verb phrases in a compound predicate. Incorrect: I turned the corner, and ran smack into a patrol car. 14. Don't put ...
... 12. Don't use a comma to separate the subject from the verb. Incorrect: An eighteen-year old in California, is now considered an adult. 13. Don't put a comma between the two verbs or verb phrases in a compound predicate. Incorrect: I turned the corner, and ran smack into a patrol car. 14. Don't put ...
Grammar Notes - Mrs. Freeman
... or indirect object of a verb or as the object of a preposition. • Examples: • Whom did you ask? (direct object) • From whom did you get the information? (object of a preposition) ...
... or indirect object of a verb or as the object of a preposition. • Examples: • Whom did you ask? (direct object) • From whom did you get the information? (object of a preposition) ...
Slide 1 - Amy Benjamin
... drafting stages, the writer may develop a new conception of where the whole piece wants to go. Organization: The writer may rearrange sentences or paragraphs. The writer will probably want to add transitions: in and out of paragraphs and from sentence to sentence within paragraphs Language: The writ ...
... drafting stages, the writer may develop a new conception of where the whole piece wants to go. Organization: The writer may rearrange sentences or paragraphs. The writer will probably want to add transitions: in and out of paragraphs and from sentence to sentence within paragraphs Language: The writ ...
2002.finalbbookclas
... “See also” is used for an additional source which supports the proposition and where the sources which directly state or support the proposition have already been discussed. A parenthetical should explain the relevance of the source. ...
... “See also” is used for an additional source which supports the proposition and where the sources which directly state or support the proposition have already been discussed. A parenthetical should explain the relevance of the source. ...
Handout II
... is held to be, not about a and b directly, but rather about the terms ‘a’ and ‘b’. In other words it is equivalent to: ‘a’ and ‘b’ co-refer in which ‘a’ and ‘b’ are mentioned and not used. Frege now rejects this account since it would have the consequence that an identity sentence would express ‘no ...
... is held to be, not about a and b directly, but rather about the terms ‘a’ and ‘b’. In other words it is equivalent to: ‘a’ and ‘b’ co-refer in which ‘a’ and ‘b’ are mentioned and not used. Frege now rejects this account since it would have the consequence that an identity sentence would express ‘no ...
Honors English 7: Quarter One Exam
... If the verb is one of the 12 linking verbs that can also be used as action verbs, remember to test it by replacing it with “is” or “are.” If the sentence maintains its original meaning after the substitution, then you have a LINKING VERB. If the sentence no longer makes sense, then you have an ACTIO ...
... If the verb is one of the 12 linking verbs that can also be used as action verbs, remember to test it by replacing it with “is” or “are.” If the sentence maintains its original meaning after the substitution, then you have a LINKING VERB. If the sentence no longer makes sense, then you have an ACTIO ...
15 Tips to Improve Your Conventions and Sentence Fluency
... score on your use of sentences, you need to be able to properly combine different types of clauses in different ways. The two basic clauses you need to know how to use are independent clauses and dependent clauses. Independent Clauses o Independent clauses contain both a subject and a verb and do ...
... score on your use of sentences, you need to be able to properly combine different types of clauses in different ways. The two basic clauses you need to know how to use are independent clauses and dependent clauses. Independent Clauses o Independent clauses contain both a subject and a verb and do ...
English grammar basics
... potatoes disagree and burp.”, there are five conjunctions: the first and connects two subjects (milkman and fireman); the second and connects two direct objects (sausages and pancakes); the third and connects two subjects again (kangaroos and potatoes); and the fourth and connects two verbs (disagre ...
... potatoes disagree and burp.”, there are five conjunctions: the first and connects two subjects (milkman and fireman); the second and connects two direct objects (sausages and pancakes); the third and connects two subjects again (kangaroos and potatoes); and the fourth and connects two verbs (disagre ...
Academic writing: sentence level
... it would be a major breakthrough in the world of biochemistry. ...
... it would be a major breakthrough in the world of biochemistry. ...
Grammar Notes by XX
... Likelihood of snowing today is low. 15 one of NOUN (this noun will always be plural) + PLURAL VERB 16 Great usually describes nouns which express feelings or qualities. e.g. great admiration, great anger, in great detail Large is often used with nouns concerning numbers and measurements. It is not u ...
... Likelihood of snowing today is low. 15 one of NOUN (this noun will always be plural) + PLURAL VERB 16 Great usually describes nouns which express feelings or qualities. e.g. great admiration, great anger, in great detail Large is often used with nouns concerning numbers and measurements. It is not u ...
They give it to you.
... The reason for changing "le lo" to "se lo" is merely to avoid the tongue-twisting effect of two short consecutive words that begin with the letter "l". To demonstrate this, first quickly say "les las" and then quickly say "se las." See how much easier it is to say "se las?" ...
... The reason for changing "le lo" to "se lo" is merely to avoid the tongue-twisting effect of two short consecutive words that begin with the letter "l". To demonstrate this, first quickly say "les las" and then quickly say "se las." See how much easier it is to say "se las?" ...
Sentences PPT Student Version
... subject and verb that CAN’T BE ALONE (or else it’s a fragment). __________________– a group of words with a subject and verb that CAN BE ALONE. (It could be a complete sentence) ...
... subject and verb that CAN’T BE ALONE (or else it’s a fragment). __________________– a group of words with a subject and verb that CAN BE ALONE. (It could be a complete sentence) ...