Hearing Part 2
... • Involved in understanding speech, ie recognizing temporal organization of sound • Wernicke’s area in secondary cortex when damaged patients cannot understand speech because the sounds are all out of order ...
... • Involved in understanding speech, ie recognizing temporal organization of sound • Wernicke’s area in secondary cortex when damaged patients cannot understand speech because the sounds are all out of order ...
Chapter 5: sensation PAGE 1 Table 1: Sensing the World: Some
... Bottom-up processing: analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain’s integration of sensory information Top-down processing: information processing guided by higher level mental processes, as when we construct perceptions drawing on our experience and expectations Psychoph ...
... Bottom-up processing: analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain’s integration of sensory information Top-down processing: information processing guided by higher level mental processes, as when we construct perceptions drawing on our experience and expectations Psychoph ...
Unit 4 Sensation
... Place Theory: Theory that the pitch we hear is associated with the place where the basilar membrane is stimulated. Best for explaining high-pitched tones. Frequency Theory: Theory that the rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of the tone we are hearing. Best f ...
... Place Theory: Theory that the pitch we hear is associated with the place where the basilar membrane is stimulated. Best for explaining high-pitched tones. Frequency Theory: Theory that the rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of the tone we are hearing. Best f ...
Psychophysics ppt. - Ms. Engel @ South
... rate in neurons with which these cells form synapses and so on until the information reaches the brain • Sensory experience: see color, taste bitter, hear low tone ...
... rate in neurons with which these cells form synapses and so on until the information reaches the brain • Sensory experience: see color, taste bitter, hear low tone ...
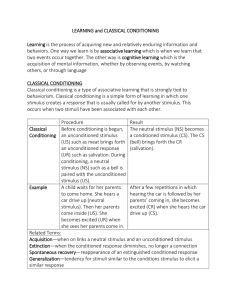
LEARNING and Classical Conditioning
... two events occur together. The other way is cognitive learning which is the acquisition of mental information, whether by observing events, by watching others, or through language CLASSICAL CONDITIONING Classical conditioning is a type of associative learning that is strongly tied to behaviorism. Cl ...
... two events occur together. The other way is cognitive learning which is the acquisition of mental information, whether by observing events, by watching others, or through language CLASSICAL CONDITIONING Classical conditioning is a type of associative learning that is strongly tied to behaviorism. Cl ...
SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY
... • an ampulla is located at the base of each canal - contains hair cells that depolarize or hyperpolarize depending on direction of movement of the fluid (endolymph) above it ...
... • an ampulla is located at the base of each canal - contains hair cells that depolarize or hyperpolarize depending on direction of movement of the fluid (endolymph) above it ...
The Senses
... Receptor cells of the inner ear sense pressure waves created by sound waves. Sound waves are mechanical energy resulting from the vibration of an object, which causes compression and decompression waves in air, water, or solid materials Sound reception in organisms other than humans o Many anima ...
... Receptor cells of the inner ear sense pressure waves created by sound waves. Sound waves are mechanical energy resulting from the vibration of an object, which causes compression and decompression waves in air, water, or solid materials Sound reception in organisms other than humans o Many anima ...
Chapter 12: Sound Localization and the Auditory Scene
... Auditory stimuli tend to group together by similarity. This includes: 1. Location - a single sound source tends to come from one location and to move continuously 2. Proximity in time - sounds that occur in rapid succession usually come from the same source – This principle was illustrated in audito ...
... Auditory stimuli tend to group together by similarity. This includes: 1. Location - a single sound source tends to come from one location and to move continuously 2. Proximity in time - sounds that occur in rapid succession usually come from the same source – This principle was illustrated in audito ...
Psychology Unit Four
... hearing music by Mozart. If he were to have the same response to any classical music, it would be called A. B. C. D. ...
... hearing music by Mozart. If he were to have the same response to any classical music, it would be called A. B. C. D. ...
MS Word - GEOCITIES.ws
... Name and describe the accessory structures of the ear. (see Auditory Accessory Structures) Describe the roles of the cochlea, basilar membrane, hair cells, and auditory nerve in the process of auditory transduction. Describe how information is relayed to the primary auditory cortex, how the c ...
... Name and describe the accessory structures of the ear. (see Auditory Accessory Structures) Describe the roles of the cochlea, basilar membrane, hair cells, and auditory nerve in the process of auditory transduction. Describe how information is relayed to the primary auditory cortex, how the c ...
Nerve cord
... “Nerve net”: Simplest nervous system are a netlike arrangement of neurons throughout the body “Nerve cord”: Most complex have a nerve cord and a brain ...
... “Nerve net”: Simplest nervous system are a netlike arrangement of neurons throughout the body “Nerve cord”: Most complex have a nerve cord and a brain ...
Cortical Representation
... • Selective response to particular patterns in auditory spectrogram – It is hypothesized that these neurons pick up “features” used in sound recognition ...
... • Selective response to particular patterns in auditory spectrogram – It is hypothesized that these neurons pick up “features” used in sound recognition ...
Chapter1 (new window)
... – Method of constant stimuli • Five to nine stimuli of different intensities are presented in random order • Multiple trials are presented • Threshold is the intensity that results in detection in 50% of trials. ...
... – Method of constant stimuli • Five to nine stimuli of different intensities are presented in random order • Multiple trials are presented • Threshold is the intensity that results in detection in 50% of trials. ...
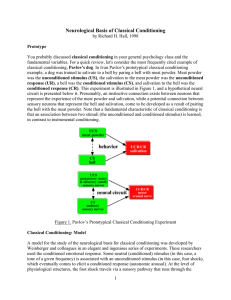
Neurological Basis of Classical Conditioning
... colleagues began by establishing the tonotopic frequency of a set of neurons within the auditory system, in particular the auditory cortex. Many cells in the auditory system are "tuned" to a given frequency, that is, they fire at a maximum rate to a certain pitch or tone. (In terms of sound waves, t ...
... colleagues began by establishing the tonotopic frequency of a set of neurons within the auditory system, in particular the auditory cortex. Many cells in the auditory system are "tuned" to a given frequency, that is, they fire at a maximum rate to a certain pitch or tone. (In terms of sound waves, t ...
The peripheral auditory system
... loud sinusoids (140dB) at low frequencies in recently deceased humans using stroboscopic illumination • Bekesy found a relative bandwidth of 0.6 – e.g., 600 Hz 10dB bandwidth when CF is 1000 Hz – Too high to account for sharp frequency resolution of ear and auditory neurons! ...
... loud sinusoids (140dB) at low frequencies in recently deceased humans using stroboscopic illumination • Bekesy found a relative bandwidth of 0.6 – e.g., 600 Hz 10dB bandwidth when CF is 1000 Hz – Too high to account for sharp frequency resolution of ear and auditory neurons! ...
Chapter 7
... The current theory of pitch perception uses a combination of the previous theories: • From 20 Hz to 400 Hz, frequency theory accounts for pitch perception (the firing rate of individual neurons in the auditory nerve directly matches the frequency of the sound). • From 400 Hz to 4 kHz, volley princip ...
... The current theory of pitch perception uses a combination of the previous theories: • From 20 Hz to 400 Hz, frequency theory accounts for pitch perception (the firing rate of individual neurons in the auditory nerve directly matches the frequency of the sound). • From 400 Hz to 4 kHz, volley princip ...
chapter 4 note sheet
... Optical Illusions - discrepancy between visual appearance and physical reality Famous optical illusions: Muller-Lyer Illusion, Ponzo Illusion, Poggendorf Illusion, Upside-Down T Illusion, Zollner Illusion, the Ames Room, and Impossible Figures Cultural differences: Perceptual hypotheses at work Hear ...
... Optical Illusions - discrepancy between visual appearance and physical reality Famous optical illusions: Muller-Lyer Illusion, Ponzo Illusion, Poggendorf Illusion, Upside-Down T Illusion, Zollner Illusion, the Ames Room, and Impossible Figures Cultural differences: Perceptual hypotheses at work Hear ...
Paper: A differentially amplified motion in the ear for near
... had different frequency dependence and a different timing from the commonly measured vibrations of the basilar membrane. However, the full resolution of this conundrum will probably require the development of new experimental techniques that can directly test the potential mechanisms mentioned above ...
... had different frequency dependence and a different timing from the commonly measured vibrations of the basilar membrane. However, the full resolution of this conundrum will probably require the development of new experimental techniques that can directly test the potential mechanisms mentioned above ...
Chapter 5: SENSATION - Charles Best Library
... rays by changing its curvature, a process called accommodation, on the retina. ...
... rays by changing its curvature, a process called accommodation, on the retina. ...
Unit 4 Tissues Pink notes
... a special type of simple, secretion and movement of mucus: nasal cavity, sinuses ...
... a special type of simple, secretion and movement of mucus: nasal cavity, sinuses ...