Animal Evolution
... I. To be on the Animal family tree A. must be multicellular B. must be heterotrophs ...
... I. To be on the Animal family tree A. must be multicellular B. must be heterotrophs ...
Introduction to Kingdom Animalia
... A. Parazoa ("beside the animal") animals that lack true tissues. e.g., Sponges B. Eumetazoa - animals with well defined tissue layers, e.g., essentially all other animals. ...
... A. Parazoa ("beside the animal") animals that lack true tissues. e.g., Sponges B. Eumetazoa - animals with well defined tissue layers, e.g., essentially all other animals. ...
Veterinary Compounding
... canines. Although the spelling is different, the name sounds similar to enalapril used in humans. ...
... canines. Although the spelling is different, the name sounds similar to enalapril used in humans. ...
Subject: Honors Biology – Content Map
... How are animals organized? How are human body systems’ structure related to function? How do organ systems work together to help animals maintain homeostasis and perform daily activities? Concept: Tissues & Organ systems 3.1.12.A5 – Analyze how structure is related to function at all levels of biolo ...
... How are animals organized? How are human body systems’ structure related to function? How do organ systems work together to help animals maintain homeostasis and perform daily activities? Concept: Tissues & Organ systems 3.1.12.A5 – Analyze how structure is related to function at all levels of biolo ...
honors biology ch. 18 notes “the evolution of invertebrate diversity”
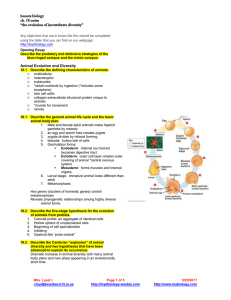
... Branch #1: no true tissues/true tissues Branch #2: Cnidarians/Eumetazoans Different: Morphological Branch #3: Deuterostomes / Protostomes o Annelids and Arthropods are shown more closely related to each other than to mollusks due to their segmented bodies Branch #3: Molecular Deuterostomes Lop ...
... Branch #1: no true tissues/true tissues Branch #2: Cnidarians/Eumetazoans Different: Morphological Branch #3: Deuterostomes / Protostomes o Annelids and Arthropods are shown more closely related to each other than to mollusks due to their segmented bodies Branch #3: Molecular Deuterostomes Lop ...
Introduction to Animals - St. Thomas the Apostle School
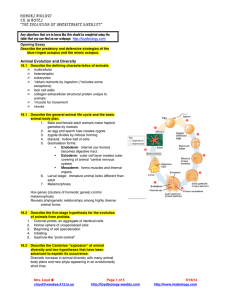
... • Protective coverings such as shells or quills help protect animals from predators. • Large size protects some animals. • Mimicry or camouflage helps other animals blend into the environment or confuse predators. ...
... • Protective coverings such as shells or quills help protect animals from predators. • Large size protects some animals. • Mimicry or camouflage helps other animals blend into the environment or confuse predators. ...
Animal Evolution and Diversity - Mrs. Loyd`s Biology
... o Annelids and Arthropods are shown more closely related to each other than to mollusks due to their segmented bodies Branch #3: Molecular ✍ Deuterostomes ✍ Lophotrochozoans ✍ Ecdysozoans o Arthropods are separated from both annelids and mollusks and are placed in the ecdysozoan clade. 18.16 Explain ...
... o Annelids and Arthropods are shown more closely related to each other than to mollusks due to their segmented bodies Branch #3: Molecular ✍ Deuterostomes ✍ Lophotrochozoans ✍ Ecdysozoans o Arthropods are separated from both annelids and mollusks and are placed in the ecdysozoan clade. 18.16 Explain ...
Biology Vocabulary 18, test on Friday, 3/6/15
... in free-living flatworms, the tubelike muscular organ that can extend out of their mouth and such food particles into the digestive tract tube-shaped, sessile body form of cnidarians away from the head end of an animal with bilateral symmetry body plan that can be divided along any plane, through a ...
... in free-living flatworms, the tubelike muscular organ that can extend out of their mouth and such food particles into the digestive tract tube-shaped, sessile body form of cnidarians away from the head end of an animal with bilateral symmetry body plan that can be divided along any plane, through a ...
ANIMAL KINGDOM
... tadpole legs & tails, sea star arms), & a small piece of an organism can become a complete new organism (flatworms). c) Most sexually reproducing animals have separate male & female adults (jellyfish, insects, clams, spiders, fish, amphibians, reptiles, & mammals). d) Hermaphrodites (earthworm) prod ...
... tadpole legs & tails, sea star arms), & a small piece of an organism can become a complete new organism (flatworms). c) Most sexually reproducing animals have separate male & female adults (jellyfish, insects, clams, spiders, fish, amphibians, reptiles, & mammals). d) Hermaphrodites (earthworm) prod ...
IB 201: LABORATORY SESSION 13: ANIMAL DIVERSITY
... Animals are by far the most diverse group of living organisms in terms of described species with well over one million species that have been named by scientists. Animal diversity is very well known relative to most other groups of organisms. There are two reasons for this. Human beings are animals ...
... Animals are by far the most diverse group of living organisms in terms of described species with well over one million species that have been named by scientists. Animal diversity is very well known relative to most other groups of organisms. There are two reasons for this. Human beings are animals ...
Invertebrate Notes
... All animals share a unique set of derived characters Animal cells are supported by __________________________. 1. three-stranded protein found in _____________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 2. Most animals have _______________________ Homeotic g ...
... All animals share a unique set of derived characters Animal cells are supported by __________________________. 1. three-stranded protein found in _____________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 2. Most animals have _______________________ Homeotic g ...
Invertebrate Power Point Sponges to Earthworms File
... 3. Most are capable of movement at some point in their lifecycle 4. Cells are organized into tissues 5. Some animals have organs and organ systems ...
... 3. Most are capable of movement at some point in their lifecycle 4. Cells are organized into tissues 5. Some animals have organs and organ systems ...
Zoology - Edublogs
... Many aquatic animals (ex: aquatic worms) rely solely on diffusion to transport oxygen & waste. ...
... Many aquatic animals (ex: aquatic worms) rely solely on diffusion to transport oxygen & waste. ...
Ch32 PowerPoint LN
... d. Types of animals fossilized: cnidarians (hydra-like) and soft-bodied mollusks ...
... d. Types of animals fossilized: cnidarians (hydra-like) and soft-bodied mollusks ...
C-LAS.4 Diseases of Laboratory Animals
... Understand diagnostic methods and appreciate their limitations. ...
... Understand diagnostic methods and appreciate their limitations. ...
kingdom animalia
... After the blastula stage, in some animals cells migrate to the interior forming the primitive gut In Protostomes the initial pore forms the mouth, while in the Deuterostomes this pore forms the anus ...
... After the blastula stage, in some animals cells migrate to the interior forming the primitive gut In Protostomes the initial pore forms the mouth, while in the Deuterostomes this pore forms the anus ...
Animals…
... Bilateral animals have… • An anterior end – usually a head with sensory organs • A posterior end – sometimes with a tail • A dorsal surface – upper or back side • A ventral surface – lower or front side ...
... Bilateral animals have… • An anterior end – usually a head with sensory organs • A posterior end – sometimes with a tail • A dorsal surface – upper or back side • A ventral surface – lower or front side ...
Animals with a body cavity lying between the digestive tract and
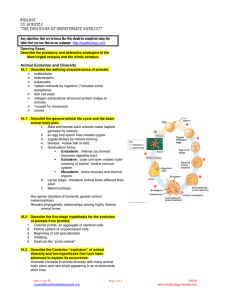
... Body Cavities • A coelom (lined with peritoneum) is a space between the gut and body wall that allows internal organs to expand and operate freely. A peritoneum is a smooth transparent membrane that lines the abdomen and doubles back over the surfaces of the internal organs to form a continuous sac ...
... Body Cavities • A coelom (lined with peritoneum) is a space between the gut and body wall that allows internal organs to expand and operate freely. A peritoneum is a smooth transparent membrane that lines the abdomen and doubles back over the surfaces of the internal organs to form a continuous sac ...
Ch. 32 An Introduction to Animal Diversity
... some undergo metamorphosis (stage that transforms animal into adult) f. Have Hox genes containing homeoboxes of DNA sequences genes that regulate expression of other genes # of Hox genes is related to complexity of anatomy believed to have evolved from colonial flagellated protist that lived 7 ...
... some undergo metamorphosis (stage that transforms animal into adult) f. Have Hox genes containing homeoboxes of DNA sequences genes that regulate expression of other genes # of Hox genes is related to complexity of anatomy believed to have evolved from colonial flagellated protist that lived 7 ...
What is an animal?
... Animals must digest their food - in some animals it is done within cells, in other animals it is done in an internal cavity ...
... Animals must digest their food - in some animals it is done within cells, in other animals it is done in an internal cavity ...
biology ch. 18 notes “the evolution of invertebrate diversity”
... o Annelids and Arthropods are shown more closely related to each other than to mollusks due to their segmented bodies Branch #3: Molecular ✍ Deuterostomes ✍ Lophotrochozoans ✍ Ecdysozoans o Arthropods are separated from both annelids and mollusks and are placed in the ecdysozoan clade. 18.16 Explain ...
... o Annelids and Arthropods are shown more closely related to each other than to mollusks due to their segmented bodies Branch #3: Molecular ✍ Deuterostomes ✍ Lophotrochozoans ✍ Ecdysozoans o Arthropods are separated from both annelids and mollusks and are placed in the ecdysozoan clade. 18.16 Explain ...
Name
... Created by Ms Foglia, adapted by Ms Rhodes, with text from Campbell and Reece Biology CHAPTER 33: Invertebrates This chapter surveys the amazing diversity of invertebrate animals. Characteristics and representatives of the major animal phyla are presented. The groups covered are the sponges, cnidari ...
... Created by Ms Foglia, adapted by Ms Rhodes, with text from Campbell and Reece Biology CHAPTER 33: Invertebrates This chapter surveys the amazing diversity of invertebrate animals. Characteristics and representatives of the major animal phyla are presented. The groups covered are the sponges, cnidari ...
Protist- Fungusdd49
... Scientists have found and described approximately 1.75 million species on Earth. New species are being discovered every day. ...
... Scientists have found and described approximately 1.75 million species on Earth. New species are being discovered every day. ...
Animal cognition

Animal cognition describes the mental capacities of animals and its study. It has developed out of comparative psychology, including the study of animal conditioning and learning, but has also been strongly influenced by research in ethology, behavioral ecology, and evolutionary psychology. The alternative name cognitive ethology is therefore sometimes used; much of what used to be considered under the title of animal intelligence is now thought of under this heading.Research has examined animal cognition in mammals (especially primates, cetaceans, elephants, dogs, cats, horses, livestock, raccoons and rodents), birds (including parrots, corvids and pigeons), reptiles (lizards and snakes), fish and invertebrates (including cephalopods, spiders and insects).