Introduction to Transit (and Secondary Eclipse) Spectroscopy
... between two stellar spectra with different effective temperatures. For HD 189733, spot is ~500 K cooler than photosphere. ...
... between two stellar spectra with different effective temperatures. For HD 189733, spot is ~500 K cooler than photosphere. ...
August Evening Skies
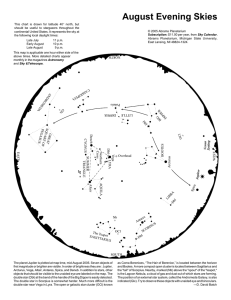
... The double star in Scorpius is somewhat harder. Much more difficult is the double star near Vega in Lyra. The open or galactic star cluster (OCl) known ...
... The double star in Scorpius is somewhat harder. Much more difficult is the double star near Vega in Lyra. The open or galactic star cluster (OCl) known ...
Determining Abundances
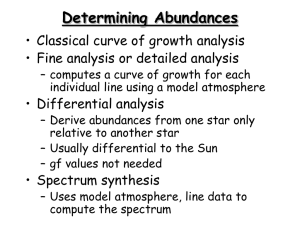
... • Derive an abundance from each line measured using fine analysis • Determine the dependence of the derived abundances on – Excitation potential – adjust temperature – Line strength – adjust microturbulence – Ionization state – adjust surface gravity ...
... • Derive an abundance from each line measured using fine analysis • Determine the dependence of the derived abundances on – Excitation potential – adjust temperature – Line strength – adjust microturbulence – Ionization state – adjust surface gravity ...
STAAR Science Tutorial 34 TEK 8.8A: Stars, Galaxies
... o Spiral galaxies have “arms” of stars that spiral outward from the center. The overall shape is round and flat like a plate, but the dense center of a spiral galaxy is spherical. Younger stars are more likely found in the arms of the spiral, and older stars are most likely found in the center sphe ...
... o Spiral galaxies have “arms” of stars that spiral outward from the center. The overall shape is round and flat like a plate, but the dense center of a spiral galaxy is spherical. Younger stars are more likely found in the arms of the spiral, and older stars are most likely found in the center sphe ...
STAAR Science Tutorial 28 TEK 8.8A: Stars
... o Spiral galaxies have “arms” of stars that spiral outward from the center. The overall shape is round and flat like a plate, but the dense center of a spiral galaxy is spherical. Younger stars are more likely found in the arms of the spiral, and older stars are most likely found in the center sphe ...
... o Spiral galaxies have “arms” of stars that spiral outward from the center. The overall shape is round and flat like a plate, but the dense center of a spiral galaxy is spherical. Younger stars are more likely found in the arms of the spiral, and older stars are most likely found in the center sphe ...
Astro 10-Lecture 5: Heat, Light and the Structure of Atoms
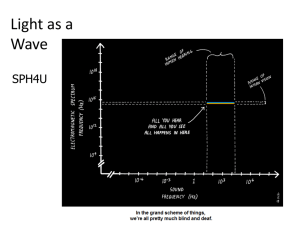
... – ROY G. BIV (red orange yellow green blue indigo violet in order low energy to high) – Wavelengths from 0.0004 millimeters to 0.0007 millimeters. Usually use nm (10-9 m or Å 10-10 m) ...
... – ROY G. BIV (red orange yellow green blue indigo violet in order low energy to high) – Wavelengths from 0.0004 millimeters to 0.0007 millimeters. Usually use nm (10-9 m or Å 10-10 m) ...
Prelab notes
... • Wave model for light was originally accepted by scientific community. • This couldn’t explain why metals heating first emitted invisible radiation and then visible radiation. ...
... • Wave model for light was originally accepted by scientific community. • This couldn’t explain why metals heating first emitted invisible radiation and then visible radiation. ...
Electron Configuration
... • Wave model for light was originally accepted by scientific community. • This couldn’t explain why metals heating first emitted invisible radiation and then visible radiation. ...
... • Wave model for light was originally accepted by scientific community. • This couldn’t explain why metals heating first emitted invisible radiation and then visible radiation. ...
21. The Milky Way Galaxy
... Also, squeezing of clouds initiates collapse within them => star formation. Bright young massive stars live and die in spiral arms. Emission nebulae mostly in spiral arms. So arms always contain same types of objects, but individual objects come and go. ...
... Also, squeezing of clouds initiates collapse within them => star formation. Bright young massive stars live and die in spiral arms. Emission nebulae mostly in spiral arms. So arms always contain same types of objects, but individual objects come and go. ...
nλ = dsinθ
... the photons associated with these spectral lines. You should also draw an energy level diagram to show which energy levels of the hydrogen atom are related to the emission of these lines. The experimental procedure for determining the diffraction angles is the same as in part 1. From the observed hy ...
... the photons associated with these spectral lines. You should also draw an energy level diagram to show which energy levels of the hydrogen atom are related to the emission of these lines. The experimental procedure for determining the diffraction angles is the same as in part 1. From the observed hy ...
Hubble`s Law and the Expansion Rate of the Universe
... There may be more than one galaxy in the image; the galaxy of interest is always the one closest to the center. To measure the size, click on opposite ends of the galaxy, at either end of the longest diameter. Try to find the farthest extents of the galaxy. If you make an error, make sure to cli ...
... There may be more than one galaxy in the image; the galaxy of interest is always the one closest to the center. To measure the size, click on opposite ends of the galaxy, at either end of the longest diameter. Try to find the farthest extents of the galaxy. If you make an error, make sure to cli ...
01 - Awtrey Middle School
... 2. During which stage of the life cycle is a star a ball of gas and dust? a. first stage b. second stage c. third stage d. last stage 3. What gas does hydrogen change into as a star becomes hotter? a. uranium b. helium c. gravity d. carbon DIFFERENT TYPES OF STARS 4. Which of the following is NOT a ...
... 2. During which stage of the life cycle is a star a ball of gas and dust? a. first stage b. second stage c. third stage d. last stage 3. What gas does hydrogen change into as a star becomes hotter? a. uranium b. helium c. gravity d. carbon DIFFERENT TYPES OF STARS 4. Which of the following is NOT a ...
Quantum Theory of the Atom
... • Electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all energies emitted from photons acting like waves. • If it is not in the visible light range, it may be giving off other forms of electromagnetic radiation like radio, microwaves, infrared, ultra violet, x-rays, or gamma rays. • Used to determine which el ...
... • Electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all energies emitted from photons acting like waves. • If it is not in the visible light range, it may be giving off other forms of electromagnetic radiation like radio, microwaves, infrared, ultra violet, x-rays, or gamma rays. • Used to determine which el ...
W - Вернуться к содержанию сайта
... Herein we shall suggest a new, universal way of smooth conversion of the optical spectrum into any other range from gamma radiation to radio radiation. In optics spectral shift based on Doppler effect is known for a long time, which is transforming the wavelength of the light λ into λ'=λ(1+Vr/c), an ...
... Herein we shall suggest a new, universal way of smooth conversion of the optical spectrum into any other range from gamma radiation to radio radiation. In optics spectral shift based on Doppler effect is known for a long time, which is transforming the wavelength of the light λ into λ'=λ(1+Vr/c), an ...
300 MHz - 3 GHz Yes, we`re interested
... • Diffuse HI (cosmic web) - IGM-galaxy feedback poorly understood aspect of galaxy formation • Local HI mass function, probe low-mass end, in various environments HVC/dwarfs ...
... • Diffuse HI (cosmic web) - IGM-galaxy feedback poorly understood aspect of galaxy formation • Local HI mass function, probe low-mass end, in various environments HVC/dwarfs ...
astrophysics - Uplift Summit Intl
... What can we say about their relative sizes and temperatures? ...
... What can we say about their relative sizes and temperatures? ...
Scale of the universe Table 1
... Irregular galaxy 1039 - 1041 kg 108 - 1010 2 raisins (1 x 10-3 kg or 1 gram) ...
... Irregular galaxy 1039 - 1041 kg 108 - 1010 2 raisins (1 x 10-3 kg or 1 gram) ...
homework answers - SPHS Devil Physics
... 2. Objectives for Tsokos Lesson 6-5, Quantum Theory and The Uncertainty Principle a. Describe emission and absorption spectra and understand their significance for atomic structure b. Explain the origin of atomic energy levels in terms of the ‘electron in a box’ model c. Describe the hydrogen atom a ...
... 2. Objectives for Tsokos Lesson 6-5, Quantum Theory and The Uncertainty Principle a. Describe emission and absorption spectra and understand their significance for atomic structure b. Explain the origin of atomic energy levels in terms of the ‘electron in a box’ model c. Describe the hydrogen atom a ...
Slide 1
... By mid 20th century -- 3 models or theories Big Bang -- Father LeMaitre, George Gamow Oscillating Universe ...
... By mid 20th century -- 3 models or theories Big Bang -- Father LeMaitre, George Gamow Oscillating Universe ...
wdm_shanghai_Mayinzhe
... For m_X > 5keV, star formation efficiency is degenerated with WDM For low mass, the two are not degenerated. This is observable by the high-redshift measurement such as square kilometer array (2020). ...
... For m_X > 5keV, star formation efficiency is degenerated with WDM For low mass, the two are not degenerated. This is observable by the high-redshift measurement such as square kilometer array (2020). ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.