Lecture 16 - Yet More Evolution of Stars
... Core collapse • Iron core is degenerate • Core grows until it is too heavy to support itself • Core collapses, density increases, normal iron nuclei are converted into neutrons with the emission of neutrinos • Core collapse stops, neutron star is formed • Rest of the star collapses in on the core, ...
... Core collapse • Iron core is degenerate • Core grows until it is too heavy to support itself • Core collapses, density increases, normal iron nuclei are converted into neutrons with the emission of neutrinos • Core collapse stops, neutron star is formed • Rest of the star collapses in on the core, ...
The new europian project ROPACS (Rocky Planets Around …
... The star system gained attention after Gliese 581 c, the first low mass extrasolar planet found to be near its star's habitable zone, was discovered in April 2007. It has since been shown that under known terrestrial planet climate models, Gliese 581 c is likely to have a runaway greenhouse effect, ...
... The star system gained attention after Gliese 581 c, the first low mass extrasolar planet found to be near its star's habitable zone, was discovered in April 2007. It has since been shown that under known terrestrial planet climate models, Gliese 581 c is likely to have a runaway greenhouse effect, ...
Document
... o However, techniques used to measure stars beyond 400 light years away are based upon many non-verifiable assumptions, some of which are incompatible with the biblical doctrine of creation (for example, the normal "life cycle" of a star). Furthermore, as with geology, these techniques assume certa ...
... o However, techniques used to measure stars beyond 400 light years away are based upon many non-verifiable assumptions, some of which are incompatible with the biblical doctrine of creation (for example, the normal "life cycle" of a star). Furthermore, as with geology, these techniques assume certa ...
Basic Characteristics of Electromagnetic Radiation.
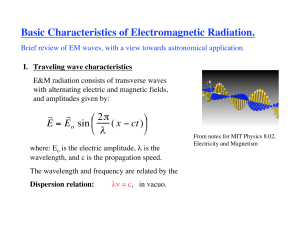
... e.g., double-slit (Young’s) pattern of interfering waves. ...
... e.g., double-slit (Young’s) pattern of interfering waves. ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • Dark Matter is dark at all wavelengths, not just visible light • The Universe as a whole consists of up to 25% of Dark ...
... • Dark Matter is dark at all wavelengths, not just visible light • The Universe as a whole consists of up to 25% of Dark ...
A-105 Homework 1
... 5. (1 pt.) How does the presence of degenerate matter in a star trigger the helium flash? ...
... 5. (1 pt.) How does the presence of degenerate matter in a star trigger the helium flash? ...
The Solar System Worksheet - Laureate International College
... Which two elements make up more than 98% of the Sun? Include their %. How are astronom ers able to estimate the Sun’s mass? What two effects does a coronal m ass ejection on the Sun have on Earth? Explain the following: (a) the process that astronomers believe created our solar system and other star ...
... Which two elements make up more than 98% of the Sun? Include their %. How are astronom ers able to estimate the Sun’s mass? What two effects does a coronal m ass ejection on the Sun have on Earth? Explain the following: (a) the process that astronomers believe created our solar system and other star ...
Supernovae - Cloudfront.net
... results can be explosive The more massive star will die first Its death will not be unlike the Sun’s though the other star will affect the form of the planetary nebula. Producing nebulae like the When the second becomes a red Rose Nebula giant it will trigger a type 1a super nova ...
... results can be explosive The more massive star will die first Its death will not be unlike the Sun’s though the other star will affect the form of the planetary nebula. Producing nebulae like the When the second becomes a red Rose Nebula giant it will trigger a type 1a super nova ...
Lecture 1: Nucleosynthesis, solar composition, chondrites, volatility
... eventually planets? 5) What evidence is available from meteorites? ...
... eventually planets? 5) What evidence is available from meteorites? ...
Which object is closest to Earth
... Stars can be classified according to their properties, such as diameter, mass, luminosity, and temperature. Some stars are so large that the orbits of the planets in our solar system would easily fit inside them. Stars are grouped together in galaxies covering vast distances. Galaxies contain from 1 ...
... Stars can be classified according to their properties, such as diameter, mass, luminosity, and temperature. Some stars are so large that the orbits of the planets in our solar system would easily fit inside them. Stars are grouped together in galaxies covering vast distances. Galaxies contain from 1 ...
Lecture 11 - University of Washington
... • Why there is an age spread of ∼ 3 Gyr among globular clusters (GCs)? We would expect < 1 Gyr spread (free-fall time). Some important questions that are left without robust answers: • Why GCs become more metal-poor with the distance from the center? • Detailed calculations of chemical enrichment pr ...
... • Why there is an age spread of ∼ 3 Gyr among globular clusters (GCs)? We would expect < 1 Gyr spread (free-fall time). Some important questions that are left without robust answers: • Why GCs become more metal-poor with the distance from the center? • Detailed calculations of chemical enrichment pr ...
Nata_Feb8 - University of Alberta
... NOTE: this defines intensity only for a non-point type object. The total luminosity L of a galaxy is difficult to define precisely for several reasons: – galaxies do not have well-defined edges, and the extended regions are faint and have a low luminosity gradient. – light from a distant galaxy is r ...
... NOTE: this defines intensity only for a non-point type object. The total luminosity L of a galaxy is difficult to define precisely for several reasons: – galaxies do not have well-defined edges, and the extended regions are faint and have a low luminosity gradient. – light from a distant galaxy is r ...
Light Years - Godley ISD
... 5. If a star located 65 light years away from Earth stops giving off light energy at this very moment, how long will it be before we can know it? Explain. ______________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ...
... 5. If a star located 65 light years away from Earth stops giving off light energy at this very moment, how long will it be before we can know it? Explain. ______________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ...
Lesson 2 | The Sun and Other Stars
... 2. sudden increases of brightness caused by violent eruptions on the Sun ...
... 2. sudden increases of brightness caused by violent eruptions on the Sun ...
ASTR101 Unit 10 Assessment Answer Key 1. Mass, luminosity, size
... 1. Mass, luminosity, size, surface temperature, and age. Ordinary stars range in mass from about 60 solar masses to about 1/12 solar mass, in luminosity from about 1,000,000 to 1/10,000 solar luminosities, in radius from about 1,000 to 1/10 solar radii, in surface temperature from about 35,000 to 3, ...
... 1. Mass, luminosity, size, surface temperature, and age. Ordinary stars range in mass from about 60 solar masses to about 1/12 solar mass, in luminosity from about 1,000,000 to 1/10,000 solar luminosities, in radius from about 1,000 to 1/10 solar radii, in surface temperature from about 35,000 to 3, ...
The Solar System
... – supernova remnants, expanding at 10,000 km/s – may trigger future star formation? – Neutron stars: mass star but just 10 km across. • Teaspoon weighs 100 million tons! • Seen as Pulsars, flashing beacons in space. ...
... – supernova remnants, expanding at 10,000 km/s – may trigger future star formation? – Neutron stars: mass star but just 10 km across. • Teaspoon weighs 100 million tons! • Seen as Pulsars, flashing beacons in space. ...
September Evening Skies
... stars are forming. The position of an external star system, called the Andromeda Galaxy after the constellation in which it appears, is also indicated (Glx). Try to observe these objects with unaided eye and binoculars. ...
... stars are forming. The position of an external star system, called the Andromeda Galaxy after the constellation in which it appears, is also indicated (Glx). Try to observe these objects with unaided eye and binoculars. ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.