Slide 1
... • Valid scientific model (testable, falsifiable) • Not in conflict with observations until Galileo (c. 1610) ...
... • Valid scientific model (testable, falsifiable) • Not in conflict with observations until Galileo (c. 1610) ...
A105 Stars and Galaxies
... The formation and evolution of these groups, which are very common in the Universe, are dominated by the gravitational pull of dark matter 4.3 Mpc or 14 million LY ...
... The formation and evolution of these groups, which are very common in the Universe, are dominated by the gravitational pull of dark matter 4.3 Mpc or 14 million LY ...
The Life Cycle of a Star
... collapse of a large red giant—heats and expels the star's outer layers, resulting in an explosion. • Also, they can form when a white dwarf ignites carbon fusion, which results in a runaway nuclear fusion reaction and causes a supernova. • Supernovae can be so immense that the energy produced can eq ...
... collapse of a large red giant—heats and expels the star's outer layers, resulting in an explosion. • Also, they can form when a white dwarf ignites carbon fusion, which results in a runaway nuclear fusion reaction and causes a supernova. • Supernovae can be so immense that the energy produced can eq ...
Mon Nov 18, 2013 THE MOON`S TIDAL LOCK The old gibbous
... Edwin Hubble on this date, November 20th, in 1889. Both these men made remarkable discoveries about our Universe. Shapley discovered that our sun and solar system were not at the center of the Milky Way Galaxy, but instead a little over halfway out, and that the Milky Way was much larger than anyone ...
... Edwin Hubble on this date, November 20th, in 1889. Both these men made remarkable discoveries about our Universe. Shapley discovered that our sun and solar system were not at the center of the Milky Way Galaxy, but instead a little over halfway out, and that the Milky Way was much larger than anyone ...
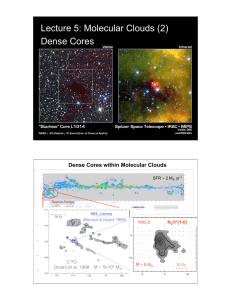
Lecture 5: Molecular Clouds (2) Dense Cores
... • Molecular lines (CO, CS, NH3, etc): different molecular lines trace conditions of different densities and temperatures (see next lecture). Also, some molecules may become frozen-out onto the surface of dust grains to form ice mantles. • sub-mm and mm dust thermal emission (Wien’s law) i.e. modifie ...
... • Molecular lines (CO, CS, NH3, etc): different molecular lines trace conditions of different densities and temperatures (see next lecture). Also, some molecules may become frozen-out onto the surface of dust grains to form ice mantles. • sub-mm and mm dust thermal emission (Wien’s law) i.e. modifie ...
Aust Curriculum Connections 2012
... such as Edwin Hubble’s observations and the detection of microwave radiation ...
... such as Edwin Hubble’s observations and the detection of microwave radiation ...
1) The following questions refer to the HR diagram
... D) they are the end-products of small, low-mass stars. E) they are the opposite of black holes. 22) What happens to the surface temperature and luminosity when a protostar radiatively contracts? A) Its surface temperature remains the same and its luminosity decreases. B) Its surface temperature and ...
... D) they are the end-products of small, low-mass stars. E) they are the opposite of black holes. 22) What happens to the surface temperature and luminosity when a protostar radiatively contracts? A) Its surface temperature remains the same and its luminosity decreases. B) Its surface temperature and ...
Week 1b_2015
... Carbonaceous chondrites are believed to represent the initial composition of the material from which the Sun and the planets formed. They contain minerals that are unstable above 100 °C. ...
... Carbonaceous chondrites are believed to represent the initial composition of the material from which the Sun and the planets formed. They contain minerals that are unstable above 100 °C. ...
Basic data of CoRoT-Exo-2b - tls
... ground based observations detect only 10% of the hot Jupiters that are in principle within reach. This is an effect of the red noise and very often also the day/night gaps of ground based observations. How do we determine the spectral types of 1000nds of stars? ...
... ground based observations detect only 10% of the hot Jupiters that are in principle within reach. This is an effect of the red noise and very often also the day/night gaps of ground based observations. How do we determine the spectral types of 1000nds of stars? ...
BROCK UNIVERSITY Return both the exam script
... (d) the Earth has greater mass, and therefore greater surface gravity. 20. The Sun (a) is much like other average stars. (b) is much larger and hotter than other average stars. (c) is much smaller and cooler than other average stars. (d) is not a star. ...
... (d) the Earth has greater mass, and therefore greater surface gravity. 20. The Sun (a) is much like other average stars. (b) is much larger and hotter than other average stars. (c) is much smaller and cooler than other average stars. (d) is not a star. ...
GOFER Module: Google Sky Please open Google Earth, then
... These two constellations lie in the direction of the center of our Milky Way galaxy. Begin to zoom in. What indirectly indicates we are gazing towards our galaxy’s center? A. There are many more stars, nebulas, and star clusters here than in other directions. B. Sagittarius and Scorpius are the larg ...
... These two constellations lie in the direction of the center of our Milky Way galaxy. Begin to zoom in. What indirectly indicates we are gazing towards our galaxy’s center? A. There are many more stars, nebulas, and star clusters here than in other directions. B. Sagittarius and Scorpius are the larg ...
Acting Out the Life Cycle of Stars - University of Texas Astronomy
... shoulder of Orion, Betelgeuse, is a red giant. e. For stars that are less than about 8 times the mass of the Sun, the envelope of the red giant will gradually float away into space (float away envelope students) as the core contracts (get cozy core students). The floating away gas that used to be th ...
... shoulder of Orion, Betelgeuse, is a red giant. e. For stars that are less than about 8 times the mass of the Sun, the envelope of the red giant will gradually float away into space (float away envelope students) as the core contracts (get cozy core students). The floating away gas that used to be th ...
March 2011
... area of sky about the same size as the full Moon. Using a pair of 10 x 50 binoculars another thirty or so fainter stars can be seen embedded within the Seven Sisters. A telescope will enable many more to be counted up to around 300 in total. Most telescopes will however have a field of view too smal ...
... area of sky about the same size as the full Moon. Using a pair of 10 x 50 binoculars another thirty or so fainter stars can be seen embedded within the Seven Sisters. A telescope will enable many more to be counted up to around 300 in total. Most telescopes will however have a field of view too smal ...
A Massive Molecular Gas Reservoir in the z= 5.3 Submillimeter
... We report the detection of CO J=2→1, 5→4, and 6→5 emission in the highest-redshift submillimeter galaxy (SMG) AzTEC-3 at z=5.298, using the Expanded Very Large Array and the Plateau de Bure Interferometer. These observations ultimately confirm the redshift, making AzTEC-3 the most submillimeter-lumi ...
... We report the detection of CO J=2→1, 5→4, and 6→5 emission in the highest-redshift submillimeter galaxy (SMG) AzTEC-3 at z=5.298, using the Expanded Very Large Array and the Plateau de Bure Interferometer. These observations ultimately confirm the redshift, making AzTEC-3 the most submillimeter-lumi ...
Earth and Space Review 2016
... Name_____________________________ Period ____ Due Date__________ Test Date___________ Electromagnetic Spectrum (EMS) 29. Using the electromagnetic spectrum, which waves have the shortest wavelength? ________________ Which ones have the longest wavelength? ________________ ...
... Name_____________________________ Period ____ Due Date__________ Test Date___________ Electromagnetic Spectrum (EMS) 29. Using the electromagnetic spectrum, which waves have the shortest wavelength? ________________ Which ones have the longest wavelength? ________________ ...
RED “O Big Red
... (all-deB-er-on) was one of the brightest stars in earth’s sky. soon the Stella was bathed in red light. “this star is enormous!” manolo shouted. “it’s 44 times wider than the sun, but its temperature is much cooler. how does such a cool star shine so brightly?” Captain Gamma turned off the cabin lig ...
... (all-deB-er-on) was one of the brightest stars in earth’s sky. soon the Stella was bathed in red light. “this star is enormous!” manolo shouted. “it’s 44 times wider than the sun, but its temperature is much cooler. how does such a cool star shine so brightly?” Captain Gamma turned off the cabin lig ...
Formation of the Universe
... contracts a huge explosion occurs. Depending on the size of the star, this explosion is called a nova or supernova. These explosions are so large that they outshine their entire galaxy. Most of these large stars become neutron stars, which are made of incredibly dense material and continue to give o ...
... contracts a huge explosion occurs. Depending on the size of the star, this explosion is called a nova or supernova. These explosions are so large that they outshine their entire galaxy. Most of these large stars become neutron stars, which are made of incredibly dense material and continue to give o ...
Mon Jul 29, 2013 SUN IN LEO? NO, CANCER!
... were at the center of our galaxy, for when you looked along the milky band of light that defines the galactic disc, you saw roughly the same number of stars throughout. Other astronomers suggested that interstellar dust clouds kept us from seeing the great wealth of stars that lay at the galaxy's he ...
... were at the center of our galaxy, for when you looked along the milky band of light that defines the galactic disc, you saw roughly the same number of stars throughout. Other astronomers suggested that interstellar dust clouds kept us from seeing the great wealth of stars that lay at the galaxy's he ...
OPTICAL MINERALOGY
... Before going on to examine how light inteacts with minerals we must define one term: RETARDATION - (delta) represents the distance that one ray lags behind another. Retardation is measured in nanometres, 1nm = 10-7cm, or the number of wavelengths by which a wave lags behind another light wave. The ...
... Before going on to examine how light inteacts with minerals we must define one term: RETARDATION - (delta) represents the distance that one ray lags behind another. Retardation is measured in nanometres, 1nm = 10-7cm, or the number of wavelengths by which a wave lags behind another light wave. The ...
Quantum Theory
... and h= 6.6 x 10-34 Joules; the wavelength of the electron is 7 nanometres; the higher the velocity, the shorter the wavelength, so electron microscopes can see things smaller than optical microscopes (wavelength 400-900 nm) ...
... and h= 6.6 x 10-34 Joules; the wavelength of the electron is 7 nanometres; the higher the velocity, the shorter the wavelength, so electron microscopes can see things smaller than optical microscopes (wavelength 400-900 nm) ...
Chapter 10 Hertzsprung-Russel Diagrams and Distance to Stars
... only its apparent brightness. As we’ve already said, a bright star that’s very far away would appear much fainter than a dim star that’s much closer. To overcome this problem, scientists began to look at stars that were found in clusters. In general, it’s safe to assume that all the stars in a clust ...
... only its apparent brightness. As we’ve already said, a bright star that’s very far away would appear much fainter than a dim star that’s much closer. To overcome this problem, scientists began to look at stars that were found in clusters. In general, it’s safe to assume that all the stars in a clust ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.