Measurements of Dark Energy Lecture 2: Expansion Kinematics
... • Correlation in redshift would allow us to probe H(z) directly In practice, the reconstructed (in slices) 3-D power spectrum (from slices) is approximately sensitive to the geometric distance measure: ...
... • Correlation in redshift would allow us to probe H(z) directly In practice, the reconstructed (in slices) 3-D power spectrum (from slices) is approximately sensitive to the geometric distance measure: ...
Michael_Chau_Laeer_Telecomunication_Report
... Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Rudimentary Laser Concept The concept of a laser involves the amplification of light into an intense ray consisting of photons. These particles have the same direction, frequency, and polarization as well as identical or a phased with a fixed d ...
... Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Rudimentary Laser Concept The concept of a laser involves the amplification of light into an intense ray consisting of photons. These particles have the same direction, frequency, and polarization as well as identical or a phased with a fixed d ...
Galaxies
... • Are galaxies isolated in space, or are they found near other galaxies? • What happens when galaxies collide with each other? • Is dark matter found in galaxies beyond the Milky Way? • How do astronomers think galaxies formed? ...
... • Are galaxies isolated in space, or are they found near other galaxies? • What happens when galaxies collide with each other? • Is dark matter found in galaxies beyond the Milky Way? • How do astronomers think galaxies formed? ...
Introduction: The Night Sky
... neutron star is about 50% more massive than Sun, but is only 20 km across basically a gigantic atomic nucleus: protons and electrons have combined to form neutrons in extreme cases even this may not be stable, and a black hole is formed instead ...
... neutron star is about 50% more massive than Sun, but is only 20 km across basically a gigantic atomic nucleus: protons and electrons have combined to form neutrons in extreme cases even this may not be stable, and a black hole is formed instead ...
Fig. 16-7, p.363
... • Almost 200 planets have now been found around other stars, but those planetary systems often have “hot Jupiters” - is our solar system weird, or are those systems weird ? • All the planets sustained heavy bombardment from remnant construction material soon after they formed; that may have set the ...
... • Almost 200 planets have now been found around other stars, but those planetary systems often have “hot Jupiters” - is our solar system weird, or are those systems weird ? • All the planets sustained heavy bombardment from remnant construction material soon after they formed; that may have set the ...
Be Sure to look at 2 things - Fort Worth Astronomical Society
... the width of your index finger held at arm's length against the sky!) Get out your binoculars or small telescope and compare the two planets. Mercury, though not as bright as Venus, is beautiful nonetheless. Mercury will then slowly move away, to be lost in the solar glare for the rest of the month. ...
... the width of your index finger held at arm's length against the sky!) Get out your binoculars or small telescope and compare the two planets. Mercury, though not as bright as Venus, is beautiful nonetheless. Mercury will then slowly move away, to be lost in the solar glare for the rest of the month. ...
quiz 1 Spring 1995
... 16)9 label the diagrams below with the sun and the moon (in the appropriate phase) for observations of the moon with the given elongations and times. The observer is looking south, into the page. ...
... 16)9 label the diagrams below with the sun and the moon (in the appropriate phase) for observations of the moon with the given elongations and times. The observer is looking south, into the page. ...
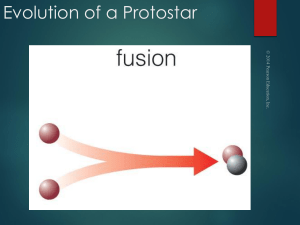
Evolution of a Protostar
... A protostar looks starlike after the surrounding gas is blown away, but its thermal energy comes from gravitational contraction, not fusion. ...
... A protostar looks starlike after the surrounding gas is blown away, but its thermal energy comes from gravitational contraction, not fusion. ...
1 Ay 124 Winter 2016 – HOMEWORK #3
... Problem 1 The nearest spiral galaxy to the Milky Way, M31, has a very concentrated nucleus. At a projected radius of 1 arcsec, stars in the nucleus have a line of sight velocity dispersion of 150 km s−1 , and are also rotating about the nucleus at 150 km s−1 . The total luminosity from within 1 arc ...
... Problem 1 The nearest spiral galaxy to the Milky Way, M31, has a very concentrated nucleus. At a projected radius of 1 arcsec, stars in the nucleus have a line of sight velocity dispersion of 150 km s−1 , and are also rotating about the nucleus at 150 km s−1 . The total luminosity from within 1 arc ...
Science Assessment Stage H--Performance Standard 12F-H
... • Analyze research and data for supporting or refuting the selected hypotheses. • Report, display and defend the data analysis of constellation members and other star groupings. • Generate further questions for star classifications. Note to teacher: This activity relates to knowledge associated with ...
... • Analyze research and data for supporting or refuting the selected hypotheses. • Report, display and defend the data analysis of constellation members and other star groupings. • Generate further questions for star classifications. Note to teacher: This activity relates to knowledge associated with ...
Astronomy Homework - Life
... 6. Stars leave the main sequence when (they fuse hydrogen in their cores/they run out of hydrogen to fuse in their cores). 7. Hydrogen begins to fuse in a (shell/core) around the contracting helium core. 8. As the core of a star contracts, the outer layers of the star (contract/expand). 9. Stars lea ...
... 6. Stars leave the main sequence when (they fuse hydrogen in their cores/they run out of hydrogen to fuse in their cores). 7. Hydrogen begins to fuse in a (shell/core) around the contracting helium core. 8. As the core of a star contracts, the outer layers of the star (contract/expand). 9. Stars lea ...
Astronomy Exam #2 for the 10
... The hot main sequence stars appear to be mostly B and A spectral type with an absolute magnitude between +2 and -5. This range in absolute magnitudes corresponds to a range in luminosity of between 16 and 10,000 solar luminosities. These stars will have a short main sequence lifetime compared to the ...
... The hot main sequence stars appear to be mostly B and A spectral type with an absolute magnitude between +2 and -5. This range in absolute magnitudes corresponds to a range in luminosity of between 16 and 10,000 solar luminosities. These stars will have a short main sequence lifetime compared to the ...
Lecture 5: Spectroscopy and Photochemistry I
... – Excites vibrational motions in molecules – With a very few exceptions, infrared radiation is not energetic enough to break molecules or initiate photochemical processes ...
... – Excites vibrational motions in molecules – With a very few exceptions, infrared radiation is not energetic enough to break molecules or initiate photochemical processes ...
1 Ay 124 Winter 2014 – HOMEWORK #3
... Problem 1 The nearest spiral galaxy to the Milky Way, M31, has a very concentrated nucleus. At a projected radius of 1 arcsec, stars in the nucleus have a line of sight velocity dispersion of 150 km s−1 , and are also rotating about the nucleus at 150 km s−1 . The total luminosity from within 1 arc ...
... Problem 1 The nearest spiral galaxy to the Milky Way, M31, has a very concentrated nucleus. At a projected radius of 1 arcsec, stars in the nucleus have a line of sight velocity dispersion of 150 km s−1 , and are also rotating about the nucleus at 150 km s−1 . The total luminosity from within 1 arc ...
The correct answers are written in bold, italic and underlined. The
... gas is governed by electron quantum mechanical effects that produce electron degeneracy pressure. The pressure of this gas • does not increase as its temperature increases. • depends on temperature, an increase in temperature leading to an increase in pressure. • decreases inversely as the temperatu ...
... gas is governed by electron quantum mechanical effects that produce electron degeneracy pressure. The pressure of this gas • does not increase as its temperature increases. • depends on temperature, an increase in temperature leading to an increase in pressure. • decreases inversely as the temperatu ...
The Components of a Spiral Galaxy
... (star formingspiral population) " • bulges are dominated by stellar absorption lines and have little 'blue' light" ...
... (star formingspiral population) " • bulges are dominated by stellar absorption lines and have little 'blue' light" ...
Cosmology with objects from the Hamburg Quasar Surveys
... measurement of the primordial deuterium abundance therefore gives the cosmic baryon density Щb. A natural place to look for primordial abundances is in high-redshift, low metal abundance intergalactic clouds where there is little contamination with processed matter ejected by stars where D is destro ...
... measurement of the primordial deuterium abundance therefore gives the cosmic baryon density Щb. A natural place to look for primordial abundances is in high-redshift, low metal abundance intergalactic clouds where there is little contamination with processed matter ejected by stars where D is destro ...
Handout Life of Stars
... is formed when gravity causes the dust and gas of a nebula to clump together in a process called accretion. As gravity continues to pull ever more matter inward towards the core, its temperature, pressure and density increases. If a critical temperature in the core of a protostar is reached, then nu ...
... is formed when gravity causes the dust and gas of a nebula to clump together in a process called accretion. As gravity continues to pull ever more matter inward towards the core, its temperature, pressure and density increases. If a critical temperature in the core of a protostar is reached, then nu ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.