Astro Unit 1 Notes - Intro to Astronomy
... About 3000 stars are visible at any one time Stars are distributed randomly but the human brain tends to find patterns ...
... About 3000 stars are visible at any one time Stars are distributed randomly but the human brain tends to find patterns ...
Stellar Temperatures
... Stellar Temperatures Since stars are not solid bodies, their “size” and “temperature” are somewhat ill-defined quantities. (The emergent flux from a star comes from different levels of the photosphere, which have different temperatures.) We define the “effective temperature” of a star is through the ...
... Stellar Temperatures Since stars are not solid bodies, their “size” and “temperature” are somewhat ill-defined quantities. (The emergent flux from a star comes from different levels of the photosphere, which have different temperatures.) We define the “effective temperature” of a star is through the ...
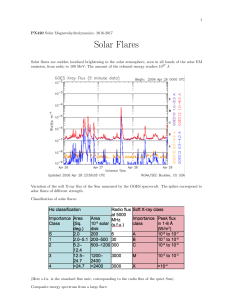
Solar Flares
... 1. Magnetic free energy is stored in the corona, due to either motions of the photospheric footpoints of loops or to the emergence of current-carrying field from below the photosphere. 2. A cool, dense filament forms, suspended by the magnetic field, over the neutral line. 3. The field evolves slowl ...
... 1. Magnetic free energy is stored in the corona, due to either motions of the photospheric footpoints of loops or to the emergence of current-carrying field from below the photosphere. 2. A cool, dense filament forms, suspended by the magnetic field, over the neutral line. 3. The field evolves slowl ...
energy
... Remember: Energy is related to frequency (and also wavelength!) • Planck’s constant has a value of 6.626 x 10–34 J · s, where J is the symbol for the joule, the SI unit of energy. • Looking at the equation, you can see that the energy of radiation increases as the radiation’s frequency, v (of “f”), ...
... Remember: Energy is related to frequency (and also wavelength!) • Planck’s constant has a value of 6.626 x 10–34 J · s, where J is the symbol for the joule, the SI unit of energy. • Looking at the equation, you can see that the energy of radiation increases as the radiation’s frequency, v (of “f”), ...
Problem Set # 8: The Last Problem Set Due Wednesday, December
... When did the individual protons and neutrons first fuse? When and where did the final carbon nucleus form? How did the carbon atom make its way ...
... When did the individual protons and neutrons first fuse? When and where did the final carbon nucleus form? How did the carbon atom make its way ...
Contents List Somerville
... Form of Lunar Spheroid Libration, Aspect, and Constitution of the Moon Rotation of Jupiter’s Satellites Section X. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………66 Rotation of the Earth invariable Decrease in the Earth’s Mean Temperature Earth originally in a State of Fusion Length of Day constant ...
... Form of Lunar Spheroid Libration, Aspect, and Constitution of the Moon Rotation of Jupiter’s Satellites Section X. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………66 Rotation of the Earth invariable Decrease in the Earth’s Mean Temperature Earth originally in a State of Fusion Length of Day constant ...
Aeroengine exhaust emissions monitoring
... White cell systems have been set up to obtain multiple passes through the plume to enhance absorption or emission intensities so that trace quantities may be detected. Figure 3 shows typical absorption and emission spectra from gas turbine engine exhausts. CO lines are observed between 2000-2200 cm- ...
... White cell systems have been set up to obtain multiple passes through the plume to enhance absorption or emission intensities so that trace quantities may be detected. Figure 3 shows typical absorption and emission spectra from gas turbine engine exhausts. CO lines are observed between 2000-2200 cm- ...
lecture2
... above the horizon is approximately the same as the observer's latitude in the Northern Hemisphere. ...
... above the horizon is approximately the same as the observer's latitude in the Northern Hemisphere. ...
red shift - Scoilnet
... When a star’s light is red shifted, the star must be moving away from us. To us, almost every star looks red shifted, which means they are all moving away. This is only possible if the Universe is expanding. The second piece of evidence is called the cosmic microwave background. When the Universe be ...
... When a star’s light is red shifted, the star must be moving away from us. To us, almost every star looks red shifted, which means they are all moving away. This is only possible if the Universe is expanding. The second piece of evidence is called the cosmic microwave background. When the Universe be ...
The Michelson Interferometer and Its Applications
... relative to this aether should exhibit observable relativistic effects. He devised and constructed an optical interferometer with which he presumed he would then be able to detect the relative motion of Ea ...
... relative to this aether should exhibit observable relativistic effects. He devised and constructed an optical interferometer with which he presumed he would then be able to detect the relative motion of Ea ...
class 2, S11
... (which is a member of the Local Group of galaxies in the Local Supercluster) • How did we come to be? • How can we know what the universe was like in the past? • Can we see the entire universe? ...
... (which is a member of the Local Group of galaxies in the Local Supercluster) • How did we come to be? • How can we know what the universe was like in the past? • Can we see the entire universe? ...
Abell 1656: the Coma Cluster of galaxies - Euro-VO
... services. Each “S” corresponds to the location of a spectrum. Open the “Hubble Space Telescope Spectra” menu and click on the QSO 1257+2840 name. This opens the Data Info Frame that gives access to information about this observation. Click on “FoV in stack” and visualize the slit location on the ima ...
... services. Each “S” corresponds to the location of a spectrum. Open the “Hubble Space Telescope Spectra” menu and click on the QSO 1257+2840 name. This opens the Data Info Frame that gives access to information about this observation. Click on “FoV in stack” and visualize the slit location on the ima ...
Solutions - Yale Astronomy
... The cycle of the seasons occurs because Earth’s axis of rotation is inclined 23.5◦ from the perpendicular to its orbital plane. Although precession moves the axis very slowly, the axis is essentially fixed in space. As Earth orbits the Sun, its axis remains pointing in the same direction in space. S ...
... The cycle of the seasons occurs because Earth’s axis of rotation is inclined 23.5◦ from the perpendicular to its orbital plane. Although precession moves the axis very slowly, the axis is essentially fixed in space. As Earth orbits the Sun, its axis remains pointing in the same direction in space. S ...
Questions For Review KEY
... galaxies. This phenomenon of galaxies moving farther away from each other is known as the red shift. As light from distant galaxies approach earth there is an increase of space between earth and the galaxy. Through a calculation involving the distance of far-off clusters and the red shift, a final e ...
... galaxies. This phenomenon of galaxies moving farther away from each other is known as the red shift. As light from distant galaxies approach earth there is an increase of space between earth and the galaxy. Through a calculation involving the distance of far-off clusters and the red shift, a final e ...
Photometry Review from Some Constellations of Autumn in the
... However they can also be designed to measure the diffusivity on any of the listed light ranges that usually cover around 200 nm - 2500 nm using different controls and calibrations. [6] Within these ranges of light, calibrations are needed on the machine using standards that vary in type depending on ...
... However they can also be designed to measure the diffusivity on any of the listed light ranges that usually cover around 200 nm - 2500 nm using different controls and calibrations. [6] Within these ranges of light, calibrations are needed on the machine using standards that vary in type depending on ...
Römer and the speed of light
... brightest stars are 1st magnitude (m=1) faintest stars are 6th magnitude (m=6) Pogson (1856): A 1st magnitude star is 100 times brighter than a 6th magnitude star! The Eye is a negative logarithmic detector. ...
... brightest stars are 1st magnitude (m=1) faintest stars are 6th magnitude (m=6) Pogson (1856): A 1st magnitude star is 100 times brighter than a 6th magnitude star! The Eye is a negative logarithmic detector. ...
Distances in space
... same scale to map the nearest star to earth you would have to use a larger reference scale because the distances are so great. For instance it is approximately 4 light years to the nearest star to our solar system. Given that a light year is approximately 63,255 AU's the distance would be (63,255 x ...
... same scale to map the nearest star to earth you would have to use a larger reference scale because the distances are so great. For instance it is approximately 4 light years to the nearest star to our solar system. Given that a light year is approximately 63,255 AU's the distance would be (63,255 x ...
Stellar Activity
... • Trace the change in the emission of the calcium K line along a slit placed across the Sun. • the amount of emission changes as the slit passes over magnetically active and quiet areas on the solar surface ...
... • Trace the change in the emission of the calcium K line along a slit placed across the Sun. • the amount of emission changes as the slit passes over magnetically active and quiet areas on the solar surface ...
CHAPTER 4 THE SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF GALAXIES 4.13
... Having looked at the properties of individual galaxies – both normal and active – in some detail, it is now appropriate to consider how these galaxies are distributed in space. Surveys of the region outside our own Milky Way show that there are galaxies all around us. Deep field images such as those ...
... Having looked at the properties of individual galaxies – both normal and active – in some detail, it is now appropriate to consider how these galaxies are distributed in space. Surveys of the region outside our own Milky Way show that there are galaxies all around us. Deep field images such as those ...
Astronomy Chapter 16 – The Milky Way Galaxy A. Main Ideas 1
... Although all stars within the Milky Way move around its center, the paths followed by stars in the disk and halo are very different. The stars in the disk orbit in the same direction and in nearly the same plane, giving the disk its flat shape. Stars in the halo and bulge follow orbits that are stee ...
... Although all stars within the Milky Way move around its center, the paths followed by stars in the disk and halo are very different. The stars in the disk orbit in the same direction and in nearly the same plane, giving the disk its flat shape. Stars in the halo and bulge follow orbits that are stee ...
Bacterial Identification: a tool for rapid identification of
... followed by etching and hydrosilylation [3]. This method isolated SiNCs with good yields, high surface coverage and exceptional control over the dimensions and optical properties of the materials. In the present work, the H-terminated nanocrystals were used as a platform for copassivation with dodec ...
... followed by etching and hydrosilylation [3]. This method isolated SiNCs with good yields, high surface coverage and exceptional control over the dimensions and optical properties of the materials. In the present work, the H-terminated nanocrystals were used as a platform for copassivation with dodec ...
Autumn - Dark Sky Discovery
... charts here are far simpler and have fewer stars. You can just hold these up in front of you when you’re facing the appropriate direction and look up! Looking North The plough is perhaps the most easily recognised group of stars in the northern sky and it is a very useful ‘skymark’. The plough is al ...
... charts here are far simpler and have fewer stars. You can just hold these up in front of you when you’re facing the appropriate direction and look up! Looking North The plough is perhaps the most easily recognised group of stars in the northern sky and it is a very useful ‘skymark’. The plough is al ...
IBM-finalrev - Madison Public Schools
... 20. Identify the color that would be seen when these opaque objects are seen on the following colors of light. a. white object in yellow light e. green object in red light b. white object in white light d. green object in white light c. green object in green light 21. Name the 3 complementary colors ...
... 20. Identify the color that would be seen when these opaque objects are seen on the following colors of light. a. white object in yellow light e. green object in red light b. white object in white light d. green object in white light c. green object in green light 21. Name the 3 complementary colors ...
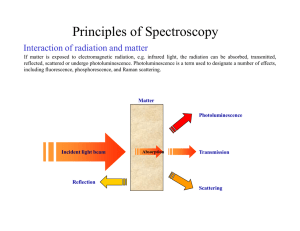
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.