Sequencing the Stars
... no one knew the process by which stars produce light. Today, we understand quite well that stars, which are composed mostly of hydrogen, produce energy by nuclear fusion. The enormous pressure created by the mass of a star causes pairs of hydrogen nuclei in its core to fuse into a helium nucleus the ...
... no one knew the process by which stars produce light. Today, we understand quite well that stars, which are composed mostly of hydrogen, produce energy by nuclear fusion. The enormous pressure created by the mass of a star causes pairs of hydrogen nuclei in its core to fuse into a helium nucleus the ...
Balmer_Prism2007
... how much the light is spread in direction. The more spread the better! Note that this spread is typically not very simple (at least not linear) because dn/dis not a constant over the wavelengths of interest. As described on page 479 for normal dispersion one can model the dispersion by the two-con ...
... how much the light is spread in direction. The more spread the better! Note that this spread is typically not very simple (at least not linear) because dn/dis not a constant over the wavelengths of interest. As described on page 479 for normal dispersion one can model the dispersion by the two-con ...
Article PDF - IOPscience
... by ATM. Direct comparison of the spectrum in the bright phase was made with standard star spectra obtained using the same telescope and instrument at a lower resolution for classification purposes. Careful inspection of both spectra shows that they are nearly identical and that they both exhibit ste ...
... by ATM. Direct comparison of the spectrum in the bright phase was made with standard star spectra obtained using the same telescope and instrument at a lower resolution for classification purposes. Careful inspection of both spectra shows that they are nearly identical and that they both exhibit ste ...
2. Answer Key Practice Test, Topic 3
... 36. Base your answer to the following question on the diagrams below. The diagrams represent the events that occur when a large meteor, such as the one believed to have caused the extinction of many organisms, impacts Earth's surface. Diagram A shows the meteor just before impact. Diagram B represe ...
... 36. Base your answer to the following question on the diagrams below. The diagrams represent the events that occur when a large meteor, such as the one believed to have caused the extinction of many organisms, impacts Earth's surface. Diagram A shows the meteor just before impact. Diagram B represe ...
Lecture 13. Black Holes - Politechnika Wrocławska
... – Astronomers classify stars based on their colors, or spectral types: from hot (violet) to cool (red) are: O, B, A, F, G, K, M ...
... – Astronomers classify stars based on their colors, or spectral types: from hot (violet) to cool (red) are: O, B, A, F, G, K, M ...
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy - University of Texas Astronomy
... The rate of fusion depends strongly on temperature, because the protons must be moving fast to get close enough together so they can be attracted by the strong force before their electrical repulsion pushes them apart. If the center of a star is too hot, fusion will run faster than energy is being r ...
... The rate of fusion depends strongly on temperature, because the protons must be moving fast to get close enough together so they can be attracted by the strong force before their electrical repulsion pushes them apart. If the center of a star is too hot, fusion will run faster than energy is being r ...
RachelStarProject
... Low-mass stars and high-mass stars take different paths at the end of their lives because high-mass stars become so compact that they have to do something different than low-mass stars. ...
... Low-mass stars and high-mass stars take different paths at the end of their lives because high-mass stars become so compact that they have to do something different than low-mass stars. ...
L16
... This background correction method is the most common method although, for reasons to be discussed shortly, it has major drawbacks and fails a lot. In this technique, radiation from a deuterium lamp and a HCL lamp alternately pass through the graphite tube analyzer. It is essential to keep the slit w ...
... This background correction method is the most common method although, for reasons to be discussed shortly, it has major drawbacks and fails a lot. In this technique, radiation from a deuterium lamp and a HCL lamp alternately pass through the graphite tube analyzer. It is essential to keep the slit w ...
Probing DM Halo Shapes Using Satellite Galaxy Kinematics
... – Only use subhalos most likely to host satellites • Most massive at infall? • Highest collapse z? • Conditional Luminosity Function? ...
... – Only use subhalos most likely to host satellites • Most massive at infall? • Highest collapse z? • Conditional Luminosity Function? ...
July 2015 - Hermanus Astronomy
... Talk and star-gazing with the Cubs On 12 June, Jenny Morris gave an introductory talk on astronomy to 22 Cubs and 5 adults. This was followed up on 19 June by a stargazing event on Rotary Way. Fine weather meant that the 19 children and 5 adults who attended had a rich viewing experience. The band o ...
... Talk and star-gazing with the Cubs On 12 June, Jenny Morris gave an introductory talk on astronomy to 22 Cubs and 5 adults. This was followed up on 19 June by a stargazing event on Rotary Way. Fine weather meant that the 19 children and 5 adults who attended had a rich viewing experience. The band o ...
Biblical Astrophysics - The Call of the Bride
... (Amos 8:8-9) The earth will tremble for your deeds, and everyone will mourn. The ground will rise like the Nile River at floodtime; it will heave up, then sink again. "In that day," says the Sovereign LORD, "I will make the sun go down at noon and darken the earth while it is still day. (The Earth's ...
... (Amos 8:8-9) The earth will tremble for your deeds, and everyone will mourn. The ground will rise like the Nile River at floodtime; it will heave up, then sink again. "In that day," says the Sovereign LORD, "I will make the sun go down at noon and darken the earth while it is still day. (The Earth's ...
History Of Astronomy
... List the planets in order of their distance from the sun. The planets in order of their distance from the sun are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. [Pluto is now a dwarf planet, FYI.] ...
... List the planets in order of their distance from the sun. The planets in order of their distance from the sun are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. [Pluto is now a dwarf planet, FYI.] ...
What is the real nature of HD 108?
... origin. This casts doubt on the possibility of applying the Conti & Alschuler criterion to this star. For the luminosity class, we use the criterion based on (Si IV λ 4088) the value of log(W 00 ) = log EW EW (He I λ 4143) . The equivalent widths (EW s) of these two absorption lines show no strong v ...
... origin. This casts doubt on the possibility of applying the Conti & Alschuler criterion to this star. For the luminosity class, we use the criterion based on (Si IV λ 4088) the value of log(W 00 ) = log EW EW (He I λ 4143) . The equivalent widths (EW s) of these two absorption lines show no strong v ...
PDF - Oxford Academic
... in which to seek Earth-like planets. Jay Farihi of the University of Cambridge and an international team used Hubble Space Telescope data from the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph to identify silicon and low levels of carbon in the atmsopheres of two white dwarfs. These are thought to be “pollution” from ...
... in which to seek Earth-like planets. Jay Farihi of the University of Cambridge and an international team used Hubble Space Telescope data from the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph to identify silicon and low levels of carbon in the atmsopheres of two white dwarfs. These are thought to be “pollution” from ...
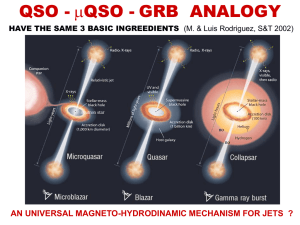
Relativistic jets in microquasars, AGN and GRBs
... • A LARGE FRACTION OF ULXs IN NEARBY GALAXIES • GRBs OF LONG DURATION IN DISTANT GALAXIES BLACK HOLE ASTROPHYSICS IS TODAY IN AN ANALOGOUS SITUATION AS WAS STELLAR ASTRONOMY IN THE FIRST HALF OF LAST CENTURY, WHEN THE HR DIAGRAM WAS ...
... • A LARGE FRACTION OF ULXs IN NEARBY GALAXIES • GRBs OF LONG DURATION IN DISTANT GALAXIES BLACK HOLE ASTROPHYSICS IS TODAY IN AN ANALOGOUS SITUATION AS WAS STELLAR ASTRONOMY IN THE FIRST HALF OF LAST CENTURY, WHEN THE HR DIAGRAM WAS ...
2 Galactic radiation fields
... • An important point to note here is that because of the Ekin,e term, the spectrum of bound-free emission consists of a continuum (albeit not a particularly flat one), rather than a series of distinct spectral lines. • It is also worth noting that although the mean kinetic energy of the electrons in ...
... • An important point to note here is that because of the Ekin,e term, the spectrum of bound-free emission consists of a continuum (albeit not a particularly flat one), rather than a series of distinct spectral lines. • It is also worth noting that although the mean kinetic energy of the electrons in ...
Slide 1
... Formation of the Solar System The “Nebular Hypothesis” A cloud of interstellar gas/dust, the "solar nebula", including material formed in previous generations of stars, is disturbed (for example, by the shock wave from a nearby ...
... Formation of the Solar System The “Nebular Hypothesis” A cloud of interstellar gas/dust, the "solar nebula", including material formed in previous generations of stars, is disturbed (for example, by the shock wave from a nearby ...
Part 1: If a 10000 K blackbody has a wavelength of peak emission at
... Here is an example that got ½ credit – again even though it’s not even close to correct: “You determine the age by looking at the stars around it. Since they are in a stellar cluster they are the same age. The age of the star is 2 times the age of the Sun.” ...
... Here is an example that got ½ credit – again even though it’s not even close to correct: “You determine the age by looking at the stars around it. Since they are in a stellar cluster they are the same age. The age of the star is 2 times the age of the Sun.” ...
Lecture 15: The Main Sequence
... More massive main-sequence stars need higher pressures to support themselves against gravitational collapse. Higher pressure=higher temperatures. The higher temperatures lead to greater rates of nuclear fusion which means higher luminosity. ...
... More massive main-sequence stars need higher pressures to support themselves against gravitational collapse. Higher pressure=higher temperatures. The higher temperatures lead to greater rates of nuclear fusion which means higher luminosity. ...
Lecture 18 - UConn Physics
... polarized in the direction of the dipole • radiation pattern is doughnut shaped & outward traveling – zero amplitude directly above and below dipole – maximum amplitude in-plane ...
... polarized in the direction of the dipole • radiation pattern is doughnut shaped & outward traveling – zero amplitude directly above and below dipole – maximum amplitude in-plane ...
Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani and Elite School of Optometry
... Course Objective: The objectives of this course are to describe the wave nature of light and apply the wave theory to explain classic phenomena such as interference, diffraction and polarization. Working of some optical instruments and a brief description of scattering and laser will also be include ...
... Course Objective: The objectives of this course are to describe the wave nature of light and apply the wave theory to explain classic phenomena such as interference, diffraction and polarization. Working of some optical instruments and a brief description of scattering and laser will also be include ...
Professor`s commentary for Theme 12 Part 1
... large number of stars that could provide suitable abodes for life. The second factor is one about which we knew little until the last few decades, and that is the number of planets that might be associated with a given star. As we now know from radio-velocity measurements, as shown on the bottom lef ...
... large number of stars that could provide suitable abodes for life. The second factor is one about which we knew little until the last few decades, and that is the number of planets that might be associated with a given star. As we now know from radio-velocity measurements, as shown on the bottom lef ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.