HR Diagram Explorer Worksheet
... In addition to the isoradius lines, check show luminosity classes. This green region (dwarfs V) is known as the main sequence and contains all stars that are fusing hydrogen into helium as their primary energy source. Over 90% of all stars fall in this region on the HR diagram. Move the active curso ...
... In addition to the isoradius lines, check show luminosity classes. This green region (dwarfs V) is known as the main sequence and contains all stars that are fusing hydrogen into helium as their primary energy source. Over 90% of all stars fall in this region on the HR diagram. Move the active curso ...
Oct 06, 2001
... 11. Which of the lettered stars would be a blue supergiant? A B C D E 12. Which of the lettered stars on the HR diagram is about 100 times more luminous than the Sun? A B C D E 13. Briefly describe what changes in temperature and radius must occur to Star C to transform it into Star E? 14. Briefly d ...
... 11. Which of the lettered stars would be a blue supergiant? A B C D E 12. Which of the lettered stars on the HR diagram is about 100 times more luminous than the Sun? A B C D E 13. Briefly describe what changes in temperature and radius must occur to Star C to transform it into Star E? 14. Briefly d ...
Major Themes of “ The First Stars ”
... - blue colors and unusual emission lines (He II) with JWST and 30-m - color and luminosity evolution in evolved populations - GP effect and other tracers of reionization (CMB, 21 cm, LAEs) However. . . . . . these tests require facilities that are some years away (2013+), and . . . they detect direc ...
... - blue colors and unusual emission lines (He II) with JWST and 30-m - color and luminosity evolution in evolved populations - GP effect and other tracers of reionization (CMB, 21 cm, LAEs) However. . . . . . these tests require facilities that are some years away (2013+), and . . . they detect direc ...
Part 2
... Note the following defect of the Saha-equation: the ionization increases with T and decreases with P . When T ≈ const., as in stellar cores, the ionization degree should decrease, which is unphysical. The explanation lies in the fact that the ionization potential is suppressed, if the atoms approach ...
... Note the following defect of the Saha-equation: the ionization increases with T and decreases with P . When T ≈ const., as in stellar cores, the ionization degree should decrease, which is unphysical. The explanation lies in the fact that the ionization potential is suppressed, if the atoms approach ...
Electrons in Atoms
... signals, and for radar equipment Radio telescopes view planets, comets, giant clouds of gas and dust, stars, and galaxies ...
... signals, and for radar equipment Radio telescopes view planets, comets, giant clouds of gas and dust, stars, and galaxies ...
Answers
... H Balmer absorption: Consider both fraction ionised (Saha equation) and fraction excited to n=2 level (Boltzmann) Hot, O stars: practically 100% ionisation, hence small neutral population for absorption, hence very weak Balmer absorption Cooler, G stars, temperature insufficient for high degree of i ...
... H Balmer absorption: Consider both fraction ionised (Saha equation) and fraction excited to n=2 level (Boltzmann) Hot, O stars: practically 100% ionisation, hence small neutral population for absorption, hence very weak Balmer absorption Cooler, G stars, temperature insufficient for high degree of i ...
distant stars nearby star parallax angle The principle of geometrical
... One of the hardest things to do in astronomy is to determine how far away things are. Does the star Vega in Lyra appear exceptionally bright because it’s an intrinsically bright star, or simply because it’s unusually close by? What about Betelgeuse in Orion? If we didn’t know the distances to these ...
... One of the hardest things to do in astronomy is to determine how far away things are. Does the star Vega in Lyra appear exceptionally bright because it’s an intrinsically bright star, or simply because it’s unusually close by? What about Betelgeuse in Orion? If we didn’t know the distances to these ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... and begins a nuclear reaction that causes hydrogen to form helium, releasing energy in the form of heat and light. A low mass star will stay in this MAIN SEQUENCE phase for a long time, until it begins to use up all of it’s hydrogen. ...
... and begins a nuclear reaction that causes hydrogen to form helium, releasing energy in the form of heat and light. A low mass star will stay in this MAIN SEQUENCE phase for a long time, until it begins to use up all of it’s hydrogen. ...
Light - FT HELP
... this make shadow. Second, we can reflect it, it means change its path with mirror. And third way how controlling the light, we can bend it, it means change its direction by making it pass into another transparent material of different density, like glass or water. There are actually other ways to be ...
... this make shadow. Second, we can reflect it, it means change its path with mirror. And third way how controlling the light, we can bend it, it means change its direction by making it pass into another transparent material of different density, like glass or water. There are actually other ways to be ...
Nuclear Astrophysics (a Cosmic Cookbook)
... = 30,000 trillion, trillion x Annual U.S Energy Consumption Can outshine the entire Galaxy it occurs in! More energy than our sun will generate in its lifetime! ...
... = 30,000 trillion, trillion x Annual U.S Energy Consumption Can outshine the entire Galaxy it occurs in! More energy than our sun will generate in its lifetime! ...
From Supernovae to Planets - Astronomical Society of the Pacific
... cloud of hot gas and dust. • Scientists had evidence of such dust formation, but couldn’t be sure that the dust wasn’t destroyed in the “rebound” shock wave when the expanding supernova remnant collided with the interstellar medium of thinly scattered material, creating another shock wave traveling ...
... cloud of hot gas and dust. • Scientists had evidence of such dust formation, but couldn’t be sure that the dust wasn’t destroyed in the “rebound” shock wave when the expanding supernova remnant collided with the interstellar medium of thinly scattered material, creating another shock wave traveling ...
Print Activity - Let`s Talk Science
... 7. You’ve found the North Star! If you face towards the North Star, you will be facing north. What’s happening? A constellation is a group of stars in the sky that form a fixed pattern in relation to each other, as viewed from the Earth. Astronomers currently recognize 88 constellations in the North ...
... 7. You’ve found the North Star! If you face towards the North Star, you will be facing north. What’s happening? A constellation is a group of stars in the sky that form a fixed pattern in relation to each other, as viewed from the Earth. Astronomers currently recognize 88 constellations in the North ...
PHY216_lect1_2014 - Astrophysics Research Institute
... set in the west. The hour angle tells you how long it will be before the star transits (or how much time has passed since it transited!) • Hour Angle - angle between a star's current position and the meridian (measured WESTWARD in hours, where 1 hour is equivalent to 15 degrees – because 24 hours = ...
... set in the west. The hour angle tells you how long it will be before the star transits (or how much time has passed since it transited!) • Hour Angle - angle between a star's current position and the meridian (measured WESTWARD in hours, where 1 hour is equivalent to 15 degrees – because 24 hours = ...
(Star Stuff) ( 11-9-10)
... 3. High mass star (M > 4 solar masses) •Fusion of He,C,O,…..but not Fe (Iron) fusion Faster and faster Core collapses Supernova Produces all elements heavier than Fe and blows envelope apart ejecting to interstellar space most of its mass ...
... 3. High mass star (M > 4 solar masses) •Fusion of He,C,O,…..but not Fe (Iron) fusion Faster and faster Core collapses Supernova Produces all elements heavier than Fe and blows envelope apart ejecting to interstellar space most of its mass ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 12. Trace the variation in the duration of day and night during the year for a place in the north torrid zone. 13. The altitude of a star is observed, and found to be the angle whose sine is 5/13, calculate the true position of the star, assuming the amount of refraction at an altitude of 45 o to be ...
... 12. Trace the variation in the duration of day and night during the year for a place in the north torrid zone. 13. The altitude of a star is observed, and found to be the angle whose sine is 5/13, calculate the true position of the star, assuming the amount of refraction at an altitude of 45 o to be ...
File
... - Hertzsprung and Russell began comparing the surface temperature of stars with the stars’ brightness (luminosity). Look at Figure 1.18 on p. 385. - Nebulae: vast clouds of gas (mostly hydrogen) and dust in space, where stars form. - Prostar: the first stage in a star’s formation. As the process of ...
... - Hertzsprung and Russell began comparing the surface temperature of stars with the stars’ brightness (luminosity). Look at Figure 1.18 on p. 385. - Nebulae: vast clouds of gas (mostly hydrogen) and dust in space, where stars form. - Prostar: the first stage in a star’s formation. As the process of ...
Galaxy evolution - Pontifical Academy of Sciences
... It is widely accepted that galaxy evolution occurs within the framework of a ⌳ Cold Dark Matter cosmology; that is to say that clustering and merging is how galaxies gain in mass, and can also determine the shape and structure of galaxies. Galaxy formation and evolution is a complex combination of h ...
... It is widely accepted that galaxy evolution occurs within the framework of a ⌳ Cold Dark Matter cosmology; that is to say that clustering and merging is how galaxies gain in mass, and can also determine the shape and structure of galaxies. Galaxy formation and evolution is a complex combination of h ...
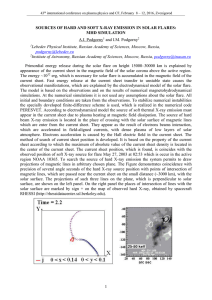
sources of hard and soft x-ray emission in solar flares: mhd simulation
... current sheet. Fast energy release at the current sheet transfer to unstable state causes the observational manifestations, which are explained by the electrodynamical model of the solar flare. The model is based on the observations and on the results of numerical magnetohydrodynamical simulations. ...
... current sheet. Fast energy release at the current sheet transfer to unstable state causes the observational manifestations, which are explained by the electrodynamical model of the solar flare. The model is based on the observations and on the results of numerical magnetohydrodynamical simulations. ...
The Ever-Changing Sky
... what is in it, and how things are moving around, as if we can elevate ourselves to a vintage point outside Earth. In this chapter, we will move ourselves back to Earth. Knowing how Earth is moving in the universe, with respect to the distant stars, and with respect to the Sun, allows us to explain w ...
... what is in it, and how things are moving around, as if we can elevate ourselves to a vintage point outside Earth. In this chapter, we will move ourselves back to Earth. Knowing how Earth is moving in the universe, with respect to the distant stars, and with respect to the Sun, allows us to explain w ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.