Week 10
... Procyon is 0.29 arcseconds. If you were to measure Procyon’s parallax angle from Venus, what would the parallax angle be? (Note: Venus’ orbit is smaller than Earth’s orbit.) A. More than 0.29 arcseconds B. 0.29 arcseconds C. Less than 0.29 arcseconds D. Zero arcseconds (no parallax) ...
... Procyon is 0.29 arcseconds. If you were to measure Procyon’s parallax angle from Venus, what would the parallax angle be? (Note: Venus’ orbit is smaller than Earth’s orbit.) A. More than 0.29 arcseconds B. 0.29 arcseconds C. Less than 0.29 arcseconds D. Zero arcseconds (no parallax) ...
This is the Earth! This is where you live.
... BUT LET’S THINK BIGGER. IN JUST THIS PICTURE TAKEN BY THE HUBBLE TELESCOPE, THERE ARE THOUSANDS AND THOUSANDS OF GALAXIES, EACH CONTAINING MILLIONS OF STARS, EACH WITH THEIR OWN PLANETS. ...
... BUT LET’S THINK BIGGER. IN JUST THIS PICTURE TAKEN BY THE HUBBLE TELESCOPE, THERE ARE THOUSANDS AND THOUSANDS OF GALAXIES, EACH CONTAINING MILLIONS OF STARS, EACH WITH THEIR OWN PLANETS. ...
Birth of Stars
... visible light, but only with infrared and radio telescopes The timescale for the initial collapse is estimated to be very short astronomically (thousands of years), implying that stars undergoing the collapse process are relatively few The collapse of a new star occurs in a region so small that in m ...
... visible light, but only with infrared and radio telescopes The timescale for the initial collapse is estimated to be very short astronomically (thousands of years), implying that stars undergoing the collapse process are relatively few The collapse of a new star occurs in a region so small that in m ...
The Melbourne Solar System Trail
... Uranus, its equator has been tilted m ore than ninety degrees to its orbit. Perhaps early in its history it collided with a huge unknown object. In 1781 it was the first new planet to be discovered since antiquity. Neptune is a distant gas giant. It is bluer than Uranus because it has m ore m ethane ...
... Uranus, its equator has been tilted m ore than ninety degrees to its orbit. Perhaps early in its history it collided with a huge unknown object. In 1781 it was the first new planet to be discovered since antiquity. Neptune is a distant gas giant. It is bluer than Uranus because it has m ore m ethane ...
L11
... The convective core becomes exhausted homogeneously, while it contracts to a smaller volume and becomes hotter. The star also develops a H-burning shell around the He dominated core. The temperature at the bottom of the hydrogen envelope is too high to sustain hydrostatic equilibrium. The envelope e ...
... The convective core becomes exhausted homogeneously, while it contracts to a smaller volume and becomes hotter. The star also develops a H-burning shell around the He dominated core. The temperature at the bottom of the hydrogen envelope is too high to sustain hydrostatic equilibrium. The envelope e ...
MSci Astrophysics 210PHY412 - Queen's University Belfast
... The He burning core is surrounded by a H-burning shell The triple- process liberates less energy per unit mass than for H-burning (~10%). Hence the lifetime is shorter, again around 10% There is no He-flash as densities in the He-core are not high enough for ...
... The He burning core is surrounded by a H-burning shell The triple- process liberates less energy per unit mass than for H-burning (~10%). Hence the lifetime is shorter, again around 10% There is no He-flash as densities in the He-core are not high enough for ...
MHD Simulations of Line-Driven Hot-Star Winds
... magnetic equator wind collision heating of the gas (see below) X-ray. Wind material stagnated after the shock: dense and slow radiative force inefficient gravity wins: infall of wind material in the form of dense knots onto the stellar surface. Infall of dense knots: semi-regular, about every 20 ...
... magnetic equator wind collision heating of the gas (see below) X-ray. Wind material stagnated after the shock: dense and slow radiative force inefficient gravity wins: infall of wind material in the form of dense knots onto the stellar surface. Infall of dense knots: semi-regular, about every 20 ...
StarCharacteristics
... The diameters of stars range from as little as 1/10 the Sun’s diameter to hundreds of times larger. The mass of stars can be from less than 1/100 to 20 or more times that of our Sun. Stars over 50 times the Sun’s mass are extremely rare. Our Sun is a medium sized star. ...
... The diameters of stars range from as little as 1/10 the Sun’s diameter to hundreds of times larger. The mass of stars can be from less than 1/100 to 20 or more times that of our Sun. Stars over 50 times the Sun’s mass are extremely rare. Our Sun is a medium sized star. ...
Heart of Darkness - Princeton University Press Blog
... Over the past thirty years, scientists have learned that two little-understood components—dark matter and dark energy— comprise most of the known cosmos, explain the growth of all cosmic structure, and hold the key to the universe’s fate. The story of how evidence for the so-called “Lambda-Cold Dark ...
... Over the past thirty years, scientists have learned that two little-understood components—dark matter and dark energy— comprise most of the known cosmos, explain the growth of all cosmic structure, and hold the key to the universe’s fate. The story of how evidence for the so-called “Lambda-Cold Dark ...
Determining the Sizes & Distances of Stars Using the H
... mass loss causes the star to eject its outer layers, which continue expanding out into space to form a planetary nebulae. For example, a star like the Sun will loose approximately 60% of its mass as it evolves to become a white dwarf. White dwarfs are low in luminosity, because fusion can no longer ...
... mass loss causes the star to eject its outer layers, which continue expanding out into space to form a planetary nebulae. For example, a star like the Sun will loose approximately 60% of its mass as it evolves to become a white dwarf. White dwarfs are low in luminosity, because fusion can no longer ...
April 2013
... abundance fraction is only 10–9 in stars, it is believed that LiBeB cosmic rays are produced almost entirely as a result of fragmentation reactions of heavier cosmic-ray nuclei (e.g., carbon and oxygen) with interstellar material. Most stable nucleides of lithium, beryllium, and boron are thought to ...
... abundance fraction is only 10–9 in stars, it is believed that LiBeB cosmic rays are produced almost entirely as a result of fragmentation reactions of heavier cosmic-ray nuclei (e.g., carbon and oxygen) with interstellar material. Most stable nucleides of lithium, beryllium, and boron are thought to ...
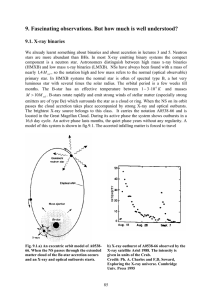
9. Fascinating observations. But how much is well understood?
... 9.1. X-ray binaries We already learnt something about binaries and about accretion in lectures 3 and 5. Neutron stars are more abundant than BHs. In most X-ray emitting binary systems the compact component is a neutron star. Astronomers distinguish between high mass x-ray binaries (HMXB) and low mas ...
... 9.1. X-ray binaries We already learnt something about binaries and about accretion in lectures 3 and 5. Neutron stars are more abundant than BHs. In most X-ray emitting binary systems the compact component is a neutron star. Astronomers distinguish between high mass x-ray binaries (HMXB) and low mas ...
Here`s
... new composite image of Abell 2744. The blue shows a map of the total mass concentration (mostly dark matter). By fitting a theoretical model of the composition of the Universe to the combined set of cosmological observations, scientists have come up with the composition that we described above, ~68% ...
... new composite image of Abell 2744. The blue shows a map of the total mass concentration (mostly dark matter). By fitting a theoretical model of the composition of the Universe to the combined set of cosmological observations, scientists have come up with the composition that we described above, ~68% ...
November 2014 - Hermanus Astronomy
... Andromedae). Andromeda was the daughter of the mythical queen Cassiopeia whose constellation lies further north, and is not fully visible this far south. Although the 19th largest constellation contains several features visible through a small telescope, Andromeda is most famous for its galaxy. The ...
... Andromedae). Andromeda was the daughter of the mythical queen Cassiopeia whose constellation lies further north, and is not fully visible this far south. Although the 19th largest constellation contains several features visible through a small telescope, Andromeda is most famous for its galaxy. The ...
Light Waves
... control tower that is a.analyzed by a Doppler scanner on the ground. b.reflected off a plane back to the control tower. c.increased in intensity as it passes through the atmosphere. d.scanned and analyzed by a receiver on board an airplane. ...
... control tower that is a.analyzed by a Doppler scanner on the ground. b.reflected off a plane back to the control tower. c.increased in intensity as it passes through the atmosphere. d.scanned and analyzed by a receiver on board an airplane. ...
Composition Of The Solar System
... visible from the southern hemisphere. They are called the Large Magellanic Cloud and the Small Magellanic Cloud. The nearest large galaxy is the Andromeda Galaxy. It is a spiral galaxy like the Milky Way but is 4 times as massive and is 2 million light years away. The planets, most of the satellites ...
... visible from the southern hemisphere. They are called the Large Magellanic Cloud and the Small Magellanic Cloud. The nearest large galaxy is the Andromeda Galaxy. It is a spiral galaxy like the Milky Way but is 4 times as massive and is 2 million light years away. The planets, most of the satellites ...
Light waves Review
... control tower that is analyzed by a Doppler scanner on the ground. b) reflected off a plane back to the control tower. c) increased in intensity as it passes through the atmosphere. d) scanned and analyzed by a receiver on board an airplane. a) ...
... control tower that is analyzed by a Doppler scanner on the ground. b) reflected off a plane back to the control tower. c) increased in intensity as it passes through the atmosphere. d) scanned and analyzed by a receiver on board an airplane. a) ...
Slide 1
... • Earth is a giant electromagnet. • The northern and southern lights (auroras) are global, dynamic glowing light displays originating at the boundary between Earth’s atmosphere and space. • The Sun’s particles affect the magnetic field surrounding Earth in a dynamic way. ...
... • Earth is a giant electromagnet. • The northern and southern lights (auroras) are global, dynamic glowing light displays originating at the boundary between Earth’s atmosphere and space. • The Sun’s particles affect the magnetic field surrounding Earth in a dynamic way. ...
Black Holes
... Like a rubber sheet, but in three dimensions, curvature dictates how all objects, including light, move when close to a mass. ...
... Like a rubber sheet, but in three dimensions, curvature dictates how all objects, including light, move when close to a mass. ...
Electromagnetic Propagation
... he observed radio waves coming from the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. – Not allowed to investigate more . . . ...
... he observed radio waves coming from the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. – Not allowed to investigate more . . . ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.