Size and Scale of the Universe
... Examples: Parallax, Moving Clusters, Time Delays, Water MASERs Considered to be a direct or absolute measurement ...
... Examples: Parallax, Moving Clusters, Time Delays, Water MASERs Considered to be a direct or absolute measurement ...
Laser Spectroscopy of Rubidium - University of San Diego Home
... The diagram in FIG. (2) shows the relevant block diagram and general set-up for the experiment. First we have a 780.2 nm tunable laser diode to sweep through the resonant frequency range from the ground state to the first excited state of Rb. The laser first gets split so one path leads to the etalo ...
... The diagram in FIG. (2) shows the relevant block diagram and general set-up for the experiment. First we have a 780.2 nm tunable laser diode to sweep through the resonant frequency range from the ground state to the first excited state of Rb. The laser first gets split so one path leads to the etalo ...
CosmologyL2
... …………………… The outstanding feature, is the possibility that the velocitydistance relation may represent the de Sitter effect, and hence that numerical data may be introduced into discussions of the general curvature of space. In the de Sitter cosmology, displacements of the spectra arise from two sour ...
... …………………… The outstanding feature, is the possibility that the velocitydistance relation may represent the de Sitter effect, and hence that numerical data may be introduced into discussions of the general curvature of space. In the de Sitter cosmology, displacements of the spectra arise from two sour ...
P3 Further Physics - The Thomas Cowley High School
... – Increases with more current and a stronger field. – Is at right angles to the magnetic field and current. – Is reversed if the current or field is reversed. ...
... – Increases with more current and a stronger field. – Is at right angles to the magnetic field and current. – Is reversed if the current or field is reversed. ...
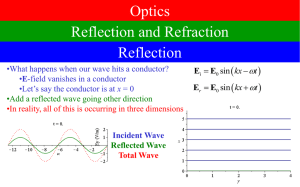
Reflect/Refract
... •Confusingly, its dependence is often given as a function of wavelength in vacuum •Called dispersion •This means that different types of light bend by different amounts in any given material •For most materials, the index of refraction is higher for short wavelength Red Refracts Rotten Blue Bends Be ...
... •Confusingly, its dependence is often given as a function of wavelength in vacuum •Called dispersion •This means that different types of light bend by different amounts in any given material •For most materials, the index of refraction is higher for short wavelength Red Refracts Rotten Blue Bends Be ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... Protostars emit mostly IR thermal radiation as they generate energy by converting gravitational potential energy into heat during collapse. The IR thermal radiation can pass through significant amounts of dust without attenuation. Thus, the dust is transparent to IR radiation and we can “see” the st ...
... Protostars emit mostly IR thermal radiation as they generate energy by converting gravitational potential energy into heat during collapse. The IR thermal radiation can pass through significant amounts of dust without attenuation. Thus, the dust is transparent to IR radiation and we can “see” the st ...
EBB 424E Semiconductor Devices and Optoelectronics
... energy unit. The size of the unit – photon. Explain the photoelectric effect - electron can be emitted if light is shone on a piece of metal Energy of the light beam is not spread but propagate like particles ...
... energy unit. The size of the unit – photon. Explain the photoelectric effect - electron can be emitted if light is shone on a piece of metal Energy of the light beam is not spread but propagate like particles ...
Astrosat (India) - X-ray Astronomy Group at ISAS
... Photon counting + CCD based UV and optical detectors Filters: FUV: 135 nm, CIV (155 nm), 165 nm; NUV: CIII (190.9 nm), 225 nm, CII (235 nm), O II (247 nm), 255 nm, 285 nm ...
... Photon counting + CCD based UV and optical detectors Filters: FUV: 135 nm, CIV (155 nm), 165 nm; NUV: CIII (190.9 nm), 225 nm, CII (235 nm), O II (247 nm), 255 nm, 285 nm ...
Parallax, Apparent Magnitude and Absolute Magnitude
... nearby star observed six months apart. As the Earth orbits the Sun, its line of sight towards the star changes, which makes the star’s position shift against the (more distant) background stars (see Figure 2). Because the stars are so far away, this shift is tiny – even the nearest star, Proxima Cen ...
... nearby star observed six months apart. As the Earth orbits the Sun, its line of sight towards the star changes, which makes the star’s position shift against the (more distant) background stars (see Figure 2). Because the stars are so far away, this shift is tiny – even the nearest star, Proxima Cen ...
Integrated Science Concepts COS 2010 2011
... Describe how ions are formed when an atom or a group of atoms acquire an unbalanced charge by gaining or losing one or more electrons Name the (physical and chemical) types of properties that can be used to help identify an object/material. Identify specific information able to be obtained about a p ...
... Describe how ions are formed when an atom or a group of atoms acquire an unbalanced charge by gaining or losing one or more electrons Name the (physical and chemical) types of properties that can be used to help identify an object/material. Identify specific information able to be obtained about a p ...
H-R Diagram
... To identify the characteristics of a star from data in the diagram To classify a star by its position in the diagram To compare the life cycle stages of stars based on their positions in the diagram Background The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, or H-R diagram, is a graph in which a star's temperature ...
... To identify the characteristics of a star from data in the diagram To classify a star by its position in the diagram To compare the life cycle stages of stars based on their positions in the diagram Background The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, or H-R diagram, is a graph in which a star's temperature ...
Final Review Sheet
... Very tenuous gas. On the average about an atom every cm**3 dust is about 1% by mass of the ISM Has complex history and ecology. Left over from galaxy formation (an ongoing process), then additions from stellar winds, planetary nebulae, and supernovae. Provides the necessary matter to make new stars. ...
... Very tenuous gas. On the average about an atom every cm**3 dust is about 1% by mass of the ISM Has complex history and ecology. Left over from galaxy formation (an ongoing process), then additions from stellar winds, planetary nebulae, and supernovae. Provides the necessary matter to make new stars. ...
All About MACHO
... dence comes from the speeds of stars and hydrogen gas clouds moving in spiral galaxies. These speeds, accurately measured using the Doppler effect, are much faster than can be explained if only the gravity from observed stars, gas, and dust is taken into account. Especially in the outer reaches of s ...
... dence comes from the speeds of stars and hydrogen gas clouds moving in spiral galaxies. These speeds, accurately measured using the Doppler effect, are much faster than can be explained if only the gravity from observed stars, gas, and dust is taken into account. Especially in the outer reaches of s ...
Article 8
... So what is this magical thing called "nuclear fusion" and why does it start happening inside the ball of gas and dust? It happens like this..... As the contraction of the gas and dust progresses and the temperature reaches 15 million degrees or so, the pressure at the center of the ball becomes enor ...
... So what is this magical thing called "nuclear fusion" and why does it start happening inside the ball of gas and dust? It happens like this..... As the contraction of the gas and dust progresses and the temperature reaches 15 million degrees or so, the pressure at the center of the ball becomes enor ...
MODERN PHYSICS
... 1. Briefly and clearly answer the following questions: (a) Briefly describe Rutherford’s model of the atom. What are the major drawbacks of his model? Explain your answer briefly. (4+4=8 pts) ...
... 1. Briefly and clearly answer the following questions: (a) Briefly describe Rutherford’s model of the atom. What are the major drawbacks of his model? Explain your answer briefly. (4+4=8 pts) ...
2.8 Atomic Spectra of Hydrogen For some time scientist had known
... ordinary temperature, hydrogen atom, as well as most other atoms and molecules are found almost exclusively in their ground electronic states. The states of higher energy are called excited states and are generally unstable with respect to the ground state. An atom or a molecule in an excited state ...
... ordinary temperature, hydrogen atom, as well as most other atoms and molecules are found almost exclusively in their ground electronic states. The states of higher energy are called excited states and are generally unstable with respect to the ground state. An atom or a molecule in an excited state ...
Lecture 24
... Pigments absorb specific colors, so they subtract colors from a painting or document. To mix pigments, we choose pigments that absorb just one color: ...
... Pigments absorb specific colors, so they subtract colors from a painting or document. To mix pigments, we choose pigments that absorb just one color: ...
Solar System Science
... 1.2 From exo-planets to bio-markers Search for and image planets around stars other than the Sun, looking for biomarkers in their atmospheres Census of exo-planets from high accuracy astrometry Detection of planets of smaller mass in the habitable zone from high accuracy photometric ...
... 1.2 From exo-planets to bio-markers Search for and image planets around stars other than the Sun, looking for biomarkers in their atmospheres Census of exo-planets from high accuracy astrometry Detection of planets of smaller mass in the habitable zone from high accuracy photometric ...
Outline - Picnic Point High School
... The Universe began with a singularity in space-time. After the initial explosion, the Universe started to expand, cool and condense, forming matter. As part of this ongoing process the Sun and the Solar System were formed over 4x109 years ago from a gas cloud which resulted from a supernova explosio ...
... The Universe began with a singularity in space-time. After the initial explosion, the Universe started to expand, cool and condense, forming matter. As part of this ongoing process the Sun and the Solar System were formed over 4x109 years ago from a gas cloud which resulted from a supernova explosio ...
I Laser A laser is a device that emits light (electromagnetic radiation
... photon is emitted in the same direction as the light that is passing by. When the number of particles in one excited state exceeds the number of particles in some lower-energy state, population inversion is achieved and the amount of stimulated emission due to light that passes through is larger tha ...
... photon is emitted in the same direction as the light that is passing by. When the number of particles in one excited state exceeds the number of particles in some lower-energy state, population inversion is achieved and the amount of stimulated emission due to light that passes through is larger tha ...
Siriusposter
... white dwarfs. At these energies, white dwarfs are far brighter than most normal stars, and with ROSAT’s help we have been able to identify over 20 of these degenerate objects in binaries with bright, normal companions, just like the Sirius system. At optical wavelengths the white dwarfs are unresolv ...
... white dwarfs. At these energies, white dwarfs are far brighter than most normal stars, and with ROSAT’s help we have been able to identify over 20 of these degenerate objects in binaries with bright, normal companions, just like the Sirius system. At optical wavelengths the white dwarfs are unresolv ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.