APS Centenary Poster - Bartol Research Institute
... But massive stars show the strongest winds, with speeds sometimes exceeding 3000 km/s, and mass loss rates up to a billion times the solar wind, i.e. ~ 10-5 MO/yr ! This is large enough that, during the course of their relatively brief (~107 yr) evolutionary lifetime, such massive stars can be str ...
... But massive stars show the strongest winds, with speeds sometimes exceeding 3000 km/s, and mass loss rates up to a billion times the solar wind, i.e. ~ 10-5 MO/yr ! This is large enough that, during the course of their relatively brief (~107 yr) evolutionary lifetime, such massive stars can be str ...
Ion-supported tori: a thermal bremsstrahlung model for the X
... emerged in relation to recent discussions of energy advection solutions (see Begelman 1978 and Abramowicz et al. 1988, for high-M, optically thick systems, and Rees et al. 1982; Abramowicz et al. 1995 and Narayan & Yi 1994, 1995a, b for the low-M, optically thin solution relevant here) for accretion ...
... emerged in relation to recent discussions of energy advection solutions (see Begelman 1978 and Abramowicz et al. 1988, for high-M, optically thick systems, and Rees et al. 1982; Abramowicz et al. 1995 and Narayan & Yi 1994, 1995a, b for the low-M, optically thin solution relevant here) for accretion ...
The COMPLETE Survey of Star-Forming Regions: Why, How & When
... Doug Johnstone (HIA, Canada) Naomi Ridge (UMASS/FCRAOCfA) Scott Schnee (CfA, PhD student) Mario Tafalla (OAS, Spain) Tom Wilson (MPIfR) ...
... Doug Johnstone (HIA, Canada) Naomi Ridge (UMASS/FCRAOCfA) Scott Schnee (CfA, PhD student) Mario Tafalla (OAS, Spain) Tom Wilson (MPIfR) ...
2012-13_1st_Sem_Final_ SG
... Can you explain how a ccd camera takes a telescope picture and how that picture is unique – what information is embedded in the pixels? Can you use an image processing program to manipulate a telescope ccd image? (Either ImageJ or MicroObservatory Image); Can you download an image, open it, adjust i ...
... Can you explain how a ccd camera takes a telescope picture and how that picture is unique – what information is embedded in the pixels? Can you use an image processing program to manipulate a telescope ccd image? (Either ImageJ or MicroObservatory Image); Can you download an image, open it, adjust i ...
David S. Stevenson
... This book follows the ongoing work of researchers studying the many disparate branches of science, including astrophysics, chemistry, geology, and biology. Their aim is to create a more holistic view of habitability, based around a large number of interlinked factors. In essence, the question of hab ...
... This book follows the ongoing work of researchers studying the many disparate branches of science, including astrophysics, chemistry, geology, and biology. Their aim is to create a more holistic view of habitability, based around a large number of interlinked factors. In essence, the question of hab ...
EMR - electromagnetic radiation - Environmental Health
... ionizing radiation damage, 11. Infrared is at the border with visible light and can be felt as ____, 12. Older mammography machines typically delivered a ______ dose of radiation, 13. Of all the EMR only about one sixth of all the light can be recognized as light by by ______, 14. Microwaves range f ...
... ionizing radiation damage, 11. Infrared is at the border with visible light and can be felt as ____, 12. Older mammography machines typically delivered a ______ dose of radiation, 13. Of all the EMR only about one sixth of all the light can be recognized as light by by ______, 14. Microwaves range f ...
observation reports
... seeking out finer detail in globulars, and looking out for elusive galaxies. 21:00 UT (22:00 local) Aligned the ETX on Altair and Arcturus, followed by a warm-up session of top doubles. 21:40 (22:40) I switched to high power for a detailed look at top globulars for comparison. In the end, I was able ...
... seeking out finer detail in globulars, and looking out for elusive galaxies. 21:00 UT (22:00 local) Aligned the ETX on Altair and Arcturus, followed by a warm-up session of top doubles. 21:40 (22:40) I switched to high power for a detailed look at top globulars for comparison. In the end, I was able ...
Astronomy 122 mid Term Exam
... Here is an example that got ½ credit – again even though it’s not even close to correct: “You determine the age by looking at the stars around it. Since they are in a stellar cluster they are the same age. The age of the star is 2 times the age of the Sun.” Or “The most massive star still on the mai ...
... Here is an example that got ½ credit – again even though it’s not even close to correct: “You determine the age by looking at the stars around it. Since they are in a stellar cluster they are the same age. The age of the star is 2 times the age of the Sun.” Or “The most massive star still on the mai ...
Space revision notes
... protons which would form the first chemicals – helium and hydrogen. The matter started to come together due to gravity forming stars and galaxies. When more complex chemicals arose, planets and moons started to form. The Universe is still expanding and may go o doing so for ever. ...
... protons which would form the first chemicals – helium and hydrogen. The matter started to come together due to gravity forming stars and galaxies. When more complex chemicals arose, planets and moons started to form. The Universe is still expanding and may go o doing so for ever. ...
Earth as a transiting planet
... signal-to-noise ratio for spectral features in the primary eclipse spectrum of an Earth-like exoplanet around a Sun-like star and also M stars, for a 6.5-m telescope in space. We find that the signal to noise values for all important spectral features are on the order of unity or less per transit - ...
... signal-to-noise ratio for spectral features in the primary eclipse spectrum of an Earth-like exoplanet around a Sun-like star and also M stars, for a 6.5-m telescope in space. We find that the signal to noise values for all important spectral features are on the order of unity or less per transit - ...
the opportunities and challenges for astrometry in the 21st century
... in the infrared. Over the course of the past decade Genzel et al. (1997) and UCLA (Ghez 2008) have measured the orbital parameters of several massive stars as they orbit the center of the Galaxy. Remarkably, by observing in the infrared they can observe through 20 visual magnitudes of obscuration an ...
... in the infrared. Over the course of the past decade Genzel et al. (1997) and UCLA (Ghez 2008) have measured the orbital parameters of several massive stars as they orbit the center of the Galaxy. Remarkably, by observing in the infrared they can observe through 20 visual magnitudes of obscuration an ...
Maximum Mass Limit of Stars on the Main Sequence
... of these objects. Essentially, there are no conclusive observations that indicate whether a slow or a fast method applies to this type of stellar formation. Regardless of the approach, some of the gas in these filaments can become gravitationally bound and begin the collapse necessary to begin the ...
... of these objects. Essentially, there are no conclusive observations that indicate whether a slow or a fast method applies to this type of stellar formation. Regardless of the approach, some of the gas in these filaments can become gravitationally bound and begin the collapse necessary to begin the ...
Document
... by gravity • Elliptical-shaped galaxies are most common • Spiral galaxies look like a pinwheel • Irregular galaxies are smaller and less common than other galaxies • Earth is in a spiral galaxy called the Milky Way ...
... by gravity • Elliptical-shaped galaxies are most common • Spiral galaxies look like a pinwheel • Irregular galaxies are smaller and less common than other galaxies • Earth is in a spiral galaxy called the Milky Way ...
Star and Planet Formation - Homepages of UvA/FNWI staff
... movement of the Earth on its orbit. 2. If the Earth rotates around its axis (as required to explain day and night), things should fly off the spinning planet. 3. If the Earth rotates around the Sun, we should observe parallaxes for the fixed stars. While the first two can actually be attributed to a ...
... movement of the Earth on its orbit. 2. If the Earth rotates around its axis (as required to explain day and night), things should fly off the spinning planet. 3. If the Earth rotates around the Sun, we should observe parallaxes for the fixed stars. While the first two can actually be attributed to a ...
ph512-11-lec5
... application for the future, the information obtained by astrometric measurements is now very important in contemporary research into the kinematics and physical origin of our Solar System and our Galaxy, the Milky Way. Astrometry: the branch of astronomy concerned with the measurement of the positio ...
... application for the future, the information obtained by astrometric measurements is now very important in contemporary research into the kinematics and physical origin of our Solar System and our Galaxy, the Milky Way. Astrometry: the branch of astronomy concerned with the measurement of the positio ...
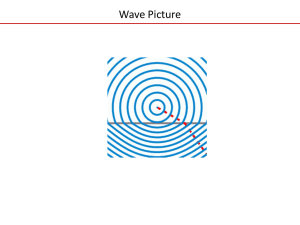
Wave Picture
... Snell's law seems to require in some cases (whenever the angle of incidence is large enough) that the sine of the angle of refraction be greater than one. This of course is impossible, and the light in such cases is completely reflected by the boundary, a phenomenon known as total internal reflectio ...
... Snell's law seems to require in some cases (whenever the angle of incidence is large enough) that the sine of the angle of refraction be greater than one. This of course is impossible, and the light in such cases is completely reflected by the boundary, a phenomenon known as total internal reflectio ...
Astro 10: Introductory Astronomy
... • The “Fast” scenario: eddys form, merge. Eddys include not just dust (which is only ~2% of total mass recall), but hydrogen and helium as well (much more mass here). The growth rate would be much faster as gravity would kick in right away for such massive objects. ...
... • The “Fast” scenario: eddys form, merge. Eddys include not just dust (which is only ~2% of total mass recall), but hydrogen and helium as well (much more mass here). The growth rate would be much faster as gravity would kick in right away for such massive objects. ...
Experimental basis for special relativity
... • If there was a medium for light wave propagation, then the speed of light must be measured relative to that medium • Thus the ether could provide an absolute reference frame for all measurements • The ether must have some strange properties – it must be solid-like to support high-frequency transve ...
... • If there was a medium for light wave propagation, then the speed of light must be measured relative to that medium • Thus the ether could provide an absolute reference frame for all measurements • The ether must have some strange properties – it must be solid-like to support high-frequency transve ...
The luminiferous ether Consequences of the ether
... • However, Einstein gave the correct explanation in terms of relativistic velocity addition. A light ray will have a different angle in different relativistic frames of reference ...
... • However, Einstein gave the correct explanation in terms of relativistic velocity addition. A light ray will have a different angle in different relativistic frames of reference ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.