Lecture 3: Specific Intensity, Flux and Optical Depth
... source. Intensity would be constant. However, the Universe is full of matter that will both absorb energy from the beam of light and add energy to it. A description of how the intensity changes as it moves through space (with matter in it) is given by the equation of radiative transfer. This may be ...
... source. Intensity would be constant. However, the Universe is full of matter that will both absorb energy from the beam of light and add energy to it. A description of how the intensity changes as it moves through space (with matter in it) is given by the equation of radiative transfer. This may be ...
The quest for cradles of life: using the fundamental metallicity
... Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) show that the three key physical properties (total stellar mass, ongoing star formation rate and gas-phase metallicity) are intricately linked with minimal scatter for more than a 140,000 galaxies in the local Universe through an intrinsic “Fundamental Metallicity Rel ...
... Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) show that the three key physical properties (total stellar mass, ongoing star formation rate and gas-phase metallicity) are intricately linked with minimal scatter for more than a 140,000 galaxies in the local Universe through an intrinsic “Fundamental Metallicity Rel ...
ph507lecnote07
... sunspot cycle. At these times, the corona is much less regular and much more extended than at sunspot minimum. Astronomers believe that coronal heating is caused by surface activity on the Sun. The changing shape and size of the corona are the direct result of variations in prominence and flare acti ...
... sunspot cycle. At these times, the corona is much less regular and much more extended than at sunspot minimum. Astronomers believe that coronal heating is caused by surface activity on the Sun. The changing shape and size of the corona are the direct result of variations in prominence and flare acti ...
Dr - srldc
... development of science is a special one. He I best known for his explanation of Universal Gravitation and three laws of motion, and he was able to prove that the reason of both the motion of objects on Earth and of celestial bodies are controlled by the same Neutral laws. These findings could make a ...
... development of science is a special one. He I best known for his explanation of Universal Gravitation and three laws of motion, and he was able to prove that the reason of both the motion of objects on Earth and of celestial bodies are controlled by the same Neutral laws. These findings could make a ...
Winter Night Sky Guide
... a bright yellowy looking star. This is Aldebaran, the eye of the bull in the constellation Taurus. Aldebaran is at the top of the lower leg of a vee-shaped group of stars. This is another open cluster called the Hyades, although Aldebaran is not actually part of this cluster because it is much close ...
... a bright yellowy looking star. This is Aldebaran, the eye of the bull in the constellation Taurus. Aldebaran is at the top of the lower leg of a vee-shaped group of stars. This is another open cluster called the Hyades, although Aldebaran is not actually part of this cluster because it is much close ...
Abstracts - Space Telescope Science Institute
... Over the past three years, two of the largest-ever HST stellar spectroscopic Guest Observer programs have been undertaken. The “Advanced Spectral Library (ASTRAL)” Project (PI = T. Ayres) consists of two Treasury Programs, the first in Cycle 18 on “Cool Stars” (GO-12278) and the second in the curren ...
... Over the past three years, two of the largest-ever HST stellar spectroscopic Guest Observer programs have been undertaken. The “Advanced Spectral Library (ASTRAL)” Project (PI = T. Ayres) consists of two Treasury Programs, the first in Cycle 18 on “Cool Stars” (GO-12278) and the second in the curren ...
Astronomy 401 Lecture 4 Kinematics of the Milky Way 1 The local
... A plot of rotational velocity vs radius is called a rotation curve. Measurements of velocities of objects at R > R0 (Cepheid variables for which we can measure distances; more on that later) show that the rotational speed V (R) doesn’t significantly decrease with distance beyond R0 . This was a big ...
... A plot of rotational velocity vs radius is called a rotation curve. Measurements of velocities of objects at R > R0 (Cepheid variables for which we can measure distances; more on that later) show that the rotational speed V (R) doesn’t significantly decrease with distance beyond R0 . This was a big ...
Revision Guide (Unit 2 Module 5) - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... • or the stars are not uniformly distributed • or it is not static (or two or all of these might be true). Today, it is generally accepted that the universe is not infinite, and that it is expanding rather than static. The Cosmological Principle states that the universe has a generally uniform app ...
... • or the stars are not uniformly distributed • or it is not static (or two or all of these might be true). Today, it is generally accepted that the universe is not infinite, and that it is expanding rather than static. The Cosmological Principle states that the universe has a generally uniform app ...
Slide 1
... Usual Observer Questions for particle acceleration people… • What fraction of free energy goes into protons vs. electrons? • What are overall acceleration efficiencies? • What’s the electron energy spectrum? [Probably there are multiple acceleration/dissipation regions – what are energy >spectra< ...
... Usual Observer Questions for particle acceleration people… • What fraction of free energy goes into protons vs. electrons? • What are overall acceleration efficiencies? • What’s the electron energy spectrum? [Probably there are multiple acceleration/dissipation regions – what are energy >spectra< ...
Binocular Sky Newsletter
... evening skies. Also look out for the nearby NGC1647. Open (also called 'Galactic') Clusters are loosely packed groups of stars that are gravitationally bound together; they may contain from a few dozen to a few thousand stars which recently formed in the galactic disk. ...
... evening skies. Also look out for the nearby NGC1647. Open (also called 'Galactic') Clusters are loosely packed groups of stars that are gravitationally bound together; they may contain from a few dozen to a few thousand stars which recently formed in the galactic disk. ...
SMA Observations of AB Aur
... The CD around AB Aur was imaged in 12CO 3-2 and 345 GHz continuum using the SMA, revealing details of structures of the CD. The dust disk was clearly resolved, showing a ring-like structure around the central star. ...
... The CD around AB Aur was imaged in 12CO 3-2 and 345 GHz continuum using the SMA, revealing details of structures of the CD. The dust disk was clearly resolved, showing a ring-like structure around the central star. ...
Chapter 2 The HRS+ Sample 2.1 The Herschel Reference Survey
... sample of 454 galaxies residing within the area of sky between 10h 17m < R.A.(2000) < 14h 43m and -6◦ < Dec. < 60◦ , shown in Figure 2.1. This sample consists of 171 early-type and 283 late-type galaxies inhabiting a range of different environments, from members in the dense center of the Virgo clus ...
... sample of 454 galaxies residing within the area of sky between 10h 17m < R.A.(2000) < 14h 43m and -6◦ < Dec. < 60◦ , shown in Figure 2.1. This sample consists of 171 early-type and 283 late-type galaxies inhabiting a range of different environments, from members in the dense center of the Virgo clus ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Neutron stars, pulsars and black holes
... • The discovery of pulsars that were spinning more than 100 times per second (the first was spinning 640 times per second) threw the field for a loop. When some millisecond pulsars were discovered in old star clusters it was even more confusing. • Eventually it was determined that all millisecond pu ...
... • The discovery of pulsars that were spinning more than 100 times per second (the first was spinning 640 times per second) threw the field for a loop. When some millisecond pulsars were discovered in old star clusters it was even more confusing. • Eventually it was determined that all millisecond pu ...
Great Migrations & other natural history tales
... parts. This was done by comparing IR spectra obtained with single dish telescopes with those obtained while combining several such telescopes into an interferometric array (this technique, long practiced by radio astronomers, allows us to achieve very good, low-angular resolution, observations). ...
... parts. This was done by comparing IR spectra obtained with single dish telescopes with those obtained while combining several such telescopes into an interferometric array (this technique, long practiced by radio astronomers, allows us to achieve very good, low-angular resolution, observations). ...
Beta Pictoris
... parts. This was done by comparing IR spectra obtained with single dish telescopes with those obtained while combining several such telescopes into an interferometric array (this technique, long practiced by radio astronomers, allows us to achieve very good, low-angular resolution, observations). ...
... parts. This was done by comparing IR spectra obtained with single dish telescopes with those obtained while combining several such telescopes into an interferometric array (this technique, long practiced by radio astronomers, allows us to achieve very good, low-angular resolution, observations). ...
Astronomy perspective
... Probability is interpreted as the frequency of the outcome of a repeatable experiment. • Bayesian The interpretation of probability is more general and includes ‘a degree of belief’. * “The information in the data” vs. “the information about something” ...
... Probability is interpreted as the frequency of the outcome of a repeatable experiment. • Bayesian The interpretation of probability is more general and includes ‘a degree of belief’. * “The information in the data” vs. “the information about something” ...
1076
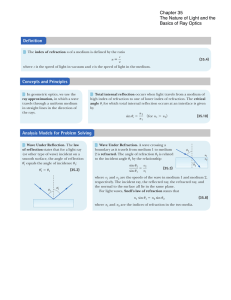
... 1. In each of the following situations, a wave passes through an opening in an absorbing wall. Rank the situations in order from the one in which the wave is best described by the ray approximation to the one in which the wave coming through the opening spreads out most nearly equally in all directi ...
... 1. In each of the following situations, a wave passes through an opening in an absorbing wall. Rank the situations in order from the one in which the wave is best described by the ray approximation to the one in which the wave coming through the opening spreads out most nearly equally in all directi ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... their spectral class which consists of a letter and a number. This historical classification is based on the strength of different spectral lines found in the spectra of the stars. It turned out later that these spectral classes are strongly related to the temperature of the star: The temperature of ...
... their spectral class which consists of a letter and a number. This historical classification is based on the strength of different spectral lines found in the spectra of the stars. It turned out later that these spectral classes are strongly related to the temperature of the star: The temperature of ...
Diffraction and Interference
... light. Colors are produced by interference between light beams. • So if you see red, what color is being cancelled? ...
... light. Colors are produced by interference between light beams. • So if you see red, what color is being cancelled? ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.