Astronomy Assignment #1
... 2. A star with the same color as the Sun is found to produce a luminosity 81 times larger. What is its radius, compared to the Sun’s? The following three problems all use the Stefan-Boltzmann Law L 4R 2 T 4 . We can avoid painful and error prone calculations, by using a ratio technique as illu ...
... 2. A star with the same color as the Sun is found to produce a luminosity 81 times larger. What is its radius, compared to the Sun’s? The following three problems all use the Stefan-Boltzmann Law L 4R 2 T 4 . We can avoid painful and error prone calculations, by using a ratio technique as illu ...
Unit 2 Lesson 1
... process of nuclear fusion. • It escapes in the form of light, other forms of radiation, heat, and wind. • Stars range in size from about the size of Earth to as much as 1,000 times the size of the sun. ...
... process of nuclear fusion. • It escapes in the form of light, other forms of radiation, heat, and wind. • Stars range in size from about the size of Earth to as much as 1,000 times the size of the sun. ...
SRP_Space_Lesson 5 - Scientist in Residence Program
... is to say, the stars do not really form that shape. The first observers of the sky thought that the stars in a constellation when connected resembled a shape that was familiar to them, and so they named it. This allowed them to map the movement of the stars throughout the seasons, which helped the d ...
... is to say, the stars do not really form that shape. The first observers of the sky thought that the stars in a constellation when connected resembled a shape that was familiar to them, and so they named it. This allowed them to map the movement of the stars throughout the seasons, which helped the d ...
Sunspots - Sage Middle School
... •temperature 1-3 million K •very irregularly shaped •strong x-ray emitter •uncertain as to why it is so hot •coronal holes are the origin of the solar wind •produces an absorption and continuous spectrum http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sunearth/news/colorful-science_prt.htm ...
... •temperature 1-3 million K •very irregularly shaped •strong x-ray emitter •uncertain as to why it is so hot •coronal holes are the origin of the solar wind •produces an absorption and continuous spectrum http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sunearth/news/colorful-science_prt.htm ...
Star Counts Lab
... sky,” but how many is that? In this lab you will make an estimate of how many stars you could see if you could see the entire sky with your naked eye. It would not be possible to count all the stars visible in the sky during a single lab meeting. For one reason, the number is very large; for another ...
... sky,” but how many is that? In this lab you will make an estimate of how many stars you could see if you could see the entire sky with your naked eye. It would not be possible to count all the stars visible in the sky during a single lab meeting. For one reason, the number is very large; for another ...
Polarization of Light Mica Sheet
... sunlight. The sun’s light is not polarized, but when it reflects off of objects, especially water, the reflected light is preferentially polarized along one direction. Therefore, by looking at an angle 90 degrees from the direction of the sun, the sky is polarized because of the light that’s reflect ...
... sunlight. The sun’s light is not polarized, but when it reflects off of objects, especially water, the reflected light is preferentially polarized along one direction. Therefore, by looking at an angle 90 degrees from the direction of the sun, the sky is polarized because of the light that’s reflect ...
Photonic Devices II Purpose of the Lab
... resonance wavelength. As mentioned above, piezo-electric crystals can be controlled such that the resulting movement is comparable with the diameter of an atom! If you want to tune a filter then of course there are two alternative approaches. You can physically move the mirrors such that the size o ...
... resonance wavelength. As mentioned above, piezo-electric crystals can be controlled such that the resulting movement is comparable with the diameter of an atom! If you want to tune a filter then of course there are two alternative approaches. You can physically move the mirrors such that the size o ...
The two components of the evolved massive binary LZ Cephei
... thus assume that the real determination of Harries et al. (1998) is l2 /l1 = 0.65 ± 0.1, which corresponds to l1 /l2 = 1.54 ± 0.3. Consequently, the discrepancy between our measurement and those of Harries et al. (1998) and Petrie (1962) is probably due to the sample of spectral lines that is larger ...
... thus assume that the real determination of Harries et al. (1998) is l2 /l1 = 0.65 ± 0.1, which corresponds to l1 /l2 = 1.54 ± 0.3. Consequently, the discrepancy between our measurement and those of Harries et al. (1998) and Petrie (1962) is probably due to the sample of spectral lines that is larger ...
NASSP Class Test – 2008 April 7th Section A
... (a) List three principal absorption or scattering processes which contribute to atmospheric extinction in the visible and near infrared and indicate what causes each. ...
... (a) List three principal absorption or scattering processes which contribute to atmospheric extinction in the visible and near infrared and indicate what causes each. ...
Name Date Life and Death of a Star 2015 1. In the main
... 29. When helium fusion takes over in a star's core, what happens? A. the energy output decreases B. energy output stays the same C. the energy output increases 30. A star that is gravitationally bound to another may be a A. binary B. red giant C. white dwarf D. constellation 31. A type II supernova ...
... 29. When helium fusion takes over in a star's core, what happens? A. the energy output decreases B. energy output stays the same C. the energy output increases 30. A star that is gravitationally bound to another may be a A. binary B. red giant C. white dwarf D. constellation 31. A type II supernova ...
Brightness + Magnitude of Stars
... A. Apparent or Relative Brightness-(cont.) *** As distance to Star Decreases brightness Increases (Inverse Relationship) *** As Luminosity of Star increases brightness Increases (Direct Relationship) B. Apparent Magnitude A number assigned to a celestial object that is a measure of its relative br ...
... A. Apparent or Relative Brightness-(cont.) *** As distance to Star Decreases brightness Increases (Inverse Relationship) *** As Luminosity of Star increases brightness Increases (Direct Relationship) B. Apparent Magnitude A number assigned to a celestial object that is a measure of its relative br ...
- saspcsus
... A. Students know the patterns of stars stay the same, although they appear to move across the sky nightly, and different stars can be seen in different seasons. B. Students know the way in which the Moon’s appearance changes during the four-week lunar cycle. C. Students know telescopes magnify the a ...
... A. Students know the patterns of stars stay the same, although they appear to move across the sky nightly, and different stars can be seen in different seasons. B. Students know the way in which the Moon’s appearance changes during the four-week lunar cycle. C. Students know telescopes magnify the a ...
Discovery of Warm and Dense Molecular Gas Surrounding the Ring
... This significant result encourages the search for molecular gas in the environs of evolved massive stars which have not yet become Wolf-Rayet. Of those, the luminous blue variable ( LBV ) stars are probably the best candidates, due to the ‘‘instantaneous’’ effect of their strong winds and spectacula ...
... This significant result encourages the search for molecular gas in the environs of evolved massive stars which have not yet become Wolf-Rayet. Of those, the luminous blue variable ( LBV ) stars are probably the best candidates, due to the ‘‘instantaneous’’ effect of their strong winds and spectacula ...
Astronomy Astrophysics IRAS 18357-0604 – an analogue of the galactic yellow hypergiant
... ∼4700–4950 Å region of the same spectrum (and also that of Klochkova et al. 2002). Given that these transitions are weaker in IRAS 1835−06 one might infer a slightly earlier spectral type for it than IRC +10420 (∼A0-2). This would also be consistent with the near-IR spectroscopic properties; the lac ...
... ∼4700–4950 Å region of the same spectrum (and also that of Klochkova et al. 2002). Given that these transitions are weaker in IRAS 1835−06 one might infer a slightly earlier spectral type for it than IRC +10420 (∼A0-2). This would also be consistent with the near-IR spectroscopic properties; the lac ...
document
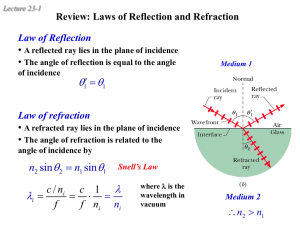
... The index of refraction of a medium is usually a function of the wavelength of the light. It is larger at shorter wavelengths. Consequently, a light beam consisting of rays of different wavelength (e.g., sun light) will be refracted at different angles at the interface of two different media. This s ...
... The index of refraction of a medium is usually a function of the wavelength of the light. It is larger at shorter wavelengths. Consequently, a light beam consisting of rays of different wavelength (e.g., sun light) will be refracted at different angles at the interface of two different media. This s ...
Understanding Waves: Seismic Waves and Ultrasound
... • Describe the parts of a wave. • Know the difference between longitudinal and transverse waves. • Use the wave equation. • Explain the processes of reflection, refraction and total internal reflection. • Know how sound waves behave and the uses of ...
... • Describe the parts of a wave. • Know the difference between longitudinal and transverse waves. • Use the wave equation. • Explain the processes of reflection, refraction and total internal reflection. • Know how sound waves behave and the uses of ...
Foundation 1 - Discovering Astronomy
... When core hydrogen fusion ceases, a main-sequence star becomes a giant • When hydrogen fusion ceases in the core, the star will collapse inward – this causes the layer just outside the core to become so hot and dense that hydrogen fusion will begin in this outer layer. • The energy produced by hydr ...
... When core hydrogen fusion ceases, a main-sequence star becomes a giant • When hydrogen fusion ceases in the core, the star will collapse inward – this causes the layer just outside the core to become so hot and dense that hydrogen fusion will begin in this outer layer. • The energy produced by hydr ...
RSP Plans
... Study the properties of this microwave selected sample of jetdominated AGN looking for: ...
... Study the properties of this microwave selected sample of jetdominated AGN looking for: ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.