Life in the galactic danger zone
... for habitability, and a lower limit that is friendlier to life, reducing the possibility that a planet will be in the firing line of a torrent of harmful rays. Gowanlock’s logic is different. Yes, the galactic centre is subject to a large number of supernovae, and these can sterilise a larger number ...
... for habitability, and a lower limit that is friendlier to life, reducing the possibility that a planet will be in the firing line of a torrent of harmful rays. Gowanlock’s logic is different. Yes, the galactic centre is subject to a large number of supernovae, and these can sterilise a larger number ...
Circumpolar constellations
... Analyzing those observations, astronomers look for patterns that result from the Earth’s rotation on its axis as well its revolution around the Sun. Observation requires patience, because some celestial motions take long periods of time to repeat. You may not notice the slow, subtle change in the po ...
... Analyzing those observations, astronomers look for patterns that result from the Earth’s rotation on its axis as well its revolution around the Sun. Observation requires patience, because some celestial motions take long periods of time to repeat. You may not notice the slow, subtle change in the po ...
Presentation
... components, exhibit hyperbolic-type dispersion in space of wave vectors. Such media are referred as hyperbolic metamaterials (HMMs). A distinctive feature of such media is a capability to support propagation of electromagnetic waves with huge wave vector components, or by other words, electromagneti ...
... components, exhibit hyperbolic-type dispersion in space of wave vectors. Such media are referred as hyperbolic metamaterials (HMMs). A distinctive feature of such media is a capability to support propagation of electromagnetic waves with huge wave vector components, or by other words, electromagneti ...
Search for Planetary Candidates within the OGLE Stars
... stars: objects capable of thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen (>0.075 Msun); Brown dwarf: capable of deuterium burning (0.013
... stars: objects capable of thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen (>0.075 Msun); Brown dwarf: capable of deuterium burning (0.013
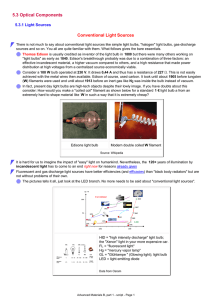
5.3 Optical Components Conventional Light Sources 5.3.1 Light Sources
... Just as important, the energy of the light produced would not be exactly ∆E but, roughly, ∆E ± kT since our excited electrons would also have some thermal energy. For a good monochromatic light, an energy or frequency spread of about 1/40 eV at room temperature is ridiculously large, so we must do s ...
... Just as important, the energy of the light produced would not be exactly ∆E but, roughly, ∆E ± kT since our excited electrons would also have some thermal energy. For a good monochromatic light, an energy or frequency spread of about 1/40 eV at room temperature is ridiculously large, so we must do s ...
r*=13.6 km MPA1 EOS
... more stars in a region only 30 light years across, which suggests that all the stars were born in a single episode of star formation. Based on optical properties such as brightness and color some of the normal stars in the cluster are known to have masses of about 40 suns. ...
... more stars in a region only 30 light years across, which suggests that all the stars were born in a single episode of star formation. Based on optical properties such as brightness and color some of the normal stars in the cluster are known to have masses of about 40 suns. ...
here
... small the gravitational force between the two objects can cause the orbiting planet’s period of rotation to become equal to its period of revolution. • This is referred to as tidal locking. The result is that only one side of the planet faces the star and is always illuminated, the other side never ...
... small the gravitational force between the two objects can cause the orbiting planet’s period of rotation to become equal to its period of revolution. • This is referred to as tidal locking. The result is that only one side of the planet faces the star and is always illuminated, the other side never ...
Astro 001 Spring 2002
... (42) The Doppler effect causes light from a source moving away to be A. shifted to shorter wavelengths. B. shifted to longer wavelengths. C. changed in velocity D. [Both A and C above.] E. [Both B and C above.] (43) We can determine the elements in the atmosphere of star by examining A. its color. B ...
... (42) The Doppler effect causes light from a source moving away to be A. shifted to shorter wavelengths. B. shifted to longer wavelengths. C. changed in velocity D. [Both A and C above.] E. [Both B and C above.] (43) We can determine the elements in the atmosphere of star by examining A. its color. B ...
CHEMICAL BONDING
... C has been found from experiment (and is now called R, the Rydberg constant) R (= C) = 1312 kJ/mol or 3.29 x 1015 cycles/sec so, E of emitted light = (3/4)R = 2.47 x 1015 sec-1 and = c/ = 121.6 nm This is exactly in agreement with experiment! ...
... C has been found from experiment (and is now called R, the Rydberg constant) R (= C) = 1312 kJ/mol or 3.29 x 1015 cycles/sec so, E of emitted light = (3/4)R = 2.47 x 1015 sec-1 and = c/ = 121.6 nm This is exactly in agreement with experiment! ...
here - Stars `r` Us!
... coolants. Cooling may prevent a cloud that is collapsing under its own weight from heating up, as gravitational potential energy is converted into heat. If the temperature remains sufficiently low, then the gas pressure will not rise enough to prevent the collapse. Something like this process must h ...
... coolants. Cooling may prevent a cloud that is collapsing under its own weight from heating up, as gravitational potential energy is converted into heat. If the temperature remains sufficiently low, then the gas pressure will not rise enough to prevent the collapse. Something like this process must h ...
Checklist for Geo- vs. Heliocentric Model of Universe
... allows galaxies to develop and die, to be replaced by new galaxies built from created matter Young galaxies should be evenly distributed, because they can be born anywhere and at any time out of the matter created in between old galaxies, but this is not backed by observation ...
... allows galaxies to develop and die, to be replaced by new galaxies built from created matter Young galaxies should be evenly distributed, because they can be born anywhere and at any time out of the matter created in between old galaxies, but this is not backed by observation ...
Word doc - UC-HiPACC - University of California, Santa Cruz
... ‘The burst of the century’ “This was the burst of the century!” exclaimed James A. Wren, an engineer at Los Alamos National Laboratory and co-author of one of the papers. Indeed, GRB 130427A (as it is now called) was the most powerful gamma-ray burst and the second-brightest optical flash measured i ...
... ‘The burst of the century’ “This was the burst of the century!” exclaimed James A. Wren, an engineer at Los Alamos National Laboratory and co-author of one of the papers. Indeed, GRB 130427A (as it is now called) was the most powerful gamma-ray burst and the second-brightest optical flash measured i ...
UMich w/s
... range of sigma is small (data <2) derivative term is (log) luminosity profile : light, NOT mass, and this is similar in scale for all the dSph (factor of few) So the derived mass really is a measure of the radial extent of the data, and only a weak function of ...
... range of sigma is small (data <2) derivative term is (log) luminosity profile : light, NOT mass, and this is similar in scale for all the dSph (factor of few) So the derived mass really is a measure of the radial extent of the data, and only a weak function of ...
Unit 3 - Lesson 8.2 2011 Sun
... The sun rotates on its axis one time every 25 days. currents are caused as a heated material is forced away from the core while cooled materials fall back down. are darker, cooler areas visible on the sun’s photosphere are found in active regions and release large quantities of gas (big bulge) _____ ...
... The sun rotates on its axis one time every 25 days. currents are caused as a heated material is forced away from the core while cooled materials fall back down. are darker, cooler areas visible on the sun’s photosphere are found in active regions and release large quantities of gas (big bulge) _____ ...
radius M
... model with Teff=1000 K, log g=5.5 (blue dotted line). The model accounts for the opacity contribution of the line wings out to 5000Å from the line centre. Two other are shown where the line opacity is accounted for out to 15000Å from the line centre (green and red lines), one where molecular opaciti ...
... model with Teff=1000 K, log g=5.5 (blue dotted line). The model accounts for the opacity contribution of the line wings out to 5000Å from the line centre. Two other are shown where the line opacity is accounted for out to 15000Å from the line centre (green and red lines), one where molecular opaciti ...
Dark matter distribution and indirect detection in dwarf spheroidal
... The gamma or neutrino flux in given by: ...
... The gamma or neutrino flux in given by: ...
Instrument Proposal Document
... that have been successfully demonstrated in the laboratory environment but have yet to be deployed in any astronomical instrument. The iBTF (imaging Bragg Tunable Filter) concept utilizes a Volume Phase Holographic (or Bragg Diffraction) Grating (VPHG) in double-pass configuration while the new Fabr ...
... that have been successfully demonstrated in the laboratory environment but have yet to be deployed in any astronomical instrument. The iBTF (imaging Bragg Tunable Filter) concept utilizes a Volume Phase Holographic (or Bragg Diffraction) Grating (VPHG) in double-pass configuration while the new Fabr ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.