An Overview of High Speed Semiconductor Lasers
... well, we should expect most of the excitons have their electron and hole either both in the quantum well or both outside the quantum well. As we have seen before, 2D exciton has 4 times larger ionization energy and therefore is much more stable than excitons outside the quantum well. ...
... well, we should expect most of the excitons have their electron and hole either both in the quantum well or both outside the quantum well. As we have seen before, 2D exciton has 4 times larger ionization energy and therefore is much more stable than excitons outside the quantum well. ...
Lab: Inverse Square Law
... Introduction: As light travels from a source it spreads out equally in all directions. The brightness of the light is the power (energy per second) per area. We all know that a light, such as a candle or a streetlight, looks dimmer the farther away from it we get. But how does the brightness change ...
... Introduction: As light travels from a source it spreads out equally in all directions. The brightness of the light is the power (energy per second) per area. We all know that a light, such as a candle or a streetlight, looks dimmer the farther away from it we get. But how does the brightness change ...
Metallicity maps
... but ram-pressure stripping is very important), they yield different metal distributions and have different time scales ram-pressure in the outskirts of clusters is sufficient to strip gas and form new stars inhomogeneous metallicity distribution, enriched material is not mixed immediately with I ...
... but ram-pressure stripping is very important), they yield different metal distributions and have different time scales ram-pressure in the outskirts of clusters is sufficient to strip gas and form new stars inhomogeneous metallicity distribution, enriched material is not mixed immediately with I ...
X-ray Optics - Studentportalen
... meV at an energy of around 20 keV. The limiting factor is here not fundamental, i. e. it is not dependent on how many contributing layers, but rather practical: How well can the scattering angles be determined. The quality of the crystals of course become crucial at some point, but as long as one ca ...
... meV at an energy of around 20 keV. The limiting factor is here not fundamental, i. e. it is not dependent on how many contributing layers, but rather practical: How well can the scattering angles be determined. The quality of the crystals of course become crucial at some point, but as long as one ca ...
Calculating Parallax Lab
... One of the most difficult problems in astronomy is determining the distances to objects in the sky. There are four basic methods of determining distances: radar, parallax, standard candles, and the Hubble Law. Each of these methods is most useful at certain distances, with radar being useful nearby ...
... One of the most difficult problems in astronomy is determining the distances to objects in the sky. There are four basic methods of determining distances: radar, parallax, standard candles, and the Hubble Law. Each of these methods is most useful at certain distances, with radar being useful nearby ...
The ExOoS Mission - Extraterrestrial Octopus on Steroids
... Astrobiology is one of the fields with the fastest development in the last years (Harrison et al. 2013; Seager et al. 2012). Advances in molecular techniques and technology have allowed the detection and the study of living organisms and their traces in environments traditionally unconceivable to ho ...
... Astrobiology is one of the fields with the fastest development in the last years (Harrison et al. 2013; Seager et al. 2012). Advances in molecular techniques and technology have allowed the detection and the study of living organisms and their traces in environments traditionally unconceivable to ho ...
E3 – Stellar distances
... Spectroscopic parallax - Example • A main sequence star emits most of its energy at λ = 2.4 x 10-7 m. Its apparent brightness is measured to be 4.3 x 10-9 W.m-2. How far away is the star? • λ 0T = 2.9 x 10-3 Km • T = 2.9 x 10-3 / 4.3 x 10-9 = 12000K ...
... Spectroscopic parallax - Example • A main sequence star emits most of its energy at λ = 2.4 x 10-7 m. Its apparent brightness is measured to be 4.3 x 10-9 W.m-2. How far away is the star? • λ 0T = 2.9 x 10-3 Km • T = 2.9 x 10-3 / 4.3 x 10-9 = 12000K ...
Characterizing the Cool KOIs
... • The Kepler-32 planets are representative of all of Keplerʼs M dwarf planets, and therefore M dwarfs throughout the Galaxy " • These are powerful constraints on the timescale and nature of the mechanisms that form some of the most numerous planetary systems in the Galaxy!" • The Solar System is ...
... • The Kepler-32 planets are representative of all of Keplerʼs M dwarf planets, and therefore M dwarfs throughout the Galaxy " • These are powerful constraints on the timescale and nature of the mechanisms that form some of the most numerous planetary systems in the Galaxy!" • The Solar System is ...
Time-Gated Photoionization Spectroscopy Demonstrated for Cesium Rydberg Wave Packets
... the interpretation of cesium time-gated spectra will follow in the remainder of this Letter, we would like to stress here that the time dependent flux into the atomic streak camera cannot be predicted from measurements of the energy dependent photoionization cross section (conventional spectroscopy) ...
... the interpretation of cesium time-gated spectra will follow in the remainder of this Letter, we would like to stress here that the time dependent flux into the atomic streak camera cannot be predicted from measurements of the energy dependent photoionization cross section (conventional spectroscopy) ...
Oxidation of Silicon
... typically in the range of 900-1200 degrees C. The atmosphere in the furnace where oxidation takes place can either contain pure oxygen or water vapor. Both of these molecules diffuse easily through the growing SiO2 layer at these high temperatures. Oxygen arriving at the silicon surface can then com ...
... typically in the range of 900-1200 degrees C. The atmosphere in the furnace where oxidation takes place can either contain pure oxygen or water vapor. Both of these molecules diffuse easily through the growing SiO2 layer at these high temperatures. Oxygen arriving at the silicon surface can then com ...
Absolute magnitude of type Ia supernovae
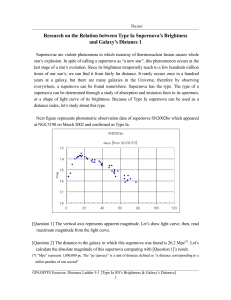
... times of our sun’s, we can find it from fairly far distance. It rarely occurs once in a hundred years at a galaxy, but there are many galaxies in the Universe, therefore by observing everywhere, a supernova can be found somewhere. Supernova has the type. The type of a supernova can be determined thr ...
... times of our sun’s, we can find it from fairly far distance. It rarely occurs once in a hundred years at a galaxy, but there are many galaxies in the Universe, therefore by observing everywhere, a supernova can be found somewhere. Supernova has the type. The type of a supernova can be determined thr ...
Waves Notes - Animated Science
... Waves can be produced in ropes, springs and on the surface of water. When waves travel along ropes or springs or across the surface of water they set up regular patterns of disturbance. They are a way of transferring energy from one point to another without transferring matter. The maximum disturb ...
... Waves can be produced in ropes, springs and on the surface of water. When waves travel along ropes or springs or across the surface of water they set up regular patterns of disturbance. They are a way of transferring energy from one point to another without transferring matter. The maximum disturb ...
1 - www2
... Examples. 1) Compare the brightness of the Sun with that of a typical He-Ne gas laser. The Sun has a surface temperature of ~ 6,000 K and the power density of its radiation is ρ = σ T4 = 5.6696·10−8 ·(6,000)4 W·m-2 = 7.4·107 W·m-2 derived from the Stefan-Boltzmann’s law. Thus, the brightness of the ...
... Examples. 1) Compare the brightness of the Sun with that of a typical He-Ne gas laser. The Sun has a surface temperature of ~ 6,000 K and the power density of its radiation is ρ = σ T4 = 5.6696·10−8 ·(6,000)4 W·m-2 = 7.4·107 W·m-2 derived from the Stefan-Boltzmann’s law. Thus, the brightness of the ...
A Drastic Chemical Change Occurring in Birth of Planetary System
... far, most of them have focused on a change in the physical structure and kinematics during the formation process. However, it was very difficult to distinguish the protoplanetary disk from the infalling envelope clearly with such conventional approaches. On the other hand, the chemical evolution ass ...
... far, most of them have focused on a change in the physical structure and kinematics during the formation process. However, it was very difficult to distinguish the protoplanetary disk from the infalling envelope clearly with such conventional approaches. On the other hand, the chemical evolution ass ...
10 New Constellations
... the primary component is a blue star with a radius 3 times greater than our sun with surface temperatures more than twice as hot. Alpheratz is officially the brightest star in Andromeda, it is also considered as part of Pegasus as it connects both constellations. M31 The most interesting object in t ...
... the primary component is a blue star with a radius 3 times greater than our sun with surface temperatures more than twice as hot. Alpheratz is officially the brightest star in Andromeda, it is also considered as part of Pegasus as it connects both constellations. M31 The most interesting object in t ...
Moving Stars and Their Planets Answer Key
... There is a lot of noise in the real-world data. Even though modern telescopes have less “noise” than earlier telescopes, the data are still not perfect signals. This could lead scientists to be unsure about whether a tiny signal is part of the noise or if it is a real signal that a star is moving du ...
... There is a lot of noise in the real-world data. Even though modern telescopes have less “noise” than earlier telescopes, the data are still not perfect signals. This could lead scientists to be unsure about whether a tiny signal is part of the noise or if it is a real signal that a star is moving du ...
A massive hypergiant star as the progenitor of the supernova SN
... shells4,28, along with very luminous optical displays, during which the luminosity of the star may increase by an order of magnitude or more. These events (sometimes called supernova impostors26) can therefore be confused with genuine supernova explosions. b, Collisions between a faster massive ejec ...
... shells4,28, along with very luminous optical displays, during which the luminosity of the star may increase by an order of magnitude or more. These events (sometimes called supernova impostors26) can therefore be confused with genuine supernova explosions. b, Collisions between a faster massive ejec ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.