The Onset of Matter-Wave Amplification in a Superradiant Bose
... momentum បk is scattered off a condensate atom (zero momentum), thereby producing a scattered photon with momentum ប(k ⫺ q) and a recoiling atom with momentum បq, q ⫽ 公2 k. In contrast, backward peaks [label (2)] are produced when a previously scattered photon is scattered back into the pump mode, t ...
... momentum បk is scattered off a condensate atom (zero momentum), thereby producing a scattered photon with momentum ប(k ⫺ q) and a recoiling atom with momentum បq, q ⫽ 公2 k. In contrast, backward peaks [label (2)] are produced when a previously scattered photon is scattered back into the pump mode, t ...
High-resolution Measurement of Refractive Index Based on Resonant Tunneling Effect
... We have presented a measurement device of refractive index with high transmissivity and Q factor based on resonant tunneling effect. Our device is constructed by one dimensional PC with a defect which gives rise to different resonant peaks in PC band gap. These peaks are sensitive to the medium whic ...
... We have presented a measurement device of refractive index with high transmissivity and Q factor based on resonant tunneling effect. Our device is constructed by one dimensional PC with a defect which gives rise to different resonant peaks in PC band gap. These peaks are sensitive to the medium whic ...
View/Open - Dora.dmu.ac.uk
... terms in its definition such as diffraction and interference. The main focus of this paper is to briefly explain these terms using analogies and discuss the construction details of the CυBE. The CυBE has got a vast number of applications in Display Holography. In academia there is an increasing dema ...
... terms in its definition such as diffraction and interference. The main focus of this paper is to briefly explain these terms using analogies and discuss the construction details of the CυBE. The CυBE has got a vast number of applications in Display Holography. In academia there is an increasing dema ...
ELECTRO-OPTICS
... We begin with a simple description of the electro-optic effect and the principles of electro-optic modulation and scanning (Sec. 18.1). The initial presentation is simplified by deferring the detailed consideration of anisotropic effects to Sec. 18.2. Section 18.3 is devoted to the electro-optic pro ...
... We begin with a simple description of the electro-optic effect and the principles of electro-optic modulation and scanning (Sec. 18.1). The initial presentation is simplified by deferring the detailed consideration of anisotropic effects to Sec. 18.2. Section 18.3 is devoted to the electro-optic pro ...
P - University of South Florida
... Three-dimensional microscopic imaging that reveals the tomographic structure of biological tissues or other materials has a variety of applications in clinical and laboratory studies. Recently developed optical coherence tomography [1] (OCT) is a scanning microscopic technique that is suitable for h ...
... Three-dimensional microscopic imaging that reveals the tomographic structure of biological tissues or other materials has a variety of applications in clinical and laboratory studies. Recently developed optical coherence tomography [1] (OCT) is a scanning microscopic technique that is suitable for h ...
Observation of modulational instability in Bose
... due to the presence of a partial pulse reshaping when using exact experimental conditions, as well as to losses and antitrapping potential not taken into account in our theoretical model. Note also that below as = −1.2 stable soliton solutions of the initial condensate do not exist, as determined by ...
... due to the presence of a partial pulse reshaping when using exact experimental conditions, as well as to losses and antitrapping potential not taken into account in our theoretical model. Note also that below as = −1.2 stable soliton solutions of the initial condensate do not exist, as determined by ...
HEAVY ION BEAM ACCELERATION
... optical condition for vertical transmission has been the same as 90 degree horizontal analysing magnet. The 90 degree bending magnet has same specification like 90 degree analyser. From this point the axial magnetic field contribution has to be taken into account for further beam optics calculation ...
... optical condition for vertical transmission has been the same as 90 degree horizontal analysing magnet. The 90 degree bending magnet has same specification like 90 degree analyser. From this point the axial magnetic field contribution has to be taken into account for further beam optics calculation ...
CfE Advanced Higher Physics – Unit 2 – Waves
... pendulum, a bobbing mass in water, all come to rest eventually. We say that their motion is damped. This means that the amplitude of the motion decreases to zero because energy is transformed from the system. A simple pendulum takes a long time to come to rest because the frictional effect supplied ...
... pendulum, a bobbing mass in water, all come to rest eventually. We say that their motion is damped. This means that the amplitude of the motion decreases to zero because energy is transformed from the system. A simple pendulum takes a long time to come to rest because the frictional effect supplied ...
Wave Optics and Gaussian Beams
... Gaussian Spherical Waves Higher-Order Gaussian Modes • Lowest Order Mode using differential approach • The ”standard” Hermite Polynomial solutions • The ”elegant” Hermite Polynomial solutions ...
... Gaussian Spherical Waves Higher-Order Gaussian Modes • Lowest Order Mode using differential approach • The ”standard” Hermite Polynomial solutions • The ”elegant” Hermite Polynomial solutions ...
Flat optics with designer metasurfaces
... light waves are gradually accumulated along the optical path. This Review focuses on recent developments on flat, ultrathin optical components dubbed ‘metasurfaces’ that produce abrupt changes over the scale of the free-space wavelength in the phase, amplitude and/or polarization of a light beam. Me ...
... light waves are gradually accumulated along the optical path. This Review focuses on recent developments on flat, ultrathin optical components dubbed ‘metasurfaces’ that produce abrupt changes over the scale of the free-space wavelength in the phase, amplitude and/or polarization of a light beam. Me ...
45.Z-scan measurement of the nonlinear refractive index of graphene
... June 1, 2012 / Vol. 37, No. 11 / OPTICS LETTERS ...
... June 1, 2012 / Vol. 37, No. 11 / OPTICS LETTERS ...
Optical path function.
... Æ No windows Æ The entire optical system must be kept under vacuum Ultrahigh vacuum conditions (P=1-2x10-9 mbar) are required: • Not to disturb the storage ring and the experiment • To avoid photon absorption in air • To protect the optical surfaces from contamination (especially from carbon) ...
... Æ No windows Æ The entire optical system must be kept under vacuum Ultrahigh vacuum conditions (P=1-2x10-9 mbar) are required: • Not to disturb the storage ring and the experiment • To avoid photon absorption in air • To protect the optical surfaces from contamination (especially from carbon) ...
Optimization of multilayer reflectors for extreme ultraviolet lithography
... systems must consist of reflective optics, since the EUV illuminating radiation 共typically in the 11- to 16-nm spectral region兲 is highly absorbed in all materials. Despite this absorption, a relatively high reflectivity is obtained with the aid of multilayer 共ML兲 deposition.2 Typically, in the 11- ...
... systems must consist of reflective optics, since the EUV illuminating radiation 共typically in the 11- to 16-nm spectral region兲 is highly absorbed in all materials. Despite this absorption, a relatively high reflectivity is obtained with the aid of multilayer 共ML兲 deposition.2 Typically, in the 11- ...
The interference characteristics of light
... The cat’s eye reflector is well designed, diffraction limited [5] and has little sensitivity to the direction of the incidence light [8], so it is a cooperative target in application. But the cat-eye optical lens is a non-cooperative target whose parameters are unknown. By using the active laser det ...
... The cat’s eye reflector is well designed, diffraction limited [5] and has little sensitivity to the direction of the incidence light [8], so it is a cooperative target in application. But the cat-eye optical lens is a non-cooperative target whose parameters are unknown. By using the active laser det ...
Beam steering with spatial light modulators: Quantisation effects
... So far, we have described the theoretical background for hologram design. From now on, we will develop the experimental details that need to be taken into consideration in hologram computation. For this purpose, we created a Matlab program. Due to the SLM non-flatness [4], a modification to the desc ...
... So far, we have described the theoretical background for hologram design. From now on, we will develop the experimental details that need to be taken into consideration in hologram computation. For this purpose, we created a Matlab program. Due to the SLM non-flatness [4], a modification to the desc ...
Stabler, Graham (2005) High resolution wide field surface plasmon
... The key problems with sensing and characterizing thin films optically, is the fact that they are thin[2]. This means that the optical path of light passing through the material is very short and the materials effect on the amplitude and phase of the light, small. This is especially so for the case o ...
... The key problems with sensing and characterizing thin films optically, is the fact that they are thin[2]. This means that the optical path of light passing through the material is very short and the materials effect on the amplitude and phase of the light, small. This is especially so for the case o ...
Ellipsometry of light scattering from multilayer coatings
... Therefore the polarimetric phase d could be basically deduced from Eq. ~12! and direct measurements made of locations and amplitudes of the extrema of G. However, the key point in ellipsometry concerns the sensitivity and accuracy of the measurements, for which reason we prefer to fit the measuremen ...
... Therefore the polarimetric phase d could be basically deduced from Eq. ~12! and direct measurements made of locations and amplitudes of the extrema of G. However, the key point in ellipsometry concerns the sensitivity and accuracy of the measurements, for which reason we prefer to fit the measuremen ...
1 Introduction 2 Theory of Optical Trapping
... Light can exert forces on small dielectric objects1,2. A tightly focused beam of light can trap micron-sized objects, such as latex beads. This “optical trapping” principle has found many applications in chemistry, physics and biology. It has found its most prominent use in biophysics, because it al ...
... Light can exert forces on small dielectric objects1,2. A tightly focused beam of light can trap micron-sized objects, such as latex beads. This “optical trapping” principle has found many applications in chemistry, physics and biology. It has found its most prominent use in biophysics, because it al ...
Lecture-12-Optics
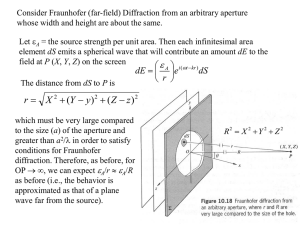
... Fresnel (Near-Field) Diffraction The basic idea is to start again with the Huygen’s-Fresnel principle for secondary spherical wave propagation. At any instant, every point on the primary wavefront is envisioned as a continuous emitter of spherical secondary wavelets. However, no reverse wave travel ...
... Fresnel (Near-Field) Diffraction The basic idea is to start again with the Huygen’s-Fresnel principle for secondary spherical wave propagation. At any instant, every point on the primary wavefront is envisioned as a continuous emitter of spherical secondary wavelets. However, no reverse wave travel ...
... Fresnel (Near-Field) Diffraction The basic idea is to start again with the Huygen’s-Fresnel principle for secondary spherical wave propagation. At any instant, every point on the primary wavefront is envisioned as a continuous emitter of spherical secondary wavelets. However, no reverse wave travel ...
Document
... The Fresnel rhomb can convert linear polarization into circular polarization, or vice versa. It is made of a transparent, homogenous, isotropic material, such as glass. Its cross-section is a parallelogram with an apex angle θ, as shown. Incoming light enters the rhomb normal to its input facet, exp ...
... The Fresnel rhomb can convert linear polarization into circular polarization, or vice versa. It is made of a transparent, homogenous, isotropic material, such as glass. Its cross-section is a parallelogram with an apex angle θ, as shown. Incoming light enters the rhomb normal to its input facet, exp ...
Self-collimation and focusing effects in zero
... prevents exactly fulfill the FP condition, the transmission pikes broaden when the spectral distance |λ0 − Λm | increases, Fig. 1b. The first and the third resonances become in this scheme large conducting bands whose upper and lower boundaries determine the zero-n̄ gap edges. The reflection spectr ...
... prevents exactly fulfill the FP condition, the transmission pikes broaden when the spectral distance |λ0 − Λm | increases, Fig. 1b. The first and the third resonances become in this scheme large conducting bands whose upper and lower boundaries determine the zero-n̄ gap edges. The reflection spectr ...
Phase-contrast X-ray imaging

Phase-contrast X-ray imaging (PCI) or phase-sensitive X-ray imaging is a general term for different technical methods that use information concerning changes in the phase of an X-ray beam that passes through an object in order to create its images. Standard X-ray imaging techniques like radiography or computed tomography (CT) rely on a decrease of the X-ray beam's intensity (attenuation) when traversing the sample, which can be measured directly with the assistance of an X-ray detector. In PCI however, the beam's phase shift caused by the sample is not measured directly, but is transformed into variations in intensity, which then can be recorded by the detector.In addition to producing projection images, PCI, like conventional transmission, can be combined with tomographic techniques to obtain the 3D distribution of the real part of the refractive index of the sample. When applied to samples that consist of atoms with low atomic number Z, PCI is more sensitive to density variations in the sample than conventional transmission-based X-ray imaging. This leads to images with improved soft tissue contrast.In the last several years, a variety of phase-contrast X-ray imaging techniques have been developed, all of which are based on the observation of interference patterns between diffracted and undiffracted waves. The most common techniques are crystal interferometry, propagation-based imaging, analyzer-based imaging, edge-illumination and grating-based imaging (see below).