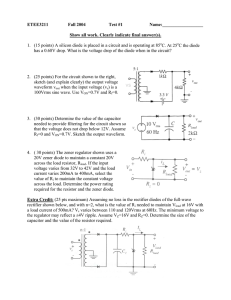
Diode Logic
... controlled by a different input signal. However, the only way the output can be pulled down to logic 0 is if both transistors are turned on by logic 1 inputs. If either input is a logic 0 that transistor cannot conduct, so there is no current through either one. The output is then a logic 1. This is ...
... controlled by a different input signal. However, the only way the output can be pulled down to logic 0 is if both transistors are turned on by logic 1 inputs. If either input is a logic 0 that transistor cannot conduct, so there is no current through either one. The output is then a logic 1. This is ...
6114.Output pulses after applying power through FETs
... This was measured at the HO and LO pin of the gate drive. As you can see the outputs were good. At this point, I have yet to supply 24V to the FETs ...
... This was measured at the HO and LO pin of the gate drive. As you can see the outputs were good. At this point, I have yet to supply 24V to the FETs ...
DM7416 Hex Inverting Buffers with High Voltage Open
... to perform when properly used in accordance with instructions for use provided in the labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in a significant injury to the ...
... to perform when properly used in accordance with instructions for use provided in the labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in a significant injury to the ...
project2 - UTK-EECS
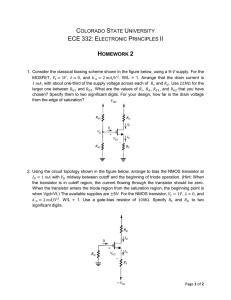
... transistor characteristics and compared with measured characteristics. (b) Design, build, and test current mirror circuits using either MOSFETs or BJTs. Procedure example using a 2N7000 MOSFET: (1) Use HP 4145B to plot transfer function (ID~VGS) and output characteristic (ID~VDS) curve of the transi ...
... transistor characteristics and compared with measured characteristics. (b) Design, build, and test current mirror circuits using either MOSFETs or BJTs. Procedure example using a 2N7000 MOSFET: (1) Use HP 4145B to plot transfer function (ID~VGS) and output characteristic (ID~VDS) curve of the transi ...
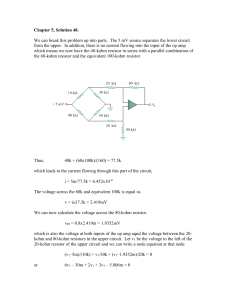
Soln0548 051017
... Chapter 5, Solution 48. We can break this problem up into parts. The 5 mV source separates the lower circuit from the upper. In addition, there is no current flowing into the input of the op amp which means we now have the 40-kohm resistor in series with a parallel combination of the 60-kohm resisto ...
... Chapter 5, Solution 48. We can break this problem up into parts. The 5 mV source separates the lower circuit from the upper. In addition, there is no current flowing into the input of the op amp which means we now have the 40-kohm resistor in series with a parallel combination of the 60-kohm resisto ...
A simple experiment was devised to check out ground-loop effects....
... sensing and drive circuitries were physically disconnected, and the driver was stimulated manually by direct connection to the driver power supply. Results (see Figure 146) proved beyond reasonable doubt that the nonlinearity observed in polysilicon resistance measurements was due to ground-loop eff ...
... sensing and drive circuitries were physically disconnected, and the driver was stimulated manually by direct connection to the driver power supply. Results (see Figure 146) proved beyond reasonable doubt that the nonlinearity observed in polysilicon resistance measurements was due to ground-loop eff ...
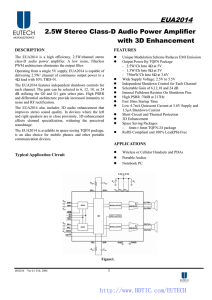
EUA2014 2.5W Stereo Class-D Audio Power Amplifier with 3D Enhancement
... The EUA2014 is a high efficiency, 2.5W/channel stereo class-D audio power amplifier. A low noise, filterless PWM architecture eliminates the output filter. Operating from a single 5V supply, EUA2014 is capable of delivering 2.5W/ channel of continuous output power to a 4Ω load with 10% THD+N. The EU ...
... The EUA2014 is a high efficiency, 2.5W/channel stereo class-D audio power amplifier. A low noise, filterless PWM architecture eliminates the output filter. Operating from a single 5V supply, EUA2014 is capable of delivering 2.5W/ channel of continuous output power to a 4Ω load with 10% THD+N. The EU ...
Transistor–transistor logic

Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function (e.g., AND) and the amplifying function are performed by transistors (contrast with RTL and DTL).TTL is notable for being a widespread integrated circuit (IC) family used in many applications such as computers, industrial controls, test equipment and instrumentation, consumer electronics, synthesizers, etc. The designation TTL is sometimes used to mean TTL-compatible logic levels, even when not associated directly with TTL integrated circuits, for example as a label on the inputs and outputs of electronic instruments.After their introduction in integrated circuit form in 1963 by Sylvania, TTL integrated circuits were manufactured by several semiconductor companies, with the 7400 series (also called 74xx) by Texas Instruments becoming particularly popular. TTL manufacturers offered a wide range of logic gate, flip-flops, counters, and other circuits. Several variations from the original bipolar TTL concept were developed, giving circuits with higher speed or lower power dissipation to allow optimization of a design. TTL circuits simplified design of systems compared to earlier logic families, offering superior speed to resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and easier design layout than emitter-coupled logic (ECL). The design of the input and outputs of TTL gates allowed many elements to be interconnected.TTL became the foundation of computers and other digital electronics. Even after much larger scale integrated circuits made multiple-circuit-board processors obsolete, TTL devices still found extensive use as the ""glue"" logic interfacing more densely integrated components. TTL devices were originally made in ceramic and plastic dual-in-line (DIP) packages, and flat-pack form. TTL chips are now also made in surface-mount packages. Successors to the original bipolar TTL logic often are interchangeable in function with the original circuits, but with improved speed or lower power dissipation.