Delta T calculation for plate heat exchangers
... Viscosity is a measure of the ease of flow of a liquid. The lower the viscosity, the more easily it flows. Viscosity is expressed in centipoise (cP) or centistokes (cSt). Overall heat transfer coefficient Overall heat transfer coefficient (k) is a measure of the resistance to heat flow, made up of t ...
... Viscosity is a measure of the ease of flow of a liquid. The lower the viscosity, the more easily it flows. Viscosity is expressed in centipoise (cP) or centistokes (cSt). Overall heat transfer coefficient Overall heat transfer coefficient (k) is a measure of the resistance to heat flow, made up of t ...
callister7e_sm_ch10_..
... necessary to heat above about 720°C, allow complete austenitization, then cool to room temperature at a rate between 0.02 and 0.006°C/s. (b) To convert from (martensite + ferrite + bainite) to spheroidite the alloy must be heated to about 700°C for several hours. (c) In order to convert from (marten ...
... necessary to heat above about 720°C, allow complete austenitization, then cool to room temperature at a rate between 0.02 and 0.006°C/s. (b) To convert from (martensite + ferrite + bainite) to spheroidite the alloy must be heated to about 700°C for several hours. (c) In order to convert from (marten ...
Chem 1010 Tutorials Tutorial 9A – Heat and Work Fall 2013
... In order to raise the temperature of a particular pond by 2.3 K, 5.2 x 1028 kJ of heat are required. a) What is the mass of the pond? (specific heat of water is 4.184 J·g–1·°C –1) b) What is the heat capacity of the pond? c) How much heat would be given off if the temperature of the pond decreased b ...
... In order to raise the temperature of a particular pond by 2.3 K, 5.2 x 1028 kJ of heat are required. a) What is the mass of the pond? (specific heat of water is 4.184 J·g–1·°C –1) b) What is the heat capacity of the pond? c) How much heat would be given off if the temperature of the pond decreased b ...
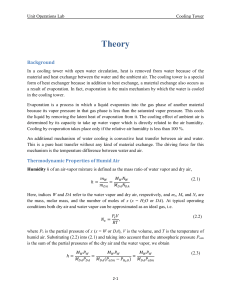
Theory
... In a cooling tower with open water circulation, heat is removed from water because of the material and heat exchange between the water and the ambient air. The cooling tower is a special form of heat exchanger because in addition to heat exchange, a material exchange also occurs as a result of evapo ...
... In a cooling tower with open water circulation, heat is removed from water because of the material and heat exchange between the water and the ambient air. The cooling tower is a special form of heat exchanger because in addition to heat exchange, a material exchange also occurs as a result of evapo ...
Chapter 6 Scaling Laws in Miniaturization
... where Q: total heat flow between two plates; q: heat flux; A: cross-sectional area for the heat flow; h: heat transfer coefficient; ∆T : temperature difference between these two points. - h: depends primarily on the fluid velocity, which does not play a significant role in the scaling of the heat fl ...
... where Q: total heat flow between two plates; q: heat flux; A: cross-sectional area for the heat flow; h: heat transfer coefficient; ∆T : temperature difference between these two points. - h: depends primarily on the fluid velocity, which does not play a significant role in the scaling of the heat fl ...
First Law of Thermodynamics
... Reversible process is one where thermal equilibrium is maintained throughout, such as the sufficiently slow compression of a piston in an insulated cylinder. Irreversible process is one in which thermal system’s changes cannot be retraced, such as gas expanding to fill a vacuum through an open stopc ...
... Reversible process is one where thermal equilibrium is maintained throughout, such as the sufficiently slow compression of a piston in an insulated cylinder. Irreversible process is one in which thermal system’s changes cannot be retraced, such as gas expanding to fill a vacuum through an open stopc ...
Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection and Latent Heat In addition
... (Of course, the Earth gets its energy from the sun, so ultimately it does all come from the sun....just not directly) ...
... (Of course, the Earth gets its energy from the sun, so ultimately it does all come from the sun....just not directly) ...
Fabric and ventilation heat loss
... Impact of ventilation and infiltration. • Ventilation and infiltration both bring outside air into the building, forcing out the air that was inside the building. • In winter time, the cold outside air replaces the warm inside air. • To keep the temperature inside at about 20 Deg C, the heating sys ...
... Impact of ventilation and infiltration. • Ventilation and infiltration both bring outside air into the building, forcing out the air that was inside the building. • In winter time, the cold outside air replaces the warm inside air. • To keep the temperature inside at about 20 Deg C, the heating sys ...
Dynamic insulation

Dynamic insulation is a form of insulation where cool outside air flowing through the thermal insulation in the envelope of a building will pick up heat from the insulation fibres. Buildings can be designed to exploit this to reduce the transmission heat loss (U-value) and to provide pre-warmed, draft free air to interior spaces. This is known as dynamic insulation since the U-value is no longer constant for a given wall or roof construction but varies with the speed of the air flowing through the insulation (climate adaptive building shell). Dynamic insulation is different from breathing walls. The positive aspects of dynamic insulation need to be weighed against the more conventional approach to building design which is to create an airtight envelope and provide appropriate ventilation using either natural ventilation or mechanical ventilation with heat recovery. The air-tight approach to building envelope design, unlike dynamic insulation, results in a building envelope that provides a consistent performance in terms of heat loss and risk of interstitial condensation that is independent of wind speed and direction. Under certain wind conditions a dynamically insulated building can have a higher heat transmission loss than an air-tight building with the same thickness of insulation.