Calculating the Loads for Liquid cooling Systems
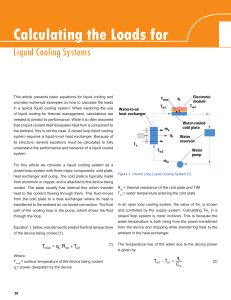
... This article presents basic equations for liquid cooling and provides numerical examples on how to calculate the loads in a typical liquid cooling system. When exploring the use of liquid cooling for thermal management, calculations are needed to predict its performance. While it is often assumed th ...
... This article presents basic equations for liquid cooling and provides numerical examples on how to calculate the loads in a typical liquid cooling system. When exploring the use of liquid cooling for thermal management, calculations are needed to predict its performance. While it is often assumed th ...
ABSTRACT: CFD analysis of flow and temperature
... food stuffs (k=0.2 W/mK, for most of the food items, the thermal conductivity range over 0.09 - 0.5 W/mK [15]) and the enclosed air region. The walls are normally made of sheet metal containing glass insulation (10 mm thick on each side). As the sheet metal thickness is about 0.5mm and is of high th ...
... food stuffs (k=0.2 W/mK, for most of the food items, the thermal conductivity range over 0.09 - 0.5 W/mK [15]) and the enclosed air region. The walls are normally made of sheet metal containing glass insulation (10 mm thick on each side). As the sheet metal thickness is about 0.5mm and is of high th ...
Lab 15. Heat Capacity
... The function of an adiabatic wall is to totally prevent thermal transfer through the walls of the system. In an adiabatic process, the change in internal energy is equal an opposite to the work performed. Unfortunately, the tube we used in the experiment was an open system. The result is that heat e ...
... The function of an adiabatic wall is to totally prevent thermal transfer through the walls of the system. In an adiabatic process, the change in internal energy is equal an opposite to the work performed. Unfortunately, the tube we used in the experiment was an open system. The result is that heat e ...
Study of the Dependence Effectiveness of Low
... energy complex will be able to effectively be operated the whole year round in the heating regime and in the conditioning regime. The conducted researches have shown that the switching over in such moments of the heat pump from ground to free air will allow to shorten by 20% the demanded of heat bor ...
... energy complex will be able to effectively be operated the whole year round in the heating regime and in the conditioning regime. The conducted researches have shown that the switching over in such moments of the heat pump from ground to free air will allow to shorten by 20% the demanded of heat bor ...
Currents experiment
... What are the three types of heat transfer? How is heat transferred through space? What is a convection current? In general, what happens to the density of a fluid as it ...
... What are the three types of heat transfer? How is heat transferred through space? What is a convection current? In general, what happens to the density of a fluid as it ...
Plural Component Equipment
... Supplies the proportioning pumps with a positive flow of material. 2:1 ratio pumps are normally used. Use 3/4” I.D. nylon lined hose rated at 500 psi. In-line 30-60 mesh filters (“Y” filters) ...
... Supplies the proportioning pumps with a positive flow of material. 2:1 ratio pumps are normally used. Use 3/4” I.D. nylon lined hose rated at 500 psi. In-line 30-60 mesh filters (“Y” filters) ...
ENGR 7901 - Heat Transfer II 1 Introduction 2 The Flat Plate
... theory may be used, i.e if the spacing between tubes exceeds three diameters. In these cases, there is sufficient fluid at free stream conditions to warrant isolation. Finally at values below the lower limit, systems behave more like porous media as free space is limited. The above results may be ex ...
... theory may be used, i.e if the spacing between tubes exceeds three diameters. In these cases, there is sufficient fluid at free stream conditions to warrant isolation. Finally at values below the lower limit, systems behave more like porous media as free space is limited. The above results may be ex ...
teaching nerve conduction to undergraduates
... the two modes of heat transfer. 1) In the combustible rod, the transfer of heat is effected by the traveling flame, whereas in the conducting rod, only the heat travels; the flame remains at its own place. 2) A conductor can be used several times over to transfer heat; a combustible rod has to be re ...
... the two modes of heat transfer. 1) In the combustible rod, the transfer of heat is effected by the traveling flame, whereas in the conducting rod, only the heat travels; the flame remains at its own place. 2) A conductor can be used several times over to transfer heat; a combustible rod has to be re ...
Basic Properties of the Atmosphere
... • The Arctic Ocean has a large amount of heat (because of large mass) even though the temperature is low. • Air in an oven at 500 F has high temperature but little heat. • However, touch anything solid in the oven, and you’ll get burned. Same temperature, much larger amount of heat. 1. Heat, Tempera ...
... • The Arctic Ocean has a large amount of heat (because of large mass) even though the temperature is low. • Air in an oven at 500 F has high temperature but little heat. • However, touch anything solid in the oven, and you’ll get burned. Same temperature, much larger amount of heat. 1. Heat, Tempera ...
Dynamic insulation

Dynamic insulation is a form of insulation where cool outside air flowing through the thermal insulation in the envelope of a building will pick up heat from the insulation fibres. Buildings can be designed to exploit this to reduce the transmission heat loss (U-value) and to provide pre-warmed, draft free air to interior spaces. This is known as dynamic insulation since the U-value is no longer constant for a given wall or roof construction but varies with the speed of the air flowing through the insulation (climate adaptive building shell). Dynamic insulation is different from breathing walls. The positive aspects of dynamic insulation need to be weighed against the more conventional approach to building design which is to create an airtight envelope and provide appropriate ventilation using either natural ventilation or mechanical ventilation with heat recovery. The air-tight approach to building envelope design, unlike dynamic insulation, results in a building envelope that provides a consistent performance in terms of heat loss and risk of interstitial condensation that is independent of wind speed and direction. Under certain wind conditions a dynamically insulated building can have a higher heat transmission loss than an air-tight building with the same thickness of insulation.