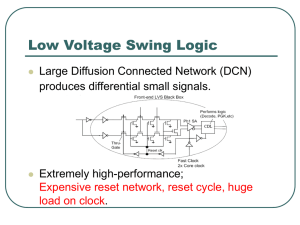
Basic Information and Definitions
... distances are referenced. For proximity switches the highest rated operating voltage must be considered as the rated isolation voltage. ...
... distances are referenced. For proximity switches the highest rated operating voltage must be considered as the rated isolation voltage. ...
Electricity & Magnetism
... There are 2 types of circuits: Circuit – there are several branching paths to the components. If the circuit is broken at any one branch, only the components on that branch will turn off. ...
... There are 2 types of circuits: Circuit – there are several branching paths to the components. If the circuit is broken at any one branch, only the components on that branch will turn off. ...
Project Summary - Berkeley Cosmology Group
... machines, too. Power, in defined in physics is the rate of energy flow. The equation to find the power is current times voltage, or energy per unit of time (E/T). You need power in order to make actions happen. If there was no power, then there will be no energy, and therefore, would be no life! To ...
... machines, too. Power, in defined in physics is the rate of energy flow. The equation to find the power is current times voltage, or energy per unit of time (E/T). You need power in order to make actions happen. If there was no power, then there will be no energy, and therefore, would be no life! To ...
transformer - Madison County Schools
... An induced current my reverse directions very quickly over and over again. A current that reverses direction repeatedly is called alternating current, or simply AC. ...
... An induced current my reverse directions very quickly over and over again. A current that reverses direction repeatedly is called alternating current, or simply AC. ...
AP B Circuit Analysis
... AP B Circuit Analysis Unlike the Regents, the AP B exam and college textbooks; ...
... AP B Circuit Analysis Unlike the Regents, the AP B exam and college textbooks; ...
A LARGE-POWER VOLTAGE SOURCE CONVERTER FOR FACTS
... This paper presents a novel large-power voltage source converter (VSC) arrangement suitable for flexible alternating current transmission system applications, achieved by combining four threelevel three-phase neutral-point-clamped inverters by means of intermediate magnetic elements with lower VA ra ...
... This paper presents a novel large-power voltage source converter (VSC) arrangement suitable for flexible alternating current transmission system applications, achieved by combining four threelevel three-phase neutral-point-clamped inverters by means of intermediate magnetic elements with lower VA ra ...
Document
... An inductor is constructed by coiling a wire around some type of form. Current flowing through the coil creates a magnetic field or flux that links the coil. Frequently the coil form is composed of a magnetic material such as iron or iron oxide that increases the magnetic flux for a given current. ...
... An inductor is constructed by coiling a wire around some type of form. Current flowing through the coil creates a magnetic field or flux that links the coil. Frequently the coil form is composed of a magnetic material such as iron or iron oxide that increases the magnetic flux for a given current. ...
Homework 1 - the GMU ECE Department
... 2. For a given product, the test specification for a given input device is a maximum leakage of 3.0mA when 2.5V. This is tested by forcing a given voltage and measuring the resultant current. The tester to be used has the following accuracy: forcing voltage +/-(0.1% +4mV+0.6mV/10mA), measured curren ...
... 2. For a given product, the test specification for a given input device is a maximum leakage of 3.0mA when 2.5V. This is tested by forcing a given voltage and measuring the resultant current. The tester to be used has the following accuracy: forcing voltage +/-(0.1% +4mV+0.6mV/10mA), measured curren ...
Reading Quizzes III
... proportional to the magnetic flux through the loop proportional to the change of the magnetic flux through the loop ...
... proportional to the magnetic flux through the loop proportional to the change of the magnetic flux through the loop ...
High Voltage Direct Current Test Procedure
... Slowly increase the voltage from 0 to 1500 volts, then to 3000 volts, and then to 4500 volts. At each step, hold for 1 minute and read the current. Record leakage current values and plot a "Leakage versus Step Voltage Curve" on a form similar to that shown in Figure 1. c) Slowly increase the voltage ...
... Slowly increase the voltage from 0 to 1500 volts, then to 3000 volts, and then to 4500 volts. At each step, hold for 1 minute and read the current. Record leakage current values and plot a "Leakage versus Step Voltage Curve" on a form similar to that shown in Figure 1. c) Slowly increase the voltage ...
Bulk power transmission
... A transmission grid is a network of power stations, transmission circuits, and substations. Energy is usually transmitted within the grid with three-phase AC. DC systems require relatively costly conversion equipment which may be economically justified for particular projects. Single phase AC is use ...
... A transmission grid is a network of power stations, transmission circuits, and substations. Energy is usually transmitted within the grid with three-phase AC. DC systems require relatively costly conversion equipment which may be economically justified for particular projects. Single phase AC is use ...
Alternating current
Alternating current (AC), is an electric current in which the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction, whereas in direct current (DC, also dc), the flow of electric charge is only in one direction. The abbreviations AC and DC are often used to mean simply alternating and direct, as when they modify current or voltage.AC is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave. In certain applications, different waveforms are used, such as triangular or square waves. Audio and radio signals carried on electrical wires are also examples of alternating current. These types of alternating current carry information encoded (or modulated) onto the AC signal, such as sound (audio) or images (video).