* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cmd - UCSD CSE
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
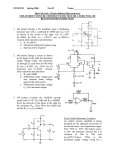
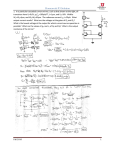
Low Voltage Swing Logic Large Diffusion Connected Network (DCN) produces differential small signals. Extremely high-performance; Expensive reset network, reset cycle, huge load on clock. Current Mode Differential Logic Utilize current mode logic to get stable lowS S voltage swing. 0 1 S1’ SA Xs Rs CDL Shunt transistors and resistors replace reset network. Small transistor count, no reset, small dynamic power, small clock load. CMDL Waveform Current Mode vs. Voltage Mode Voltage Mode Time Constant r1c1 Current Mode r2 ( )r1c1 r1 r 2 Smaller shunt resistor, faster response. Limited by threshold voltage of sense amplifier. CMDL Design Basic design rules: • • Any differential input pair must be connected through a shunt resistor or a closed transistor. (No full voltage swing in the circuit) For any differential output pair, only one shunt resistor or closed transistor on the active path. (Differential output signal can be detected) Applicable to extremely high performance low power datapath designs, such as MUX, barrel shifter and carry-skip adder. Preliminary Results Delay (ps) LVS CMDL Avg./Peak Power (mW) LVS CMDL Delay×Avg. Power LVS CMDL 32-bit Mux 47.1 58 0.81/4.56 0.54/0.90 38.15 31.32 8-bit Shifter 34 43.2 0.66/3.20 0.37/0.46 22.44 15.98 16-bit Adder 70.9 83.7 1.08/10.73 0.16/1.61 76.57 13.39 DELAY AND POWER COMPARISON BETWEEN CMDL AND LVS CIRCUITS