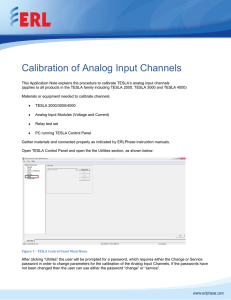
What are clippers circuits?
... Section (b) shows the same clipper configuration as it is shown in (a).but the diodes is replaced with its equivalent circuit model. When the input signal goes positive, the anode terminal of diode attains a higher potential than cathode. This makes the diode forward biased. The diode in reverse bia ...
... Section (b) shows the same clipper configuration as it is shown in (a).but the diodes is replaced with its equivalent circuit model. When the input signal goes positive, the anode terminal of diode attains a higher potential than cathode. This makes the diode forward biased. The diode in reverse bia ...
Design Review David Schlais – Robbie Wankewycz – Jamie Barber
... This circuit will take in the unregulated 7.4v battery output, which can swing between 6 and 9v in the worst cases, and convert it to 5v DC. This 5v voltage will be used to power the 7 photomultiplier tubes which require 5 volts each. The circuit will be a switching buck converter. The chip we will ...
... This circuit will take in the unregulated 7.4v battery output, which can swing between 6 and 9v in the worst cases, and convert it to 5v DC. This 5v voltage will be used to power the 7 photomultiplier tubes which require 5 volts each. The circuit will be a switching buck converter. The chip we will ...
Sensing - Low-Cost EKG Pulsometer - AN2284
... © Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, 2006-2007. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. Cypress Semiconductor Corporation assumes no responsibility for the use of any circuitry other than circuitry embodied in a Cypress product. Nor does it convey or imply any license u ...
... © Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, 2006-2007. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. Cypress Semiconductor Corporation assumes no responsibility for the use of any circuitry other than circuitry embodied in a Cypress product. Nor does it convey or imply any license u ...
Laser Listener
... DSP • Functional Description - Will smooth digital signal - Will provide squelch - Possibly perform Fourier analysis ...
... DSP • Functional Description - Will smooth digital signal - Will provide squelch - Possibly perform Fourier analysis ...
BU92001KN
... whether the destruction is short circuit mode or open circuit mode cannot be specified. Pleases take into consideration the physical countermeasures for safety, such as fusing, if a particular mode that exceeds the absolute maximum rating is assumed. (2) GND Potential Make setting of the potential o ...
... whether the destruction is short circuit mode or open circuit mode cannot be specified. Pleases take into consideration the physical countermeasures for safety, such as fusing, if a particular mode that exceeds the absolute maximum rating is assumed. (2) GND Potential Make setting of the potential o ...
Interfacing ProASIC PLUS FPGAs with 5V Input Signals
... Device reliability may be maintained with 5.5V signals as long as the voltage is limited to the ProASICPLUS Flash Family FPGAs datasheet specifications at the device input. In addition, under no circumstances should VIO exceed the VDDP of the device. For this reason, the two schemes described in thi ...
... Device reliability may be maintained with 5.5V signals as long as the voltage is limited to the ProASICPLUS Flash Family FPGAs datasheet specifications at the device input. In addition, under no circumstances should VIO exceed the VDDP of the device. For this reason, the two schemes described in thi ...
A Nyquist-Rate Pixel-Level ADC for CMOS Image Sensors
... at 0.25- m technology). On the other hand, bit-serial Nyquistrate ADC’s such as successive approximation or algorithmic ADC require complex circuits with very precise and matched analog components. As a result, they are also not suited to pixel-level implementation, especially in a standard digital ...
... at 0.25- m technology). On the other hand, bit-serial Nyquistrate ADC’s such as successive approximation or algorithmic ADC require complex circuits with very precise and matched analog components. As a result, they are also not suited to pixel-level implementation, especially in a standard digital ...
Comparators
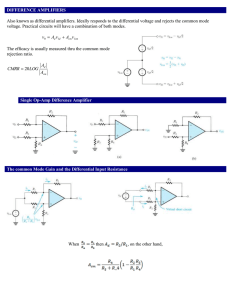
... A comparator is similar to an op amp. It has two inputs, inverting and non-inverting and an output (see Figure 1). But it is specifically designed to compare the voltages between its two inputs. Therefore it operates in a non-linear fashion. The comparator operates open-loop, providing a two-state l ...
... A comparator is similar to an op amp. It has two inputs, inverting and non-inverting and an output (see Figure 1). But it is specifically designed to compare the voltages between its two inputs. Therefore it operates in a non-linear fashion. The comparator operates open-loop, providing a two-state l ...
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... application or use of the Circuits from the Lab circuits. Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, Circuits from the Lab designs are supplied "as is" and without warranties of any kind, express, implied, or statutory including, but not limited to, any ...
... application or use of the Circuits from the Lab circuits. Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, Circuits from the Lab designs are supplied "as is" and without warranties of any kind, express, implied, or statutory including, but not limited to, any ...
Analog and Mixed Signal Design Consultancy
... signal design. We have expertise in RF, analog & mixed signal design and verification at both schematic and layout level. IC designs have been made in CMOS technologies, ranging from 0.35μm to 16nm and from very low frequencies up to 5 GHz range. ...
... signal design. We have expertise in RF, analog & mixed signal design and verification at both schematic and layout level. IC designs have been made in CMOS technologies, ranging from 0.35μm to 16nm and from very low frequencies up to 5 GHz range. ...
Representing Data as Digital Signals
... analog signal. According to a sampling theorem known as Nyquist’s Rule, if an analog signal is sampled at regular intervals and at twice the highest frequency on the line, then the sample will be an exact representation of the original signal. Even though voice transmission requires 3000 Hz bandwidt ...
... analog signal. According to a sampling theorem known as Nyquist’s Rule, if an analog signal is sampled at regular intervals and at twice the highest frequency on the line, then the sample will be an exact representation of the original signal. Even though voice transmission requires 3000 Hz bandwidt ...
JF BAI ENGINEERING 3C2 ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
... A MOS transistor has fabrication technology parameters µ nCOX = 50µAV-2, VT = 0.5V and λ=0V-1. The manufacturing process allows a minimum dimension of 0.5µm and all dimensions must be integer multiples of this. A simple common-source amplifier is to operate with a load resistance of 100kΩ and a bias ...
... A MOS transistor has fabrication technology parameters µ nCOX = 50µAV-2, VT = 0.5V and λ=0V-1. The manufacturing process allows a minimum dimension of 0.5µm and all dimensions must be integer multiples of this. A simple common-source amplifier is to operate with a load resistance of 100kΩ and a bias ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).