Wireless Communications and Networks
... Ratio of the power in a signal to the power contained in the noise that’s present at a particular point in the transmission Typically measured at a receiver Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR, or S/N) signal power ( SNR) dB 10 log 10 noise power A high SNR means a high-quality signal, low number of requir ...
... Ratio of the power in a signal to the power contained in the noise that’s present at a particular point in the transmission Typically measured at a receiver Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR, or S/N) signal power ( SNR) dB 10 log 10 noise power A high SNR means a high-quality signal, low number of requir ...
LAB #2: First-Order System Behavior
... resistor. You should see a signal flashing on the screen of your scope, and the trigger ready light will go off. However the signal is too quick for you to really see, so you will need to store the signal on the screen. Push to On (In) the 25% button and the STORE button in the ACQ section. Now you ...
... resistor. You should see a signal flashing on the screen of your scope, and the trigger ready light will go off. However the signal is too quick for you to really see, so you will need to store the signal on the screen. Push to On (In) the 25% button and the STORE button in the ACQ section. Now you ...
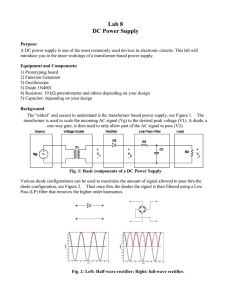
Lab 7
... 3. Insert a diode between the filter and the source, remove the shunt capacitor from the low pass Filter, and observe the resulting output of the filter in both the time and frequencies domain (using the FFT function on the oscilloscope). 4. Add the shunt capacitor back into the filter and document ...
... 3. Insert a diode between the filter and the source, remove the shunt capacitor from the low pass Filter, and observe the resulting output of the filter in both the time and frequencies domain (using the FFT function on the oscilloscope). 4. Add the shunt capacitor back into the filter and document ...
Function generators, 5 MHz with integral feedback voltage
... The outstanding feature of these instruments is the frequency counter with LED for measuring both internal and external signal frequencies. The high output voltage of max. Vpp = 30 V will satisfy the requirements of most general-purpose laboratory or service tasks as well as the needs of application ...
... The outstanding feature of these instruments is the frequency counter with LED for measuring both internal and external signal frequencies. The high output voltage of max. Vpp = 30 V will satisfy the requirements of most general-purpose laboratory or service tasks as well as the needs of application ...
PCB Layout Guidance
... and digital inputs that occur before latching the output of the analog comparator. Therefore, during any single conversion for an n-bit SAR converter, there are n windows in which large external transient voltages can easily affect the conversion result. Such glitches might originate from switching ...
... and digital inputs that occur before latching the output of the analog comparator. Therefore, during any single conversion for an n-bit SAR converter, there are n windows in which large external transient voltages can easily affect the conversion result. Such glitches might originate from switching ...
Analog Input, Sigma-Delta, 16-Bit, 6-Chan
... System analog inputs pass through a selftest network that can replace the system signals either with a precision voltage standard or with the four analog output channels, under software control. This arrangement is used during auto calibration to determine the offset and gain correction parameters f ...
... System analog inputs pass through a selftest network that can replace the system signals either with a precision voltage standard or with the four analog output channels, under software control. This arrangement is used during auto calibration to determine the offset and gain correction parameters f ...
Abstract
... In this paper, a DC/AC converter called inverter is proposed. This converter includes 12V converting 110V and 12V converting 220V circuits. In 12V/110V circuit, the IC555 generates a 240Hz signal that passes the IC4027 to obtain the 60Hz signal. By transistor C4016 and 12V/2V transformer, the signal ...
... In this paper, a DC/AC converter called inverter is proposed. This converter includes 12V converting 110V and 12V converting 220V circuits. In 12V/110V circuit, the IC555 generates a 240Hz signal that passes the IC4027 to obtain the 60Hz signal. By transistor C4016 and 12V/2V transformer, the signal ...
ECE 353 DIGITAL MICROELECTRONICS LABORATORY
... ground). Try to keep the input voltage in a range between the supply voltage "rails" (negative and positive supply voltages). Setup the power supply to deliver 5 V (on the 0-6 V output) with a current limit value of 100 mA as follows: Press +6 V to select the 0-6 V supply channel; press Display Lim ...
... ground). Try to keep the input voltage in a range between the supply voltage "rails" (negative and positive supply voltages). Setup the power supply to deliver 5 V (on the 0-6 V output) with a current limit value of 100 mA as follows: Press +6 V to select the 0-6 V supply channel; press Display Lim ...
RF Power Detector MAX2209 General Description Features
... Note 1: Package thermal resistances were obtained using the method described in JEDEC specification JESD51-7, using a 4-layer board. For detailed information on package thermal considerations, refer to www.maxim-ic.com/thermal-tutorial. Note 2: For detailed information on soldering, refer to Appli ...
... Note 1: Package thermal resistances were obtained using the method described in JEDEC specification JESD51-7, using a 4-layer board. For detailed information on package thermal considerations, refer to www.maxim-ic.com/thermal-tutorial. Note 2: For detailed information on soldering, refer to Appli ...
AD45048: Rail-to-Rail Upstream ADSL Line Driver Data Sheet
... Customer premise ADSL applications require the transmission of a 13 dBm DMT signal (20 mW into 100 Ω). DMT signals can have a crest factor (V peak/V rms ratio) as high as 5.3, requiring the line driver to provide a peak power of 560 mW. The line driver is required to drive a 7.5 V peak onto the 100 ...
... Customer premise ADSL applications require the transmission of a 13 dBm DMT signal (20 mW into 100 Ω). DMT signals can have a crest factor (V peak/V rms ratio) as high as 5.3, requiring the line driver to provide a peak power of 560 mW. The line driver is required to drive a 7.5 V peak onto the 100 ...
to - Lectrosonics.com
... Setting every component so that clipping occurs at exactly the same time in all devices. If “clip” indicator shows nothing on main console, you know everything else in your system is not going to “clip” either. All components can be driven to their maximum without danger. ...
... Setting every component so that clipping occurs at exactly the same time in all devices. If “clip” indicator shows nothing on main console, you know everything else in your system is not going to “clip” either. All components can be driven to their maximum without danger. ...
High-Speed Electronic Circuits for 100 Gb/s Transport Networks M. Möller
... important design criteria. As high-speed operation is in general supported by high operating currents, power saving is a big challenge in the development of high-speed circuits for the transceivers with their various coding schemes under discussion (e.g. OOK, DP-QPSK, OFDM). This holds especially fo ...
... important design criteria. As high-speed operation is in general supported by high operating currents, power saving is a big challenge in the development of high-speed circuits for the transceivers with their various coding schemes under discussion (e.g. OOK, DP-QPSK, OFDM). This holds especially fo ...
AT6200/AT6400
... Differential line driver output. Signal high > 3.5VDC @ +30 mA, signal low < 1.0VDC @ -30 mA. +output for each differential drive is active high; output for each driver is active low. Step pulse width is 0.3µs to 20 µs (depending on the state of the PULSE command—default is 0.3 µs.) Detects unrecove ...
... Differential line driver output. Signal high > 3.5VDC @ +30 mA, signal low < 1.0VDC @ -30 mA. +output for each differential drive is active high; output for each driver is active low. Step pulse width is 0.3µs to 20 µs (depending on the state of the PULSE command—default is 0.3 µs.) Detects unrecove ...
Dec 2003 - Project Status Review IR SYSTEMS
... low/high level offset. • Histograms of D.C. input for low/high levels • Histograms of dynamic step input on even/odd channels • Sinewave input to get frequency spectrum • Sinewave input to get DNL, and maximum INL ...
... low/high level offset. • Histograms of D.C. input for low/high levels • Histograms of dynamic step input on even/odd channels • Sinewave input to get frequency spectrum • Sinewave input to get DNL, and maximum INL ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).