SCC-CI20 Current Input Module User Guide and Specifications
... USER GUIDESCC-CI20 Current Input Module The SCC-CI20 converts current to voltage by passing it through a precision 249 Ω resistor and sending the resulting voltage to the E Series DAQ device as a 0 to +5 V signal. The SCC-CI20 accepts up to two current sources at a maximum of 20 mA. A differential i ...
... USER GUIDESCC-CI20 Current Input Module The SCC-CI20 converts current to voltage by passing it through a precision 249 Ω resistor and sending the resulting voltage to the E Series DAQ device as a 0 to +5 V signal. The SCC-CI20 accepts up to two current sources at a maximum of 20 mA. A differential i ...
EVALUATION AND DESIGN SUPPORT CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... There are several methods to power the weigh scale system. It can be powered from the main power supply bus or it can be powered from the ADP3303 (3.3 V). When the weigh scale is excited with 5 V, then the main power supply bus must be used. When exciting the load cell with 3.3 V, the main power sup ...
... There are several methods to power the weigh scale system. It can be powered from the main power supply bus or it can be powered from the ADP3303 (3.3 V). When the weigh scale is excited with 5 V, then the main power supply bus must be used. When exciting the load cell with 3.3 V, the main power sup ...
Linear Integrated Circuits
... Tracking or servo converter. Successive approximation type converter ...
... Tracking or servo converter. Successive approximation type converter ...
A 12-Bit High-Speed Column-Parallel Two-Step Single
... high-speed SS ADCs have been recently reported [5], they use very high clock frequency which in turn leads to high power consumption. To solve the problem of low speed, two-step SS ADCs have been recently reported in [6–10]. In these types, the analog-to-digital (AD) conversion is carried out using ...
... high-speed SS ADCs have been recently reported [5], they use very high clock frequency which in turn leads to high power consumption. To solve the problem of low speed, two-step SS ADCs have been recently reported in [6–10]. In these types, the analog-to-digital (AD) conversion is carried out using ...
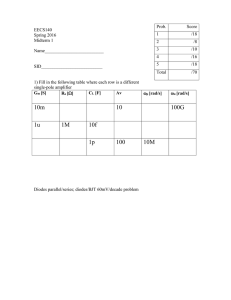
16spMid1b
... the output are both biased at 1V. You find that to get 11uA of current to flow, you need to either increase the input voltage by 10mV, or the output voltage by 10V. Estimate the transconductance, output resistance, and intrinsic gain of the transistor (give numerical answers). What is the gain if th ...
... the output are both biased at 1V. You find that to get 11uA of current to flow, you need to either increase the input voltage by 10mV, or the output voltage by 10V. Estimate the transconductance, output resistance, and intrinsic gain of the transistor (give numerical answers). What is the gain if th ...
SSM2142 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... balanced-pair interface systems. Just as in transformer-based circuits, identical but opposite currents are generated by the output pair which can be ground-referenced if desired and transmitted on a single wire. Single-ended operation requires that the unused side of the output pair be grounded to ...
... balanced-pair interface systems. Just as in transformer-based circuits, identical but opposite currents are generated by the output pair which can be ground-referenced if desired and transmitted on a single wire. Single-ended operation requires that the unused side of the output pair be grounded to ...
An Introduction to Sigma Delta Converters
... Now you can figure out which parameters (oversampling rate and order) of the modulator are required to obtain which noise. If a signal must be quantized, you may decide either the quantization noise or the conversion noise to be the bottle neck of the overall noise performance. In case that both sha ...
... Now you can figure out which parameters (oversampling rate and order) of the modulator are required to obtain which noise. If a signal must be quantized, you may decide either the quantization noise or the conversion noise to be the bottle neck of the overall noise performance. In case that both sha ...
In your lab journal, provide a detailed circuit analysis that shows that
... Your supervisor has decided to use seven LEDs in the display. An octal 0 is indicated when all of the LEDs are off. Each increment in the octal number will light an additional LED. Her technique for decoding the analog signal is to use an A/D (analog to digital) converter called a flash converter. H ...
... Your supervisor has decided to use seven LEDs in the display. An octal 0 is indicated when all of the LEDs are off. Each increment in the octal number will light an additional LED. Her technique for decoding the analog signal is to use an A/D (analog to digital) converter called a flash converter. H ...
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE)
... require one timing capacitor, one output resistor, and an integrating or filter capacitor. When the input stage changes state (due to a suitable zero crossing or differential voltage on the input) the timing capacitor is either charged or discharged linearly between two voltages whose difference is ...
... require one timing capacitor, one output resistor, and an integrating or filter capacitor. When the input stage changes state (due to a suitable zero crossing or differential voltage on the input) the timing capacitor is either charged or discharged linearly between two voltages whose difference is ...
Circuit Note CN-0365
... with the sampling rate, making the ADC well suited for both high and low sampling rates (even as low as a few Hz) and enables very low power consumption for battery-powered systems. Additionally, oversampling techniques can be used to increase the effective resolution for low speed signals. ...
... with the sampling rate, making the ADC well suited for both high and low sampling rates (even as low as a few Hz) and enables very low power consumption for battery-powered systems. Additionally, oversampling techniques can be used to increase the effective resolution for low speed signals. ...
doc
... intended for high-speed digitisation, bypassing the peak-hold/mux stages. It is possible to resolve closely separated pulses on a single channel, where the separation might be too small for the peak-hold. These outputs have high-speed buffers (~10ns rise-time) in order to retain information about th ...
... intended for high-speed digitisation, bypassing the peak-hold/mux stages. It is possible to resolve closely separated pulses on a single channel, where the separation might be too small for the peak-hold. These outputs have high-speed buffers (~10ns rise-time) in order to retain information about th ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).