* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Buck–boost converter - 123SeminarsOnly.com
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
HVDC converter wikipedia , lookup
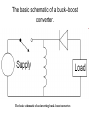
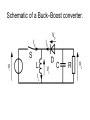
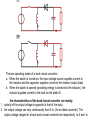
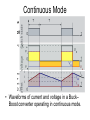
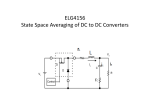
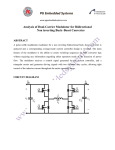
Buck–boost converter TE – FTIK – UHT Djogi Lubis Ir, M.A.P The basic schematic of a buck–boost converter. The basic schematic of an inverting buck–boost converter. • The basic principle of the buck–boost converter is fairly simple (see figure 2): • while in the On-state, the input voltage source is directly connected to the inductor (L). This results in accumulating energy in L. In this stage, the capacitor supplies energy to the output load. • while in the Off-state, the inductor is connected to the output load and capacitor, so energy is transferred from L to C and R. • Compared to the buck and boost converters, the characteristics of the buck–boost converter are mainly: polarity of the output voltage is opposite to that of the input; ∞ • the output voltage can vary continuously from 0 to (for an ideal converter). The output voltage ranges for a buck and a boost converter are respectively 0 to Vi and Vi to ∞ . Schematic of a Buck–Boost converter. The two operating states of a buck–boost converter: a. When the switch is turned-on, the input voltage source supplies current to the inductor and the capacitor supplies current to the resistor (output load). b. When the switch is opened (providing energy is stored into the inductor), the inductor supplies current to the load via the diode D. the characteristics of the buck–boost converter are mainly: 1. polarity of the output voltage is opposite to that of the input; 2. the output voltage can vary continuously from 0 to (for an ideal converter). The output voltage ranges for a buck and a boost converter are respectively to 0 and to Continuous Mode • Waveforms of current and voltage in a Buck– Boost converter operating in continuous mode.